Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
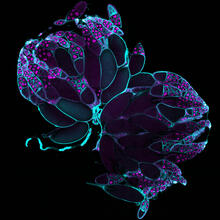
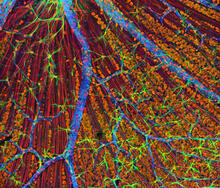
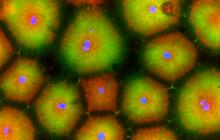
Fruit fly ovaries
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
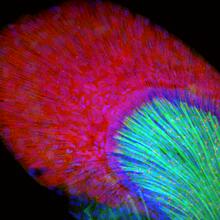
Dense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 1
5855
Superresolution microscopy work on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the peripheral areas of the cell showing details of the structure and arrangement in a complex web of tubes. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaMouse brain 2
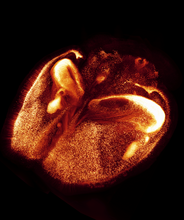
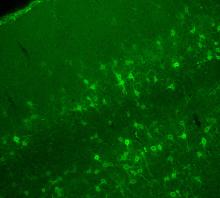
6930
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaMouse brain 3
6931
Various views of a mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaMicrotubules in hippocampal neurons
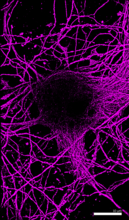
6890
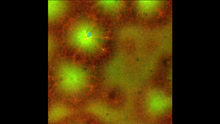
Microtubules (magenta) in neurons of the hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaSoft X-ray tomography of a pancreatic beta cell
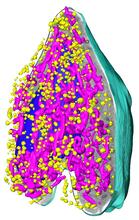
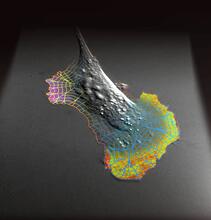
6605
A color-coded, 3D model of a rat pancreatic β cell. This type of cell produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco. View MediaZebrafish head vasculature
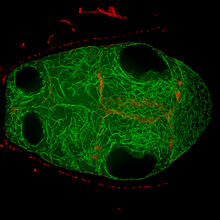
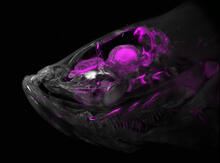
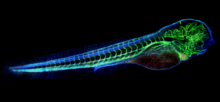
6934
A zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFly cells
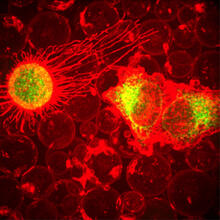
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaRSV-Infected Cell
3567
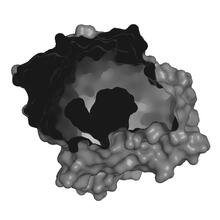
Viral RNA (red) in an RSV-infected cell. Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University View MediaCryo-EM reveals how the HIV capsid attaches to a human protein to evade immune detection
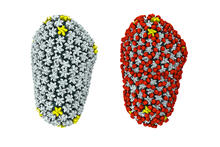
3755
The illustration shows the capsid of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) whose molecular features were resolved with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Juan R. Perilla, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaMicroscopy image of bird-and-flower DNA origami
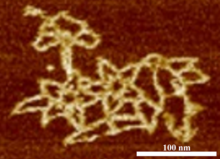
3690
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 3
6589
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Video created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 1
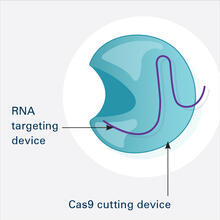
6465
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the first frame in a series of four. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaPig trypsin (3)
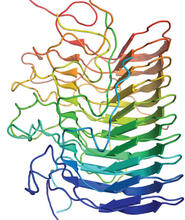
2414
Crystals of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
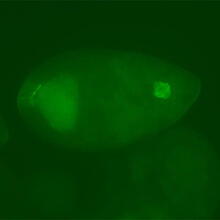
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaMicrofluidic chip
3265
Microfluidic chips have many uses in biology labs. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaRabbit GPDA
2405
A crystal of rabbit GPDA protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCRISPR illustration
3719
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaZebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
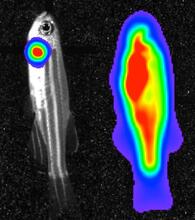
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6765
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaMouse Retina
3309
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 2
3414
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaStructure of amyloid-forming prion protein
