Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
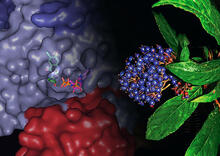
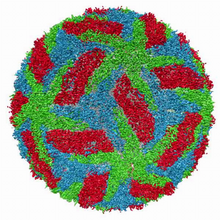
Human Adenovirus
6347
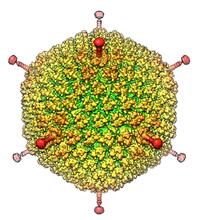
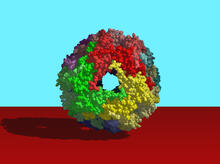
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaThymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime
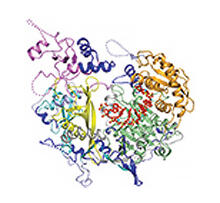
2387
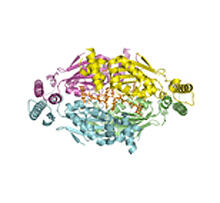
A model of thymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime. Joint Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaIntracellular forces
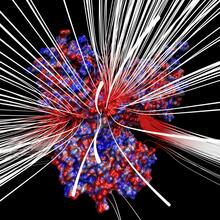
2799
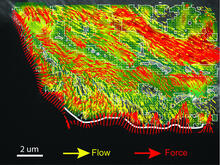
Force vectors computed from actin cytoskeleton flow. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaHistone deacetylases
7001
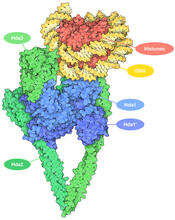
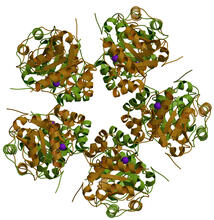
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaCatalase diversity
7003
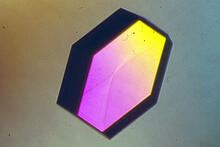
Catalases are some of the most efficient enzymes found in cells. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaPig trypsin (1)
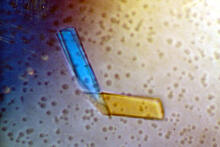
2400
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCrane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
6898
A crane fly spermatocyte during metaphase of meiosis-I, a step in the production of sperm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaEarly life of a protein
2740
This illustration represents the early life of a protein—specifically, apomyoglobin—as it is synthesized by a ribosome and emerges from the ribosomal tunnel, which contains the newly formed protein's Silvia Cavagnero, University of Wisconsin, Madison View MediaRelapsing fever bacterium (gray) and red blood cells
3585
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaHeat shock protein complex from Methanococcus jannaschii
2385
Model based on X-ray crystallography of the structure of a small heat shock protein complex from the bacteria, Methanococcus jannaschii. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI-1 View MediaMyotonic dystrophy type 2 genetic defect
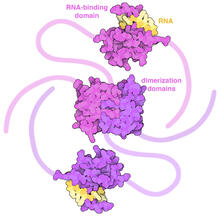
3573
Scientists revealed a detailed image of the genetic defect that causes myotonic dystrophy type 2 and used that information to design drug candidates to counteract the disease. Matthew Disney, Scripps Research Institute and Ilyas Yildirim, Northwestern University View MediaStructure of heme, side view
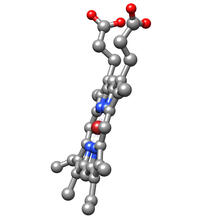
3540
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaH1 histamine receptor
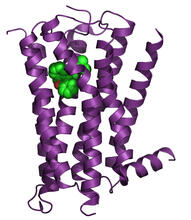
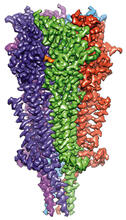
3360
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, doxepin. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaSARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
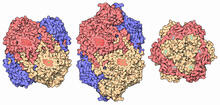
6991
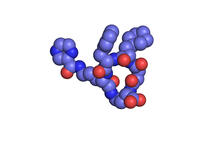
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaBence Jones protein MLE
2399
A crystal of Bence Jones protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaProtein from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicam
2374
A knotted protein from an archaebacterium called Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicam. This organism breaks down waste products and produces methane gas. Midwest Center For Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaProtein from Arabidopsis thaliana
2339
