Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
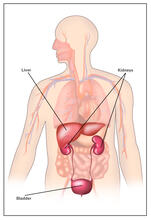
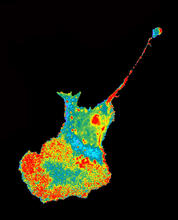
Body toxins (with labels)
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly ovary
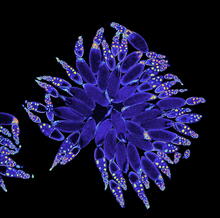
3607
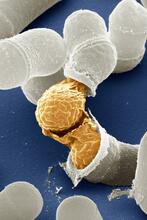
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaNCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
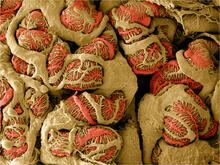
3392
Stained glomeruli in the kidney. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBiofilm blocking fluid flow
3446
This time-lapse movie shows that bacterial communities called biofilms can create blockages that prevent fluid flow in devices such as stents and catheters over a period of about 56 hours. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaMitosis - telophase
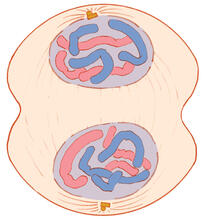
1332
Telophase during mitosis: Nuclear membranes form around each of the two sets of chromosomes, the chromosomes begin to spread out, and the spindle begins to break down. Judith Stoffer View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs
6587
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaVideo of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
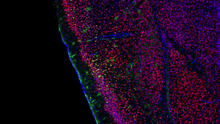
6781
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. NIH Director's Blog View MediaNucleus and rough ER
1290
The nucleus contains the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaDrugs enter skin (with labels)
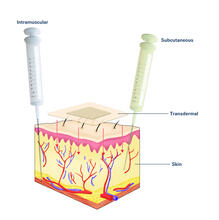
2532
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2531 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 07
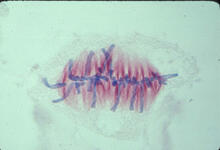
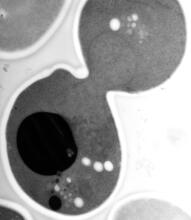
1017
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaDraper, shown in the fatbody of a Drosophila melanogaster larva
2757
The fly fatbody is a nutrient storage and mobilization organ akin to the mammalian liver. The engulfment receptor Draper (green) is located at the cell surface of fatbody cells. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaNucleolinus
2762
The nucleolinus is a cellular compartment that has been a lonely bystander in scientific endeavors. Mary Anne Alliegro, Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaBlinking bacteria
2724
Like a pulsing blue shower, E. coli cells flash in synchrony. Genes inserted into each cell turn a fluorescent protein on and off at regular intervals. Jeff Hasty, University of California, San Diego View MediaGlowing fish
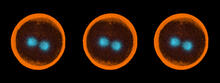
2667
Professor Marc Zimmer's family pets, including these fish, glow in the dark in response to blue light. Featured in the September 2009 issue of Findings. View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
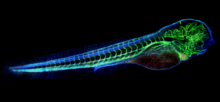
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaHydra 02
2438
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaDisease-resistant Arabidopsis leaf
2781
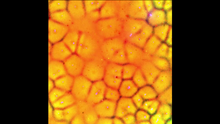
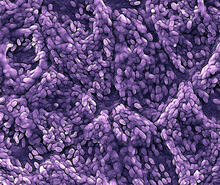
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf a few days after being exposed to the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaHeLa cells
3518
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaHair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
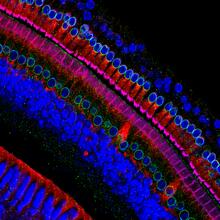
3618
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
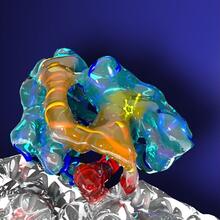
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaCryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
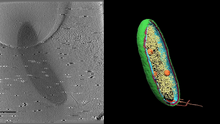
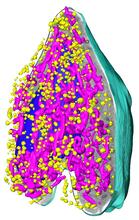
6569
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaSticky stem cells
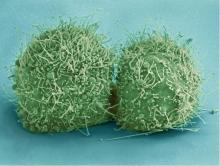
3457
Like a group of barnacles hanging onto a rock, these human cells hang onto a matrix coated glass slide. Ankur Singh and Andrés García, Georgia Institute of Technology View MediaG switch (with labels)
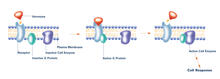
2537
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
3286
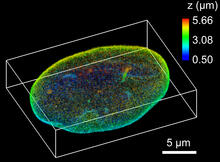
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View MediaNuclear Lamina
6572
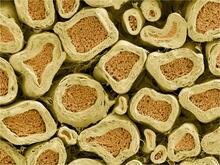
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaMyelinated axons 2
3397
Top view of myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBirth of a yeast cell
3614
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany View MediaYeast cell
1092
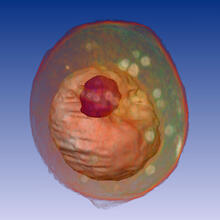
A whole yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell viewed by X-ray microscopy. Inside, the nucleus and a large vacuole (red) are visible. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaCells use bubble-like structures called vesicles to transport cargo
3634
Cells use bubble-like structures called vesicles (yellow) to import, transport, and export cargo and in cellular communication. A single cell may be filled with thousands of moving vesicles.Tatyana Svitkina, University of Pennsylvania View Media
Sea urchin embryo 04
1050
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaActin flow
2798
Speckle microscopy analysis of actin cytoskeleton force. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
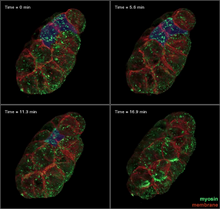
3334
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaEar hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
3272
Mouse embryonic stem cells matured into this bundle of hair cells similar to the ones that transmit sound in the ear. Stefen Heller, Stanford University, via CIRM View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
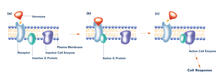
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly ovary_2
3656
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit--they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaMouse heart fibroblasts
3281
This image shows mouse fetal heart fibroblast cells. The muscle protein actin is stained red, and the cell nuclei are stained blue. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaPolarized cells- 02
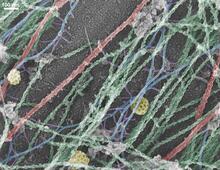
3333
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 04
2454
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaQuartered torso
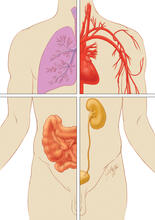
1280
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaDividing yeast cells with spindle pole bodies and contractile rings
6796
During cell division, spindle pole bodies (glowing dots) move toward the ends of yeast cells to separate copied genetic information. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaSoft X-ray tomography of a pancreatic beta cell
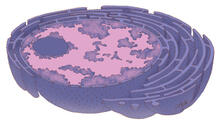
6605
A color-coded, 3D model of a rat pancreatic β cell. This type of cell produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco. View MediaLarvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
3627
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner View MediaMitochondrion from insect flight muscle
3662
This is a tomographic reconstruction of a mitochondrion from an insect flight muscle. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaSuicidal Stem Cells
3341
Embryonic stem cells store pre-activated Bax (red) in the Golgi, near the nucleus (blue). Featured in the June 21, 2012, issue of Biomedical Beat. Mohanish Deshmukh View Media