Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
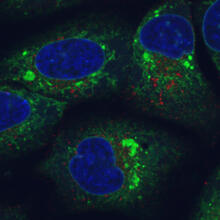
Endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
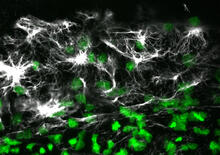
2807
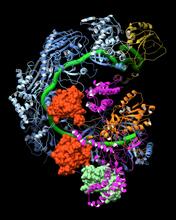
Confocal image showing high levels of the protein vimentin (white) at the edge zone of a quail embryo. Cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 4
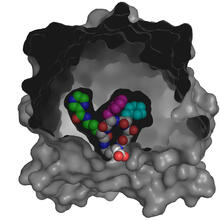
3416
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaRNase A (1)
2398
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
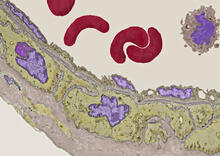
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
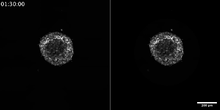
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaTracking cells in a gastrulating zebrafish embryo
6776
During development, a zebrafish embryo is transformed from a ball of cells into a recognizable body plan by sweeping convergence and extension cell movements. This process is called gastrulation. Liliana Solnica-Krezel, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaPig trypsin (1)
2400
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaBreast cancer cells change migration phenotypes
6986
Cancer cells can change their migration phenotype, which includes their shape and the way that they move to invade different tissues. Bo Sun, Oregon State University. View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaMouse retina
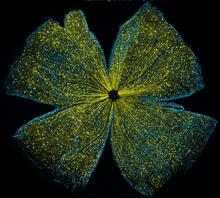
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
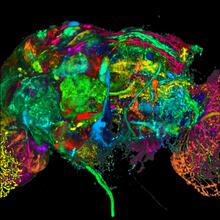
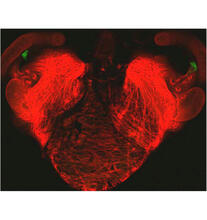
5868
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
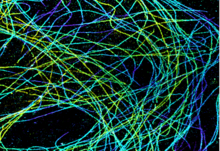
6891
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaStatistical cartography
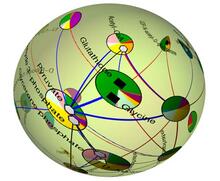
2331
Like a world of its own, this sphere represents all the known chemical reactions in the E. coli bacterium. Luis A. Nunes Amaral, Northwestern University View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
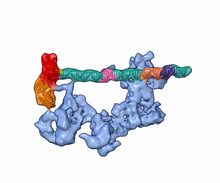
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaAxolotls showing nervous system components
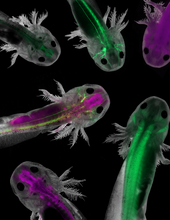
6928
Axolotls—a type of salamander—that have been genetically modified so that various parts of their nervous systems glow purple and green. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
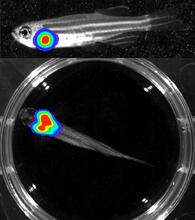
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaNuclear Lamina
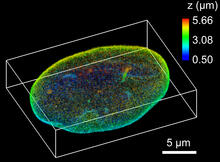
6572
The 3D single-molecule super-resolution reconstruction of the entire nuclear lamina in a HeLa cell was acquired using the TILT3D platform. Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D. View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaBacterial cells aggregating above the light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7018
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media