Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
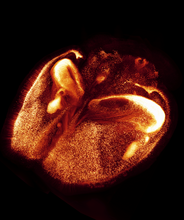
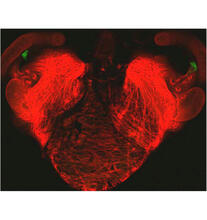
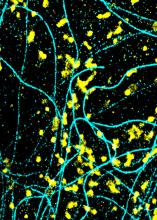
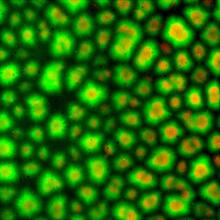
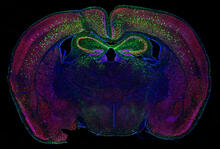
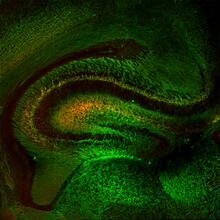
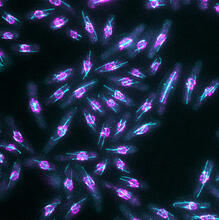
Mouse brain 2
6930
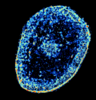
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaHeLa cells
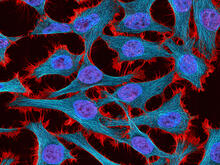
3521
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaDividing cell
6965
As this cell was undergoing cell division, it was imaged with two microscopy techniques: differential interference contrast (DIC) and confocal. The DIC view appears in blue and shows the entire cell. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaA molecular switch strips transcription factor from DNA
3729
In this video, Rice University scientists used molecular modeling with a mathematical algorithm called AWSEM (for associative memory, water-mediated, structure and energy model) and structural data to Davit Potoyan and Peter Wolynes View MediaGolden gene chips
2455
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (2)
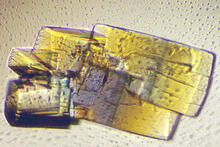
2404
Crystals of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 6
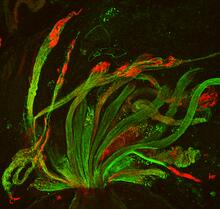
6593
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaBioluminescence in a Tube
5895
Details about the basic biology and chemistry of the ingredients that produce bioluminescence are allowing scientists to harness it as an imaging tool. Credit: Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute. Nathan Shaner, Scintillon Institute View MediaHeLa cells
3520
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells with cytoskeletal microtubules (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
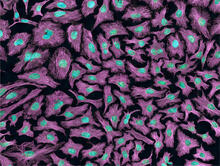
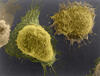
6789
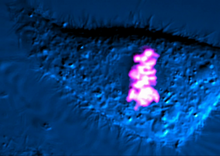
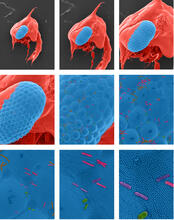
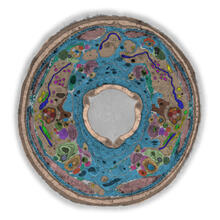
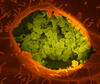
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaBacterial cells aggregating above the light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7018
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaATP Synthase
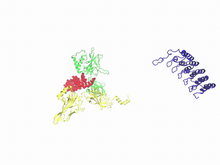
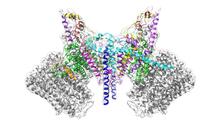
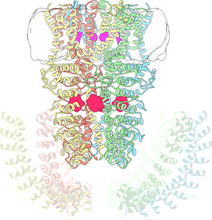
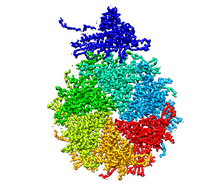
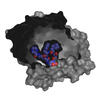
6353
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaFruit fly spermatids
3590
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada View MediaRNase A (2)
2402
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCell division and cell death
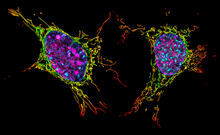
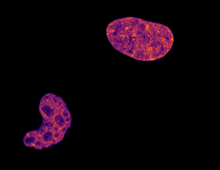
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaLysosomes and microtubules
6889
Lysosomes (yellow) and detyrosinated microtubules (light blue). Lysosomes are bubblelike organelles that take in molecules and use enzymes to break them down. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaVideo of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
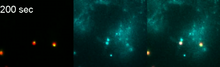
6781
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. NIH Director's Blog View MediaCrab larva eye
1251
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaBacterial alpha amylase
2401
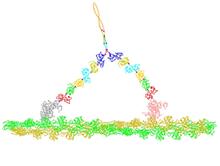
A crystal of bacterial alpha amylase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaSnowflake DNA origami
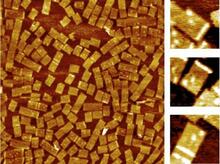
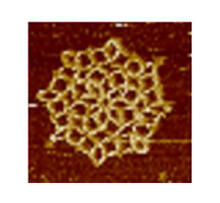
3724
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. The image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Holiday-Themed Collection. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCryo-electron microscopy revealing the "wasabi receptor"
3747
The TRPA1 protein is responsible for the burn you feel when you taste a bite of sushi topped with wasabi. Jean-Paul Armache, UCSF View MediaPrecisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Nature Nanotechnology View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (1)
