Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
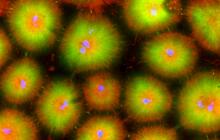
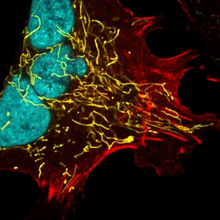
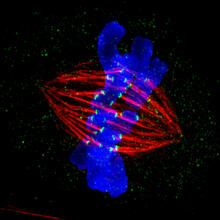
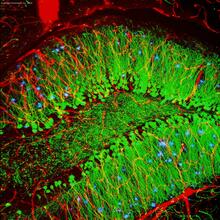
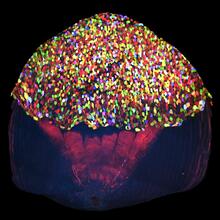
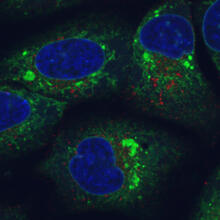
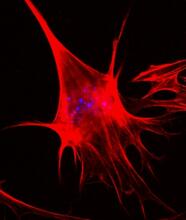
Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
6591
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaPigment cells in the fin of pearl danio
5757
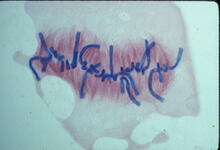
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaLily mitosis 05
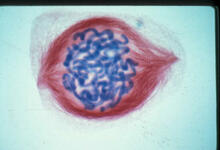
1015
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared-labeled
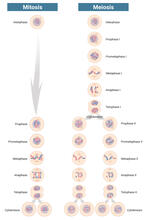
6788
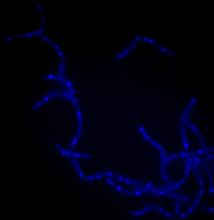
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
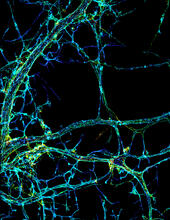
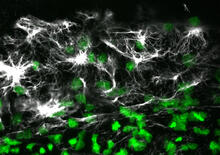
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaFlower-forming cells in a small plant related to cabbage (Arabidopsis)
3606
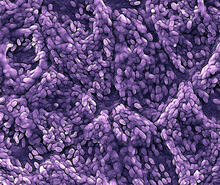
In plants, as in animals, stem cells can transform into a variety of different cell types. The stem cells at the growing tip of this Arabidopsis plant will soon become flowers. Arun Sampathkumar and Elliot Meyerowitz, California Institute of Technology View MediaCaulobacter
3262
A study using Caulobacter crescentus showed that some bacteria use just-in-time processing, much like that used in industrial delivery, to make the glue that allows them to attach to surfaces, Yves Brun, Indiana University View MediaDynamin structure
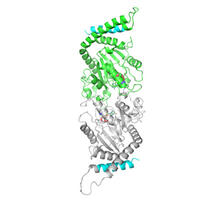
2744
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaNuclear Lamina
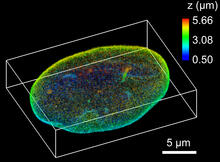
6572
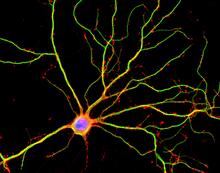
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaHippocampal neuron in culture
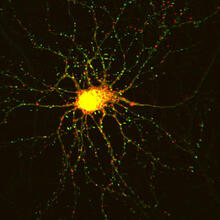
3687
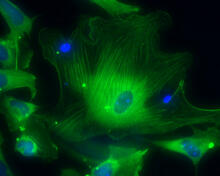
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaColorful cells
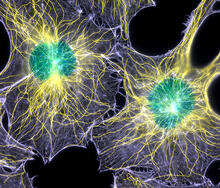
2428
Actin (purple), microtubules (yellow), and nuclei (green) are labeled in these cells by immunofluorescence. This image won first place in the Nikon 2003 Small World photo competition. Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3525
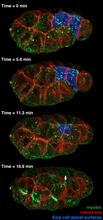
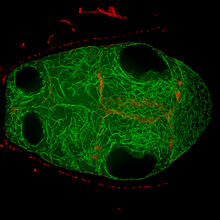
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. Kenneth Keiler, Penn State University View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
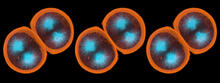
3297
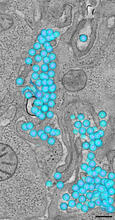
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaMultinucleated cancer cell
6967
A cancer cell with three nuclei, shown in turquoise. The abnormal number of nuclei indicates that the cell failed to go through cell division, probably more than once. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaMitochondrion from insect flight muscle
3662
This is a tomographic reconstruction of a mitochondrion from an insect flight muscle. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaHydra 06
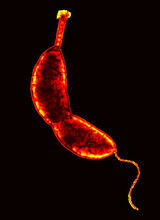
2442
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaMouse retina
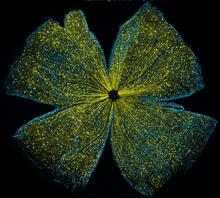
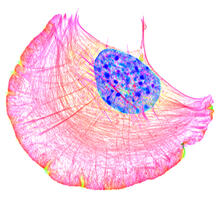
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaSmooth muscle from mouse stem cells
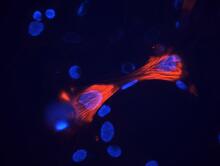
3289
These smooth muscle cells were derived from mouse neural crest stem cells. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, blue indicates nuclei. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institutes, via CIRM View MediaDeveloping fruit fly nerve cord
2435
The glial cells (black dots) and nerve cells (brown bands) in this developing fruit fly nerve cord formed normally despite the absence of the SPITZ protein, which blocks their impending suicide. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaNucleus and rough ER
1290
The nucleus contains the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaOptic nerve astrocytes
5852
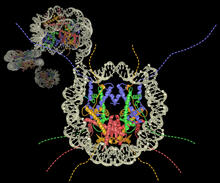
Astrocytes in the cross section of a human optic nerve head Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaNucleosome