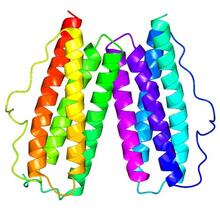
NMR solution structure of a plant protein that may function in host defense. This protein was expressed in a convenient and efficient wheat germ cell-free system. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaPanB from M. tuberculosis (1)
2380
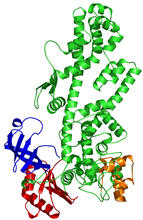
Model of an enzyme, PanB, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. This enzyme is an attractive drug target. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaVDAC-1 (2)
2491
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaProtein folding video
3391
Proteins are long chains of amino acids. Each protein has a unique amino acid sequence. It is still a mystery how a protein folds into the proper shape based on its sequence. Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
3611
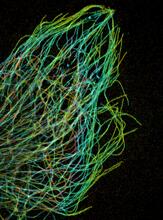
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaProtein rv2844 from M. tuberculosis
2343
This crystal structure shows a conserved hypothetical protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Only 12 other proteins share its sequence homology, and none has a known function. Integrated Center for Structure and Function Innovation View MediaDimeric association of receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase
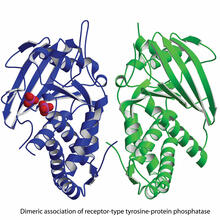
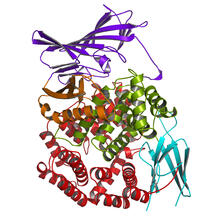
2349
Model of the catalytic portion of an enzyme, receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase from humans. The enzyme consists of two identical protein subunits, shown in blue and green. New York Structural GenomiX Research Consortium, PSI View MediaCells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
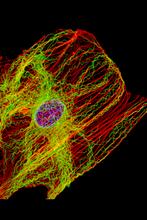
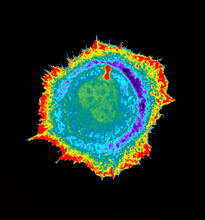
3617
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University View MediaInsulin and protein interact in pancreatic beta cells
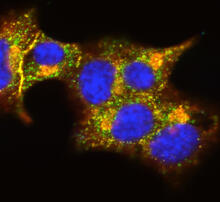
3546
A large number of proteins interact with the hormone insulin as it is produced in and secreted from the beta cells of the pancreas. William E. Balch, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
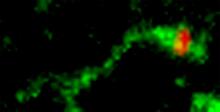
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaIntasome
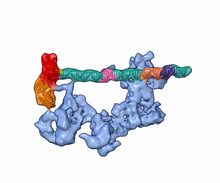
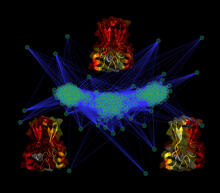
6346
Salk researchers captured the structure of a protein complex called an intasome (center) that lets viruses similar to HIV establish permanent infection in their hosts. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products
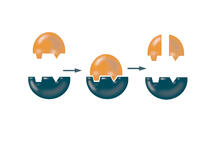
2521
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2522 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaAminopeptidase N from N. meningitidis
2341
Model of the enzyme aminopeptidase N from the human pathogen Neisseria meningitidis, which can cause meningitis epidemics. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaWeblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616
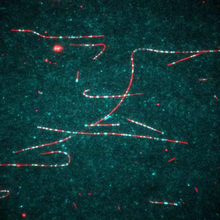
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University. View MediaMicroscopy image of bird-and-flower DNA origami
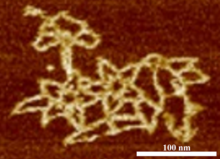
3690
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaFull-length serotonin receptor (ion channel)
6579
