Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
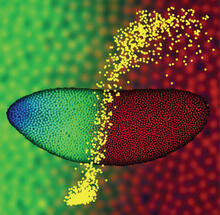
Precise development in the fruit fly embryo
2593
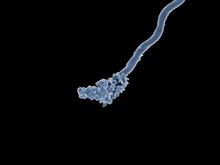
This 2-hour-old fly embryo already has a blueprint for its formation, and the process for following it is so precise that the difference of just a few key molecules can change the plans. Thomas Gregor, Princeton University View MediaRelapsing fever bacterium (gray) and red blood cells
3585
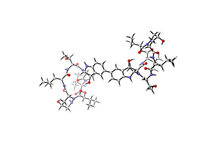
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaHimastatin
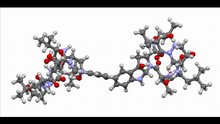
6848
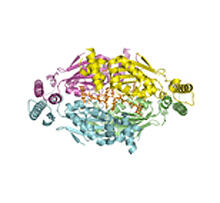
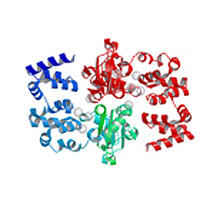
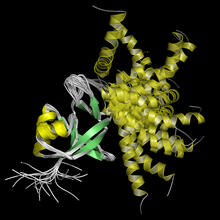
A model of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaThymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime
2387
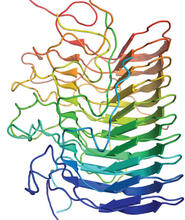
A model of thymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime. Joint Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaVDAC video 03
2572
This video shows the structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaHuman Adenovirus
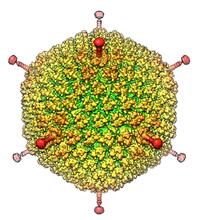
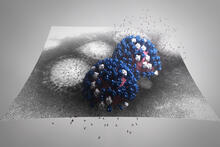
6347
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaCell Nucleus and Lipid Droplets
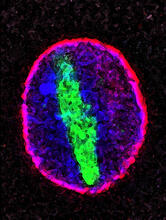
6547
A cell nucleus (blue) surrounded by lipid droplets (yellow). James Olzmann, University of California, Berkeley View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaIntasome
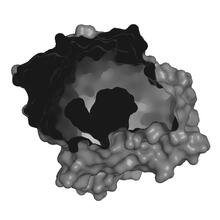
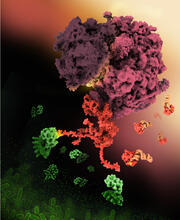
6346
Salk researchers captured the structure of a protein complex called an intasome (center) that lets viruses similar to HIV establish permanent infection in their hosts. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaA dynamic model of the DNA helicase protein complex
3750
This short video shows a model of the DNA helicase in yeast. This DNA helicase has 11 proteins that work together to unwind DNA during the process of copying it, called DNA replication. Huilin Li, Stony Brook University View MediaA molecular switch strips transcription factor from DNA
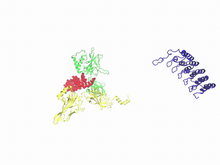
3729
In this video, Rice University scientists used molecular modeling with a mathematical algorithm called AWSEM (for associative memory, water-mediated, structure and energy model) and structural data to Davit Potoyan and Peter Wolynes View MediaAntitoxin GhoS (Illustration 1)
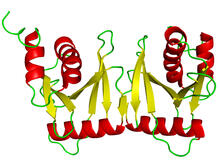
3427
Structure of the bacterial antitoxin protein GhoS. GhoS inhibits the production of a bacterial toxin, GhoT, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Rebecca Page and Wolfgang Peti, Brown University and Thomas K. Wood, Pennsylvania State University View MediaSerum albumin structure 1
3744
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. Wladek Minor, University of Virginia View MediaFlower-forming cells in a small plant related to cabbage (Arabidopsis)
3606
In plants, as in animals, stem cells can transform into a variety of different cell types. The stem cells at the growing tip of this Arabidopsis plant will soon become flowers. Arun Sampathkumar and Elliot Meyerowitz, California Institute of Technology View MediaCysteine dioxygenase from mouse
2347
Model of the mammalian iron enzyme cysteine dioxygenase from a mouse. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaPig trypsin (1)
2400
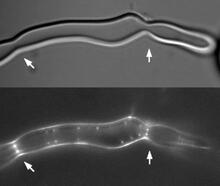
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View MediaThe Structure of Cilia’s Doublet Microtubules
6549
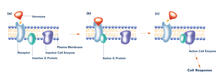
Cilia (cilium in singular) are complex molecular machines found on many of our cells. Brown Lab, Harvard Medical School and Veronica Falconieri Hays View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaDiversity oriented synthesis: generating skeletal diversity using folding processes
3327
This 1 1/2-minute video animation was produced for chemical biologist Stuart Schreiber's lab page. The animation shows how diverse chemical structures can be produced in the lab. Eric Keller View MediaRNase A (1)
2398
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediatRNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans
2351
An NMR solution structure model of the transfer RNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans (subunit Sen15). This represents the first structure of a eukaryotic tRNA splicing endonuclease subunit. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaAtomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
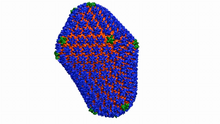
6601
