Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
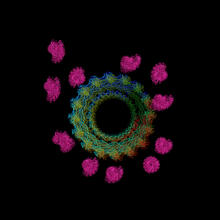
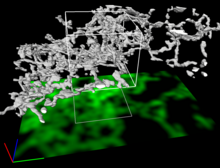
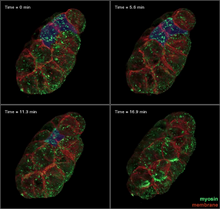
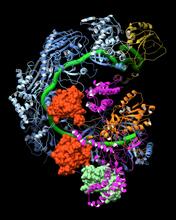
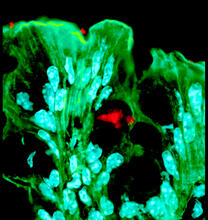
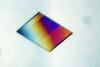
Actin filaments bundled around the dynamin helical polymer
6571
Multiple actin filaments (magenta) are organized around a dynamin helical polymer (rainbow colored) in this model derived from cryo-electron tomography. Elizabeth Chen, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
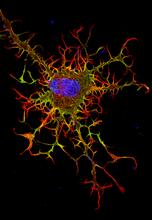
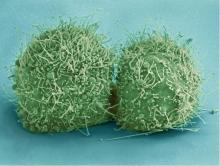
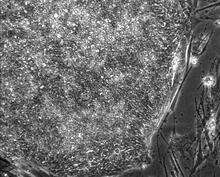
3613
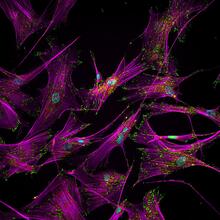
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaARTS triggers apoptosis
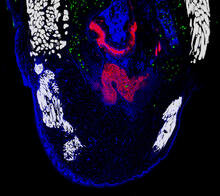
2432
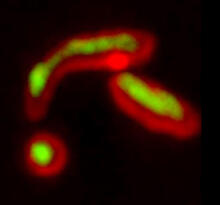
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaRegenerating lizard tail
6968
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California. View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 2
5856
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View MediaQuartered torso
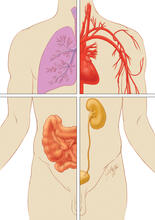
1280
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaCells frozen in time
2307
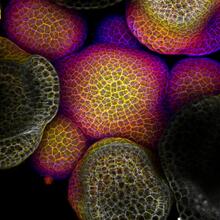
The fledgling field of X-ray microscopy lets researchers look inside whole cells rapidly frozen to capture their actions at that very moment. Here, a yeast cell buds before dividing into two. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco, and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaFlower-forming cells in a small plant related to cabbage (Arabidopsis)
3606
In plants, as in animals, stem cells can transform into a variety of different cell types. The stem cells at the growing tip of this Arabidopsis plant will soon become flowers. Arun Sampathkumar and Elliot Meyerowitz, California Institute of Technology View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
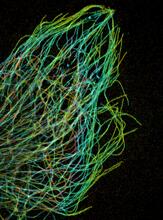
3611
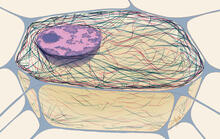
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaCytoskeleton
1272
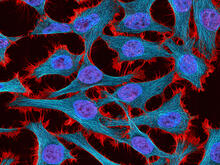
The three fibers of the cytoskeleton--microtubules in blue, intermediate filaments in red, and actin in green--play countless roles in the cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaHeLa cells
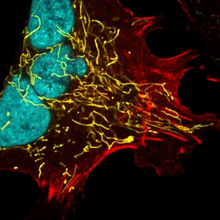
3518
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaZebrafish larva
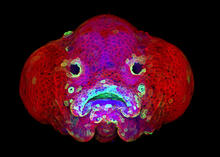
5881
You are face to face with a 6-day-old zebrafish larva. What look like eyes will become nostrils, and the bulges on either side will become eyes. Oscar Ruiz and George Eisenhoffer, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston View MediaBicycling cell
1337
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaHair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
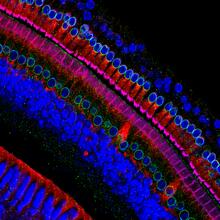
3618
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaCell in two stages of division
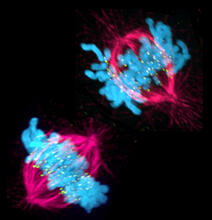
3541
This image shows a cell in two stages of division: prometaphase (top) and metaphase (bottom). Lilian Kabeche, Dartmouth View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
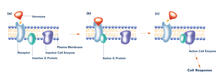
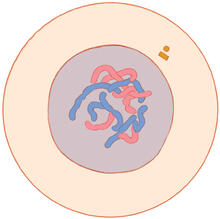
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaTime-lapse video of floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 24 hours
6550
This time-lapse video shows the emergence of a flower-like pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), that are gr L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
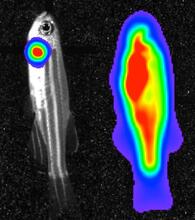
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
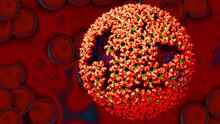
6356
Related to image 6355. Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 01
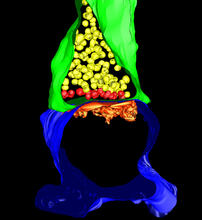
2603
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View Media3-D Architecture of a Synapse
5885