3542
This structure from an amyloid-forming prion protein shows one way beta sheets can stack. Douglas Fowler, University of Washington View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCone snail shell
2576
A shell from the venomous cone snail Conus omaria, which lives in the Pacific and Indian oceans and eats other snails. Kerry Matz, University of Utah View MediaAutomated crystal screening system
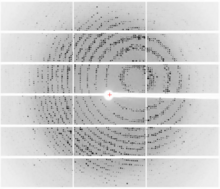
2362
Automated crystal screening systems such as the one shown here are becoming a common feature at synchrotron and other facilities where high-throughput crystal structure determination is being carried Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaCells lining the trachea
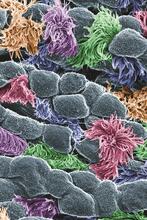
3646
In this image, viewed with a ZEISS ORION NanoFab microscope, the community of cells lining a mouse airway is magnified more than 10,000 times. Eva Mutunga and Kate Klein, University of the District of Columbia and National Institute of Standards and Technology View MediaComputer algorithm
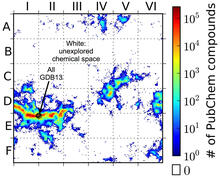
3458
This computer algorithm plots all feasible small carbon-based molecules as though they were cities on a map and identifies huge, unexplored spaces that may help fuel research into new drug therapies. Aaron Virshup, Julia Contreras-Garcia, Peter Wipf, Weitao Yang and David Beratan, University of Pittsburgh Center for Chemical Methodologies and Library Development View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
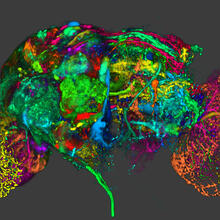
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaLab mice
1069
Many researchers use the mouse (Mus musculus) as a model organism to study mammalian biology. Bill Branson, National Institutes of Health View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaAnnotated TEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
5760
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaMapping disease spread
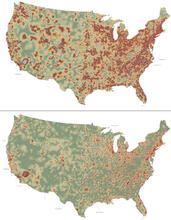
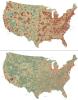
2320
How far and fast an infectious disease spreads across a community depends on many factors, including transportation. These U.S. David Chrest, RTI International View MediaTFIID complex binds DNA to start gene transcription
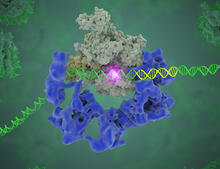
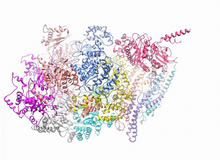
3766
Gene transcription is a process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
3742
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
6776
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaA dynamic model of the DNA helicase protein complex
3750
This short video shows a model of the DNA helicase in yeast. This DNA helicase has 11 proteins that work together to unwind DNA during the process of copying it, called DNA replication. Huilin Li, Stony Brook University View MediaStatistical cartography
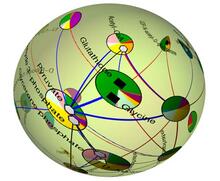
2331
Like a world of its own, this sphere represents all the known chemical reactions in the E. coli bacterium. Luis A. Nunes Amaral, Northwestern University View MediaCentromeres on human chromosomes
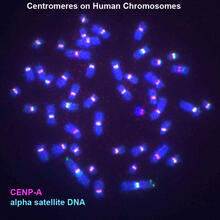
3255
Human metaphase chromosomes are visible with fluorescence in vitro hybridization (FISH). Centromeric alpha satellite DNA (green) are found in the heterochromatin at each centromere. Peter Warburton, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaYoung squids
6903
Real-time movie of young squids. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View Media