A 3D reconstruction, created using cryo-electron microscopy, of an ion channel known as the full-length serotonin receptor in complex with the antinausea drug granisetron (orange). Sudha Chakrapani, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. View MediaElectrostatic map of human spermine synthase
3658
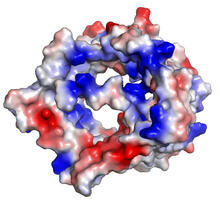
From PDB entry 3c6k, Crystal structure of human spermine synthase in complex with spermidine and 5-methylthioadenosine. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
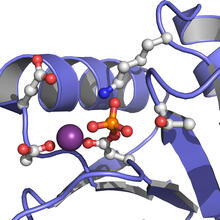
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaActive Site of E. coli response regulator PhoB
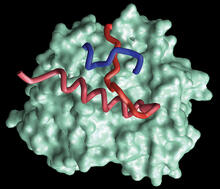
3412
Active site of E. coli response regulator PhoB. Ann Stock, Rutgers University View MediaDynein moving along microtubules
7023
Dynein (green) is a motor protein that “walks” along microtubules (red, part of the cytoskeleton) and carries its cargo along with it. This video was captured through fluorescence microscopy. Morgan DeSantis, University of Michigan. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 1
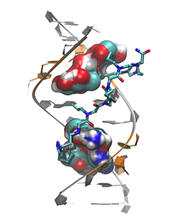
3413
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaGroup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
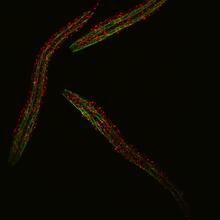
6582
Three C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaMouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
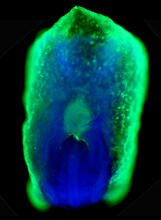
2607
This eerily glowing blob isn't an alien or a creature from the deep sea--it's a mouse embryo just eight and a half days old. The green shell and core show a protein called Smad4. Kenneth Zaret, Fox Chase Cancer Center View MediaEarly ribbon drawing of a protein
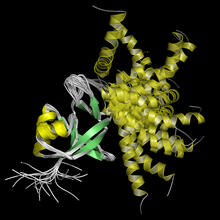
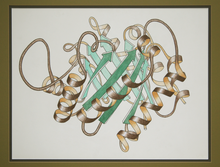
2748
This ribbon drawing of a protein hand drawn and colored by researcher Jane Richardson in 1981 helped originate the ribbon representation of proteins that is now ubiquitous in molecular graphics. Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaAntitoxin GhoS (Illustration 1)
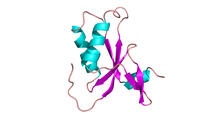
3427
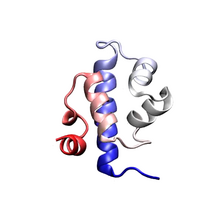
Structure of the bacterial antitoxin protein GhoS. GhoS inhibits the production of a bacterial toxin, GhoT, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Rebecca Page and Wolfgang Peti, Brown University and Thomas K. Wood, Pennsylvania State University View MediaChang Shan
3483
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaArtificial cilia exhibit spontaneous beating
3344
Researchers have created artificial cilia that wave like the real thing. Zvonimir Dogic View MediaCell Nucleus and Lipid Droplets
6547
A cell nucleus (blue) surrounded by lipid droplets (yellow). James Olzmann, University of California, Berkeley View MediaKluyveromyces polysporus Argonaute bound to guide RNA
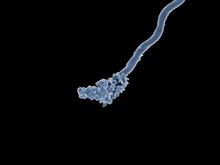
3408
A segment of siRNA, shown in red, guides a "slicer" protein called Argonaute (multi-colored twists and corkscrews) to the target RNA molecules. Kotaro Nakanishi and David Weinberg, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaCryo-electron microscopy of the dengue virus showing protective membrane and membrane proteins
3748
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
3295
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaTex protein
2338
Model of a member from the Tex protein family, which is implicated in transcriptional regulation and highly conserved in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. New York Structural GenomiX Research Consortium, PSI View Media