Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
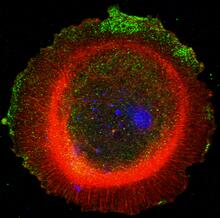
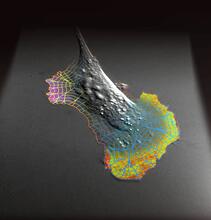
mDia1 antibody staining-01
3330
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaMisfolded proteins in mitochondria, 3-D video
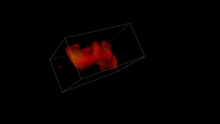
5877
Three-dimensional image of misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to image 5878. Rong Li, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane (with labels)
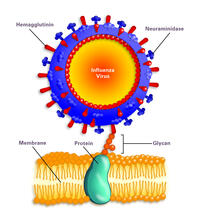
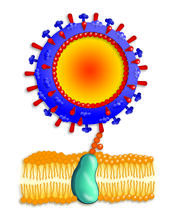
2505
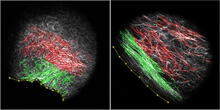
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediamDia1 antibody staining- 02
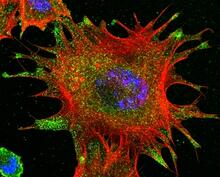
3331
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaCaulobacter
3262
A study using Caulobacter crescentus showed that some bacteria use just-in-time processing, much like that used in industrial delivery, to make the glue that allows them to attach to surfaces, Yves Brun, Indiana University View MediaNCMIR human spinal nerve
3387
Spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. They run within the spinal column to carry nerve signals to and from all parts of the body. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaDying melanoma cells
6966
Melanoma (skin cancer) cells undergoing programmed cell death, also called apoptosis. This process was triggered by raising the pH of the medium that the cells were growing in. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 72 hour
6556
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface from a small i L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaPrecisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Nature Nanotechnology View MediaLysosomes
1282
Lysosomes have powerful enzymes and acids to digest and recycle cell materials. Judith Stoffer View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaScanning electron microscopy of collagen fibers
3735
This image shows collagen, a fibrous protein that's the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen is a strong, ropelike molecule that forms stretch-resistant fibers. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAnnotated TEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
5760
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaHeLa cells
3518
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaProteasome
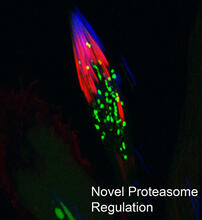
3451
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaFluorescent E. coli bacteria
3268
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. They called each blinking bacterial colony a biopixel. Thousands of fluorescent E. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaQuorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
3728
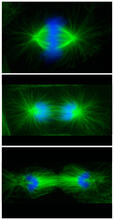
To simulate the consequences of disrupting bacterial cell-to-cell communication, called quorum sensing, in the crypts (small chambers within the colon), the researchers experimented with an inhibitor Minyoung Kevin Kim and Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaCell division phases in Xenopus frog cells
3442
These images show three stages of cell division in Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. They are (from top): metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
3571
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaBirth of a yeast cell
3614
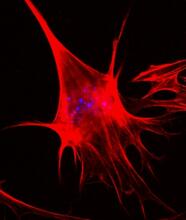
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
3613
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 2
5768
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaCellular traffic
2310
Like tractor-trailers on a highway, small sacs called vesicles transport substances within cells. This image tracks the motion of vesicles in a living cell. Alexey Sharonov and Robin Hochstrasser, University of Pennsylvania View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
6982
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaBrains of sleep-deprived and well-rested fruit flies
3490
On top, the brain of a sleep-deprived fly glows orange because of Bruchpilot, a communication protein between brain cells. These bright orange brain areas are associated with learning. Chiara Cirelli, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaClathrin-mediated endocytosis
5753
Endocytosis is the process by which cells are able to take up membrane and extracellular materials through the formation of a small intracellular bubble, called a vesicle. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah View MediaMouse heart muscle cells 02
3283
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane
2425
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
6356
Related to image 6355. Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaHippocampal neuron from rodent brain
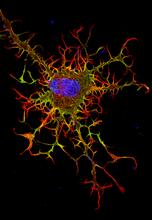
3686
Hippocampal neuron from rodent brain with dendrites shown in blue. The hundreds of tiny magenta, green and white dots are the dendritic spines of excitatory synapses. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaColorful cells
2428
Actin (purple), microtubules (yellow), and nuclei (green) are labeled in these cells by immunofluorescence. This image won first place in the Nikon 2003 Small World photo competition. Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaNeural circuits in worms similar to those in humans
3252
Green and yellow fluorescence mark the processes and cell bodies of some C. elegans neurons. Shawn Xu, University of Michigan View MediaWorms and human infertility
2333
This montage of tiny, transparent C. elegans--or roundworms--may offer insight into understanding human infertility. Abby Dernburg, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
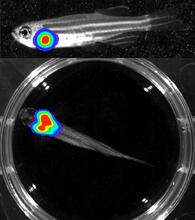
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaVibrio bacteria
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaIon channels
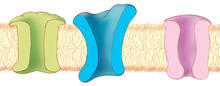
1284
The body uses a variety of ion channels to transport small molecules across cell membranes. Judith Stoffer View MediaBiosensors illustration
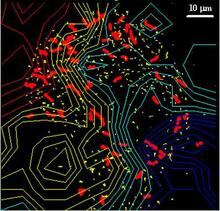
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaPolarized cells- 02
3333
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaDDR2 Receptors Attach to Collagen in Breast Tumor
3478
On the left, the boundary of a breast tumor (yellow) attaches to collagen fibers that are closest to it (green) using DDR2. On the right, a tumor without DDR2 remains disconnected from the collagen. Callie Corsa and Suzanne Ponik, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs
6587
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaDopaminergic neurons from ES cells
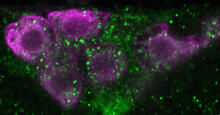
3270
Human embryonic stem cells differentiated into dopaminergic neurons, the type that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Image courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Jeannie Liu, Lab of Jan Nolta, University of California, Davis, via CIRM View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaMovements of myosin
2324
Inside the fertilized egg cell of a fruit fly, we see a type of myosin (related to the protein that helps muscles contract) made to glow by attaching a fluorescent protein. Victoria Foe, University of Washington View MediaGolgi theories
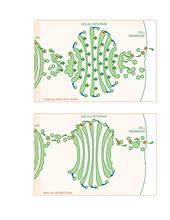
1278
Two models for how material passes through the Golgi apparatus: the vesicular shuttle model and the cisternae maturation model. Judith Stoffer View Media