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaMagnesium transporter protein from E. faecalis
2345
Structure of a magnesium transporter protein from an antibiotic-resistant bacterium (Enterococcus faecalis) found in the human gut. New York Structural GenomiX Consortium View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
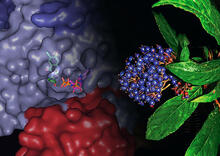
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaWreath-shaped protein from X. campestris
2372
Crystal structure of a protein with unknown function from Xanthomonas campestris, a plant pathogen. Eight copies of the protein crystallized to form a ring. Ken Schwinn and Sonia Espejon-Reynes, New York SGX Research Center for Structural Genomics View MediaStetten Lecture 2017poster image
5896
This image is featured on the poster for Dr. Rommie Amaro's 2017 Stetten Lecture. Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaArtificial cilia exhibit spontaneous beating
3344
Researchers have created artificial cilia that wave like the real thing. Zvonimir Dogic View MediaCellular aging
2578
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute View MediaProtein from Arabidopsis thaliana
2339
NMR solution structure of a plant protein that may function in host defense. This protein was expressed in a convenient and efficient wheat germ cell-free system. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaStructure of amyloid-forming prion protein
3542
This structure from an amyloid-forming prion protein shows one way beta sheets can stack. Douglas Fowler, University of Washington View MediaSpace-filling model of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6767
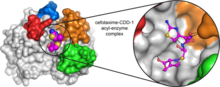
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaSARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
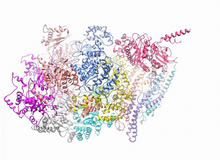
6991
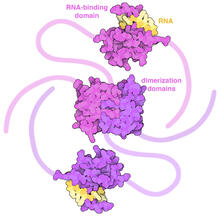
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaLife of an AIDS virus (with labels and stages)
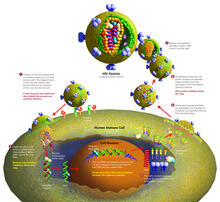
2515
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaSnowflake DNA origami
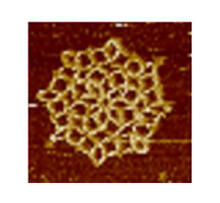
3724
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. The image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Holiday-Themed Collection. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaChang Shan
3483
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaFungal lipase (2)
2411
Crystals of fungal lipase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaHimastatin, 360-degree view
6851
A 360-degree view of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaCatalase diversity
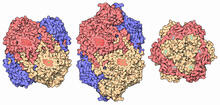
7003
Catalases are some of the most efficient enzymes found in cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaProtein map
2423
Network diagram showing a map of protein-protein interactions in a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell. This cluster includes 78 percent of the proteins in the yeast proteome. Hawoong Jeong, KAIST, Korea View MediaMeasles virus proteins
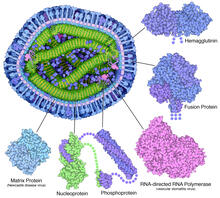
6996
A cross section of the measles virus in which six proteins (enlarged on the outside of the virus) work together to infect cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHsp33 Heat Shock Protein Inactive to Active
3402
When the heat shock protein hsp33 is folded, it is inactive and contains a zinc ion, stabilizing the redox sensitive domain (orange). Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan View MediaShiga toxin
6997
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
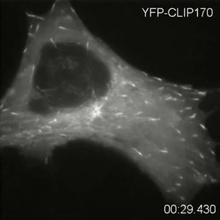
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
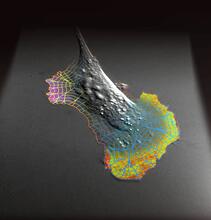
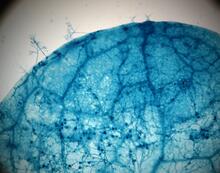
2782
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
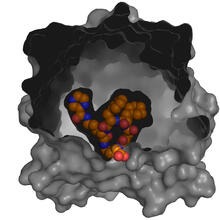
3417
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaProtein folding video
3391
Proteins are long chains of amino acids. Each protein has a unique amino acid sequence. It is still a mystery how a protein folds into the proper shape based on its sequence. Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group View MediaRNase A (2)
2402
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediadUTP pyrophosphatase from M. tuberculosis
2381
Model of an enzyme, dUTP pyrophosphatase, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drugs targeted to this enzyme might inhibit the replication of the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products
2521
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2522 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View Media