Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
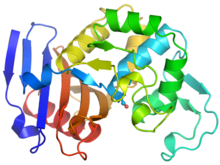
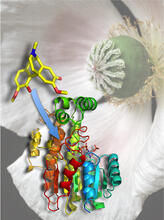
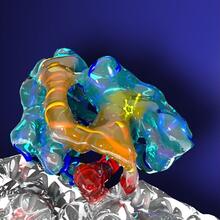
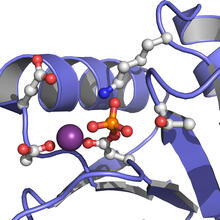
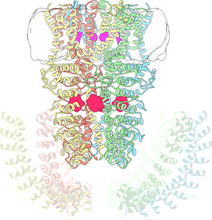
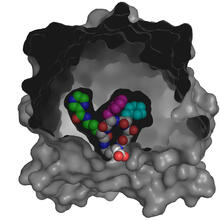
Ribbon diagram of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6766
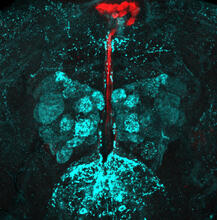
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaFruit fly brain responds to adipokines
6985
Drosophila adult brain showing that an adipokine (fat hormone) generates a response from neurons (aqua) and regulates insulin-producing neurons (red).Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View Media
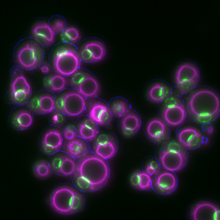
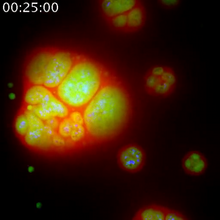
Yeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaWhite Poppy
3424
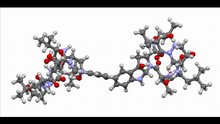
A white poppy. View cropped image of a poppy here 3423. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 01
2790
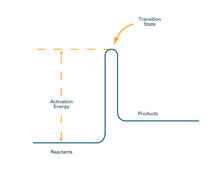
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaActivation energy
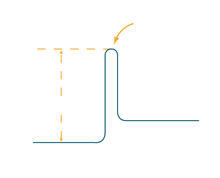
2525
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2526 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaCarbon building blocks
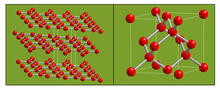
2506
The arrangement of identical molecular components can make a dramatic difference. For example, carbon atoms can be arranged into dull graphite (left) or sparkly diamonds (right). Crabtree + Company View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaHimastatin, 360-degree view
6851
A 360-degree view of the molecule himastatin, which was first isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces himastatinicus. Himastatin shows antibiotic activity. Mohammad Movassaghi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaInsulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
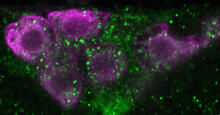
6982
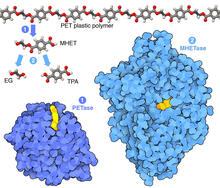
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaPlastic-eating enzymes
7000
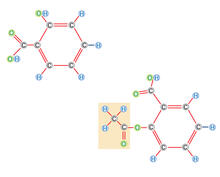
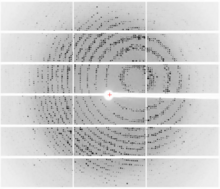
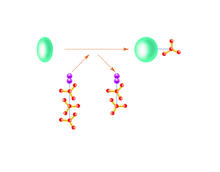
PETase enzyme degrades polyester plastic (polyethylene terephthalate, or PET) into monohydroxyethyl terephthalate (MHET). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6765
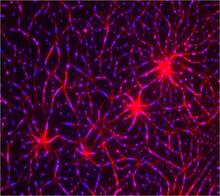
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaIn vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaHuman opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
3314
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
2526
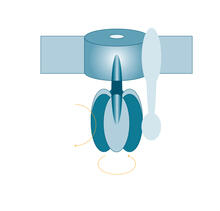
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaATP synthase
2517
The world's smallest motor, ATP synthase, generates energy for the cell. See image 2518 for a labeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3481
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. John Alumasa, Keiler Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University View MediaAtomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
3422
The atomic structure of the morphine biosynthetic enzyme salutaridine reductase bound to the cofactor NADPH. The substrate salutaridine is shown entering the active site. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaDiversity oriented synthesis: generating skeletal diversity using folding processes
3327
This 1 1/2-minute video animation was produced for chemical biologist Stuart Schreiber's lab page. The animation shows how diverse chemical structures can be produced in the lab. Eric Keller View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
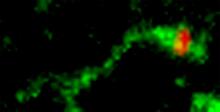
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
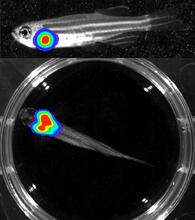
