Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
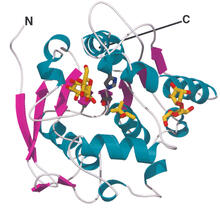
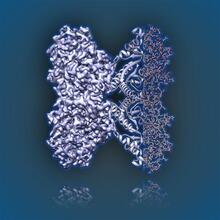
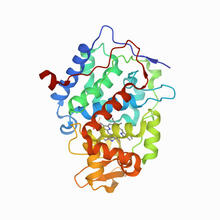
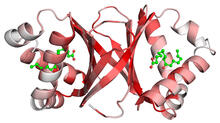
Most abundant protein in M. tuberculosis
2378
Model of a protein, antigen 85B, that is the most abundant protein exported by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaProtective membrane and membrane proteins of the dengue virus visualized with cryo-EM
3756
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaRepairing DNA
3493
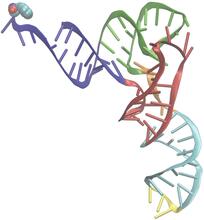
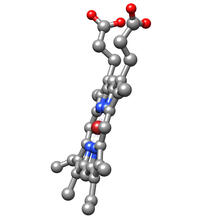
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View MediaPhenylalanine tRNA molecule
3406
Phenylalanine tRNA showing the anticodon (yellow) and the amino acid, phenylalanine (blue and red spheres). Patrick O'Donoghue and Dieter Soll, Yale University View MediaPig trypsin (2)
2413
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaATP Synthase
6353
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaAldolase
6350
2.5Å resolution reconstruction of rabbit muscle aldolase collected on a FEI/Thermo Fisher Titan Krios with energy filter and image corrector. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaStructure of heme, side view
3540
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaZebrafish embryo
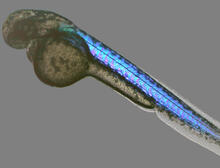
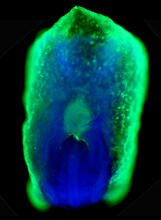
6897
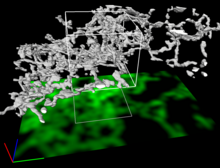
A zebrafish embryo showing its natural colors. Zebrafish have see-through eggs and embryos, making them ideal research organisms for studying the earliest stages of development. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 1
5855
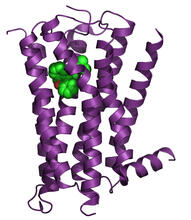
Superresolution microscopy work on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the peripheral areas of the cell showing details of the structure and arrangement in a complex web of tubes. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaNociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide opioid receptor
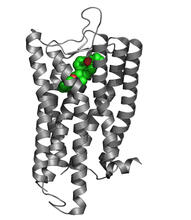
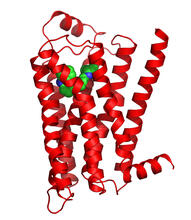
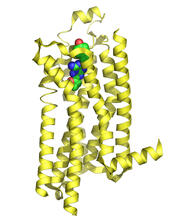
3364
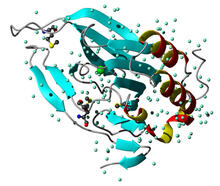
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, compound-24 Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaCCP enzyme
6762
The enzyme CCP is found in the mitochondria of baker’s yeast. Scientists study the chemical reactions that CCP triggers, which involve a water molecule, iron, and oxygen. Protein Data Bank. View MediaHuman aspartoacylase
2352
Model of aspartoacylase, a human enzyme involved in brain metabolism. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaCysteine dioxygenase from mouse
2347
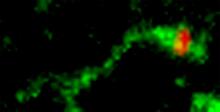
Model of the mammalian iron enzyme cysteine dioxygenase from a mouse. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
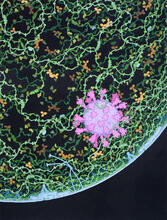
3488
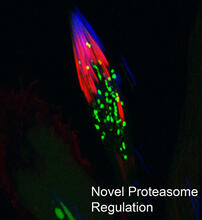
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaProteasome
3451
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
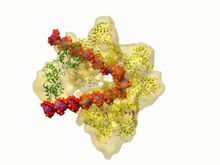
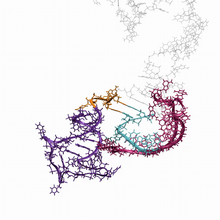
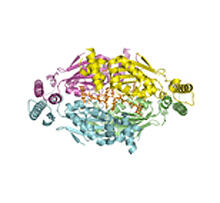
3307
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaG switch (with labels and stages)
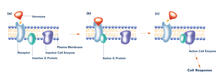
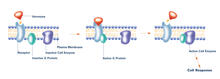
2538
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaBeta 2-adrenergic receptor
3358
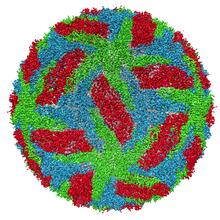
The receptor is shown bound to a partial inverse agonist, carazolol. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaPlant resistosome
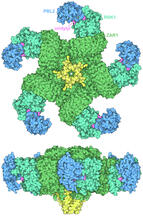
7002
The research organism Arabidopsis thaliana forms a large molecular machine called a resistosome to fight off infections. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View Media800 MHz NMR magnet
3526
Scientists use nuclear magnetic spectroscopy (NMR) to determine the detailed, 3D structures of molecules. Asokan Anbanandam, University of Kansas View MediaCryo-electron microscopy revealing the "wasabi receptor"
3747
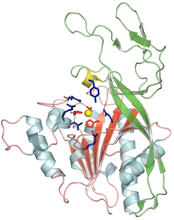
The TRPA1 protein is responsible for the burn you feel when you taste a bite of sushi topped with wasabi. Jean-Paul Armache, UCSF View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 4
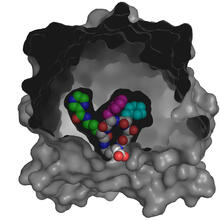
3416
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaAntitoxin GhoS (Illustration 1)
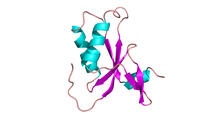
3427