This image shows the structure of a synapse, or junction between two nerve cells in three dimensions. From the brain of a mouse. Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3334
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaCell division with late aligning chromosomes
2747
This video shows an instance of abnormal mitosis where chromosomes are late to align. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaSticky stem cells
3457
Like a group of barnacles hanging onto a rock, these human cells hang onto a matrix coated glass slide. Ankur Singh and Andrés García, Georgia Institute of Technology View MediaMisfolded proteins within in the mitochondria
5878
Misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to video 5877. Rong Li rong@jhu.edu Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21218, USA. View MediaCalling Cards in a mouse brain
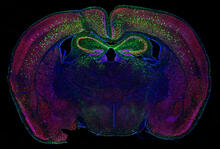
6780
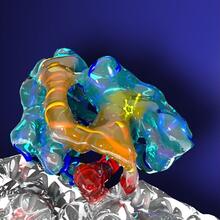
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. Allen Yen, Lab of Joseph Dougherty, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
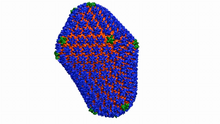
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
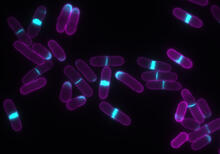
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaYeast cells with accumulated cell wall material
6797
Yeast cells that abnormally accumulate cell wall material (blue) at their ends and, when preparing to divide, in their middles. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaMolecular model of freshly made Rous sarcoma virus (RSV)
3771
Viruses have been the foes of animals and other organisms for time immemorial. Boon Chong Goh, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaEar hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
3272
Mouse embryonic stem cells matured into this bundle of hair cells similar to the ones that transmit sound in the ear. Stefen Heller, Stanford University, via CIRM View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
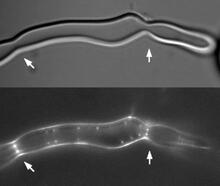
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View MediaMultinucleated cancer cell
6967
A cancer cell with three nuclei, shown in turquoise. The abnormal number of nuclei indicates that the cell failed to go through cell division, probably more than once. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaNuclear Lamina
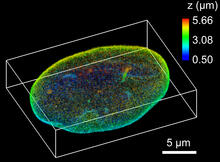
6572
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
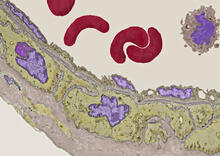
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaBiopixels
3266
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
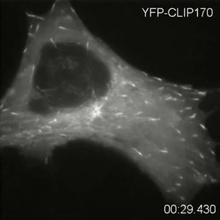
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaBacteria in the mouse colon
3527
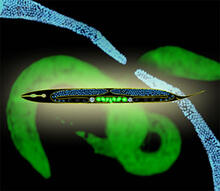
Image of the colon of a mouse mono-colonized with Bacteroides fragilis (red) residing within the crypt channel. The red staining is due to an antibody to B. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaWorms and human infertility
2333
This montage of tiny, transparent C. elegans--or roundworms--may offer insight into understanding human infertility. Abby Dernburg, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaMapping brain differences
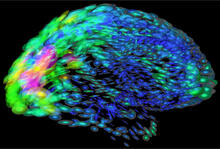
2419
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaHeLa cells
3521
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaNucleolinus
2762
The nucleolinus is a cellular compartment that has been a lonely bystander in scientific endeavors. Mary Anne Alliegro, Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaSea urchin embryo 06
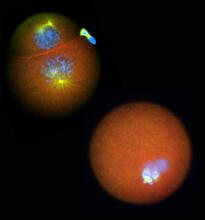
1052
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaCell cycle
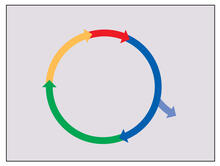
2498
Cells progress through a cycle that consists of phases for growth (blue, green, yellow) and division (red). Cells become quiescent when they exit this cycle (purple). Crabtree + Company View MediaSnowflake yeast 2
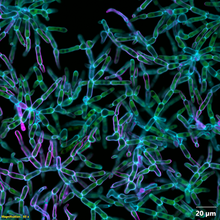
6970
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View Media