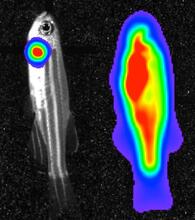
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaWhite Poppy (cropped)
3423
A cropped image of a white poppy. View poppy uncropped here 3424. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaBond types (with labels)
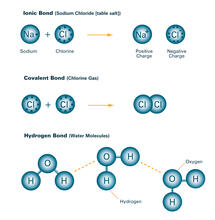
2520
Ionic and covalent bonds hold molecules, like sodium chloride and chlorine gas, together. Hydrogen bonds among molecules, notably involving water, also play an important role in biology. Crabtree + Company View MediaA Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
3718
Bacterial biofilms are tightly knit communities of bacterial cells growing on, for example, solid surfaces, such as in water pipes or on teeth. Gürol Süel, UCSD View MediaMolecular view of glutamatergic synapse
6992
This illustration highlights spherical pre-synaptic vesicles that carry the neurotransmitter glutamate. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaBioluminescence in a Tube
5895
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaDose response curves
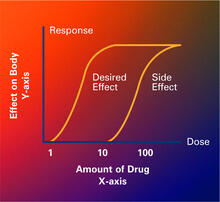
2533
Dose-response curves determine how much of a drug (X-axis) causes a particular effect, or a side effect, in the body (Y-axis). Featured in Medicines By Design. Crabtree + Company View MediaActive Site of E. coli response regulator PhoB
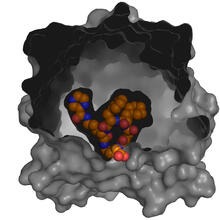
3412
Active site of E. coli response regulator PhoB. Ann Stock, Rutgers University View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaBottles of warfarin
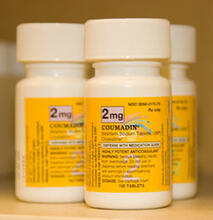
2579
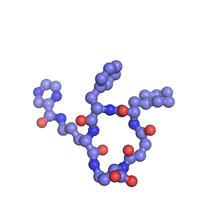
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH View MediaCas4 nuclease protein structure
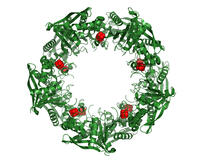
3720
This wreath represents the molecular structure of a protein, Cas4, which is part of a system, known as CRISPR, that bacteria use to protect themselves against viral invaders. Fred Dyda, NIDDK View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaMovie of in vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3786
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaCryo-electron microscopy revealing the "wasabi receptor"
3747
The TRPA1 protein is responsible for the burn you feel when you taste a bite of sushi topped with wasabi. Jean-Paul Armache, UCSF View MediaKinases
2534
Kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups (red-yellow structures) to proteins (green), assigning the proteins a code. Crabtree + Company View MediaBrain waves of a patient anesthetized with propofol
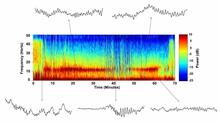
6779
A representation of a patient’s brain waves after receiving the anesthetic propofol. Emery N. Brown, M.D., Ph.D., Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 4
3416
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaAverage teen circadian cycle
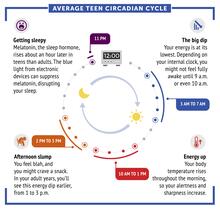
6611
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. Typical circadian rhythms lead to high energy during the middle of the day (10 a.m. NIGMS View MediaGlycan arrays
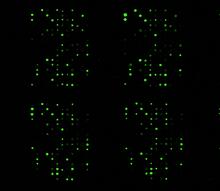
1265
The signal is obtained by allowing proteins in human serum to interact with glycan (polysaccharide) arrays. The arrays are shown in replicate so the pattern is clear. Ola Blixt, Scripps Research Institute View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
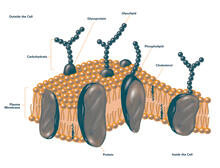
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaPlasma membrane (with labels)
2524
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2523 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 02
2795
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 01
2794
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3525
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. Kenneth Keiler, Penn State University View Media