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaSmooth muscle from human ES cells
3288
These smooth muscle cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The nuclei are stained blue, and the proteins of the cytoskeleton are stained green. Alexey Terskikh lab, Burnham Institute for Medical Research, via CIRM View MediaCentrioles anchor cilia in planaria
3292
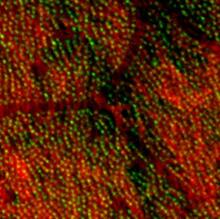
Centrioles (green) anchor cilia (red), which project on the surface of pharynx cells of the freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea. Juliette Azimzadeh, University of California, San Francisco View MediaA multicolored fish scale 2
3783
Each of the tiny colored specs in this image is a cell on the surface of a fish scale. Chen-Hui Chen and Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaNeuron with labeled synapses
3509
In this image, recombinant probes known as FingRs (Fibronectin Intrabodies Generated by mRNA display) were expressed in a cortical neuron, where they attached fluorescent proteins to either PSD95 (gre Don Arnold and Richard Roberts, University of Southern California. View MediaHIV, the AIDS virus, infecting a human cell
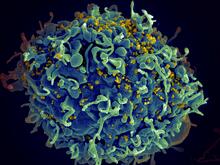
3638
This human T cell (blue) is under attack by HIV (yellow), the virus that causes AIDS. Seth Pincus, Elizabeth Fischer, and Austin Athman, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health View MediaHuman ES cells differentiating into neurons
3276
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2807
Confocal image showing high levels of the protein vimentin (white) at the edge zone of a quail embryo. Cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaConfocal microscopy image of two Drosophila ovarioles
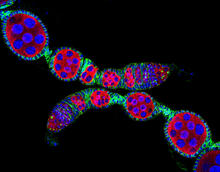
5772
Ovarioles in female insects are tubes in which egg cells (called oocytes) form at one end and complete their development as they reach the other end of the tube. 2004 Olympus BioScapes Competition View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
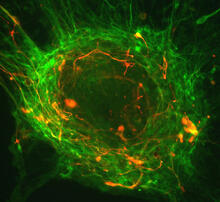
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaCrawling cell
6964
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaLily mitosis 08
1021
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
3286
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
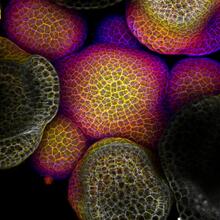
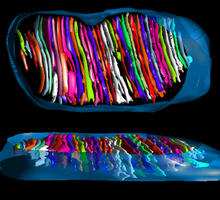
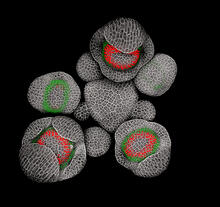
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaPolarized cells- 02
3333
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaFat cells (red) and blood vessels (green)
3600
A mouse's fat cells (red) are shown surrounded by a network of blood vessels (green). Daniela Malide, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
3571
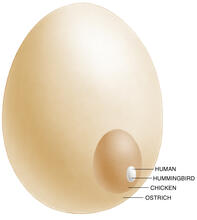
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaEgg comparison
1339
The largest human cell (by volume) is the egg. Human eggs are 150 micrometers in diameter and you can just barely see one with a naked eye. In comparison, consider the eggs of chickens...or ostriches! Judith Stoffer View MediaZebrafish embryo
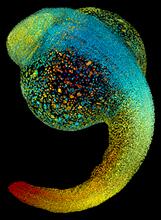
3644
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va. View MediaHydra 05
2441
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaAutofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
5755
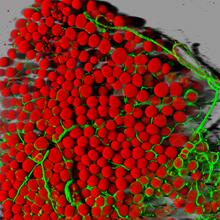
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaStress Response in Cells
6570
Two highly stressed osteosarcoma cells are shown with a set of green droplet-like structures followed by a second set of magenta droplets. Julia F. Riley and Carlos A. Castañeda, Syracuse University View MediaProteins related to myotonic dystrophy
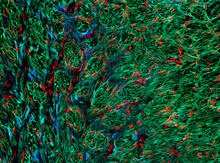
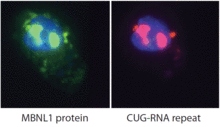
2727
Myotonic dystrophy is thought to be caused by the binding of a protein called Mbnl1 to abnormal RNA repeats. Manuel Ares, University of California, Santa Cruz View MediaBreast cancer cells change migration phenotypes
6986
Cancer cells can change their migration phenotype, which includes their shape and the way that they move to invade different tissues. Bo Sun, Oregon State University. View Media