Structure of the bacterial antitoxin protein GhoS. GhoS inhibits the production of a bacterial toxin, GhoT, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Rebecca Page and Wolfgang Peti, Brown University and Thomas K. Wood, Pennsylvania State University View MediaG switch (with labels)
2537
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaRNase A (2)
2402
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaNicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase
2355
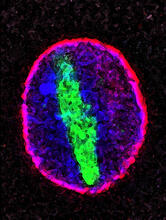
Model of the enzyme nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaOptic nerve astrocytes
5852
Astrocytes in the cross section of a human optic nerve head Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaCryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
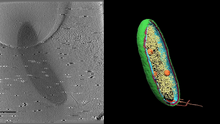
6569
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaSelf-organizing proteins
2771
Under the microscope, an E. coli cell lights up like a fireball. Each bright dot marks a surface protein that tells the bacteria to move toward or away from nearby food and toxins. View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
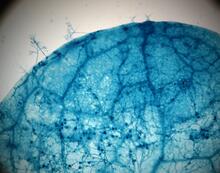
2782
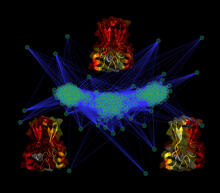
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
3295
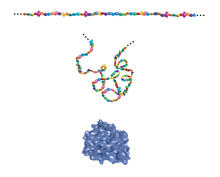
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaBuilding blocks and folding of proteins
2508
Proteins are made of amino acids hooked end-to-end like beads on a necklace. To become active, proteins must twist and fold into their final, or "native," conformation. Crabtree + Company View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 2
5856
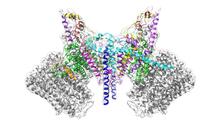
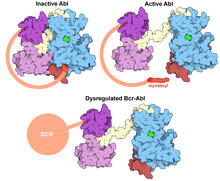
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaProtein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
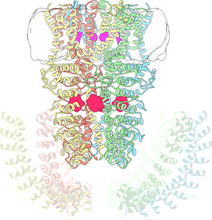
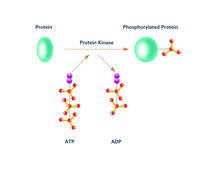
7004
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and co Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaRNA folding in action
6625
An RNA molecule dynamically refolds itself as it is being synthesized. When the RNA is short, it ties itself into a “knot” (dark purple). Julius Lucks, Northwestern University View MediaCRISPR
6351
RNA incorporated into the CRISPR surveillance complex is positioned to scan across foreign DNA. Cryo-EM density from a 3Å reconstruction is shown as a yellow mesh. NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaA2A adenosine receptor
3361
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, ZM241385. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaPartial Model of a Cilium’s Doublet Microtubule
6548
Cilia (cilium in singular) are complex molecular machines found on many of our cells. Brown Lab, Harvard Medical School and Veronica Falconieri Hays. View MediaKinases (with labels)
2535
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaH1 histamine receptor
3360
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, doxepin. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaMouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
2607
This eerily glowing blob isn't an alien or a creature from the deep sea--it's a mouse embryo just eight and a half days old. The green shell and core show a protein called Smad4. Kenneth Zaret, Fox Chase Cancer Center View MediaDNase
2410
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaThymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime
2387
A model of thymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime. Joint Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaRespiratory droplet
6994
This painting shows a cross section of a small respiratory droplet, like the ones that are thought to transmit SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaDimeric ferredoxin-like protein from an unidentified marine microbe
2340
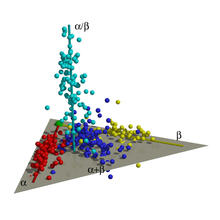
This is the first structure of a protein derived from the metagenomic sequences collected during the Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling project. Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaMap of protein structures 01
2365
A global "map of the protein structure universe." The Berkeley Structural Genomics Center has developed a method to visualize the vast universe of protein structures in which proteins of similar struc Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
3597
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaCellular aging
2578
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute View Media