Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
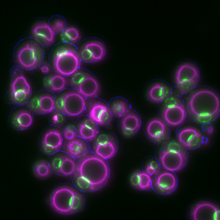
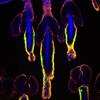
Yeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
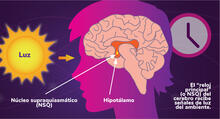
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaLos ritmos circadianos y el núcleo supraquiasmático
6614
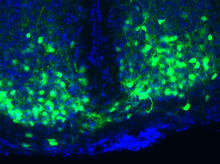
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y de comportamiento que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaMaster clock of the mouse brain
3547
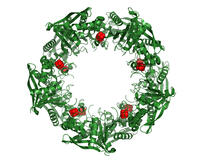
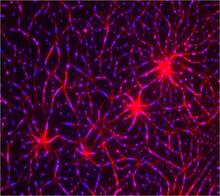
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaBottles of warfarin
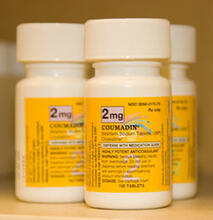
2579
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 04
2793
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
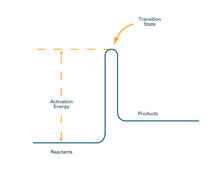
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
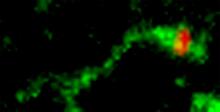
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaBond types (with labels)
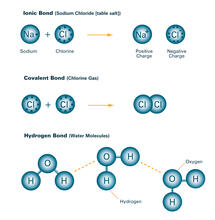
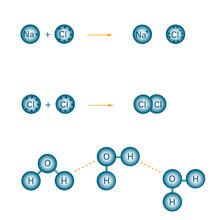
2520
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaWhite Poppy (cropped)
3423
A cropped image of a white poppy. View poppy uncropped here 3424. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaIn vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaKinases (with labels)
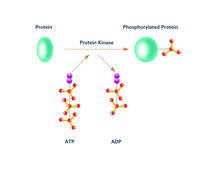
2535
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaHuman opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
3314
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
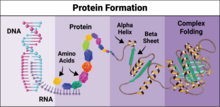
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaProtein formation
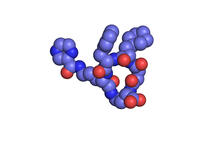
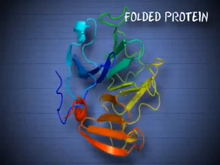
6603
Proteins are 3D structures made up of smaller units. DNA is transcribed to RNA, which in turn is translated into amino acids. NIGMS, with the folded protein illustration adapted from Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaHimastatin
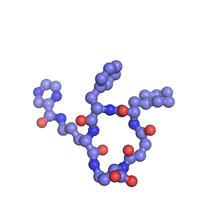
6848
A model of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaCarbon building blocks (with examples)
2507
The arrangement of identical molecular components can make a dramatic difference. For example, carbon atoms can be arranged into dull graphite (left) or sparkly diamonds (right). Crabtree + Company View MediaA drug's life in the body (with labels)
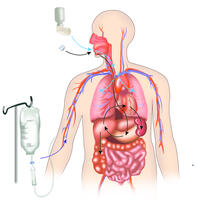
2528
A drug's life in the body. Medicines taken by mouth (oral) pass through the liver before they are absorbed into the bloodstream. Crabtree + Company View MediaSpace-filling model of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
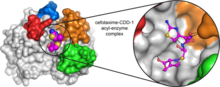
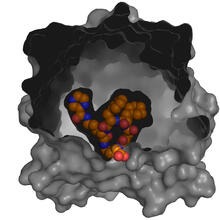
6767
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
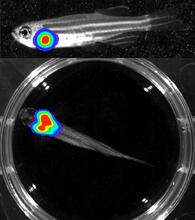
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaAspirin (with labels)
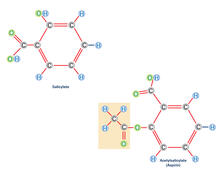
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaEnzyme transition states
3429
The molecule on the left is an electrostatic potential map of the van der Waals surface of the transition state for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Vern Schramm, Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University View MediaDose response curves
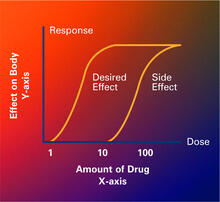
2533
Dose-response curves determine how much of a drug (X-axis) causes a particular effect, or a side effect, in the body (Y-axis). Featured in Medicines By Design. Crabtree + Company View MediaNetwork Map
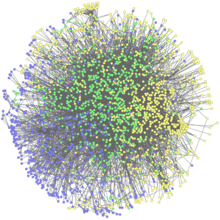
2735
This network map shows the overlap (green) between the long QT syndrome (yellow) and epilepsy (blue) protein-interaction neighborhoods located within the human interactome. Seth Berger, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaCancer Cells Glowing from Luciferin
3480
The activator cancer cell culture, right, contains a chemical that causes the cells to emit light when in the presence of immune cells. Mark Sellmyer, Stanford University School of Medicine View MediaAntibodies in silica honeycomb
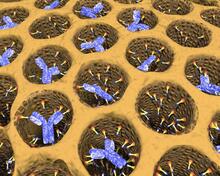
2750
Antibodies are among the most promising therapies for certain forms of cancer, but patients must take them intravenously, exposing healthy tissues to the drug and increasing the risk of side effects. Chenghong Lei, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory & Karl Erik Hellstrom, University of Washington View MediaEnzyme reaction
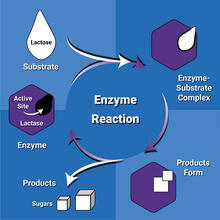
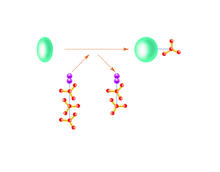
6604
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by reducing the amount of energy needed for the reactions. NIGMS View MediaMolecular view of glutamatergic synapse
6992
This illustration highlights spherical pre-synaptic vesicles that carry the neurotransmitter glutamate. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 01
2790
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBond types
2519
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaHimastatin, 360-degree view
6851
A 360-degree view of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaChang Shan
3483
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaKinases
2534
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 1
3413
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3525
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. Kenneth Keiler, Penn State University View MediaActivation energy
2525
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2526 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaHimastatin and bacteria
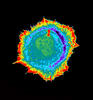
6850
A model of the molecule himastatin overlaid on an image of Bacillus subtilis bacteria. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaBioluminescence in a Tube
5895
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaPrecisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Nature Nanotechnology View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
6982
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaA drug's life in the body
2527
A drug's life in the body. Medicines taken by mouth pass through the liver before they are absorbed into the bloodstream. Crabtree + Company View MediaAtomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
3422
The atomic structure of the morphine biosynthetic enzyme salutaridine reductase bound to the cofactor NADPH. The substrate salutaridine is shown entering the active site. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 03
2796
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaMovie of in vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3786
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaSee how immune cell acid destroys bacterial proteins
6602
This animation shows the effect of exposure to hypochlorous acid, which is found in certain types of immune cells, on bacterial proteins. American Chemistry Council View Media