2397
A crystal of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaGlycan arrays
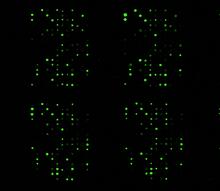
1265
The signal is obtained by allowing proteins in human serum to interact with glycan (polysaccharide) arrays. The arrays are shown in replicate so the pattern is clear. Ola Blixt, Scripps Research Institute View MediaCalling Cards in a mouse brain
6780
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. Allen Yen, Lab of Joseph Dougherty, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaTEM cross-section of C. elegans (roundworm)
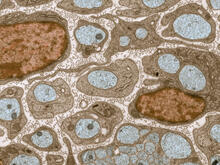
5759
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular laboratory animal because its small size and fairly simple body make it easy to study. Piali Sengupta, Brandeis University View MediaFlagellated bacterial cells
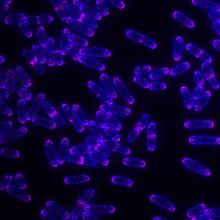
7014
Vibrio fischeri (2 mm in length) is the exclusive symbiotic partner of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaRNase A (1)
2398
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaPig trypsin (1)
2400
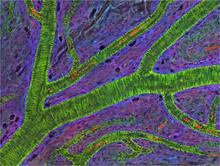
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaSmall blood vessels in a mouse retina
3400
Blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina) are used to diagnose glaucoma and diabetic eye disease. They also display characteristic changes in people with high blood pressure. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCluster analysis of mysterious protein
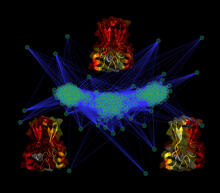
3295
Researchers use cluster analysis to study protein shape and function. Each green circle represents one potential shape of the protein mitoNEET. Patricia Jennings and Elizabeth Baxter, University of California, San Diego View MediaBiosensors illustration
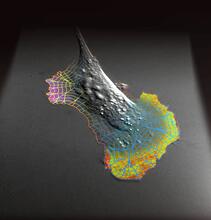
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaYeast cells with Fimbrin Fim1
6794
Yeast cells with the protein Fimbrin Fim1 shown in magenta. This protein plays a role in cell division. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View Media
Bacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaYeast cells entering mitosis
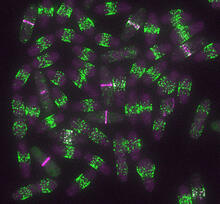
6791
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
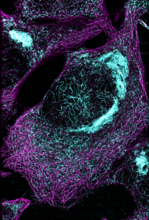
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaNeutrophil-like cells migrating in a microfluidic chip
6886
Neutrophil-like cells (blue) in a microfluidic chip preferentially migrating toward LTB4 over fMLP. Caroline Jones, University of Texas at Dallas. View MediaAxolotl
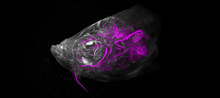
6932
An axolotl—a type of salamander—that has been genetically modified so that its developing nervous system glows purple and its Schwann cell nuclei appear light blue. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaNano-rainbow
2326
These vials may look like they're filled with colored water, but they really contain nanocrystals reflecting different colors under ultraviolet light. Shuming Nie, Emory University View MediaChromatin in human tenocyte
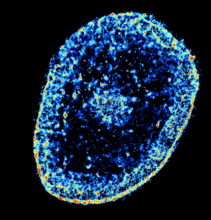
6893
The nucleus of a degenerating human tendon cell, also known as a tenocyte. It has been color-coded based on the density of chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 5
6489
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the fifthframe in a series of five. View MediaMouse Brain Cross Section
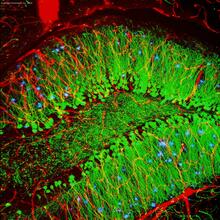
5886
The brain sections are treated with fluorescent antibodies specific to a particular protein and visualized using serial electron microscopy (SEM). Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaAdult and juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squids
7010
An adult Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, (~4 cm) surrounded by newly hatched juveniles (~2 mm) in a bowl of seawater.Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media
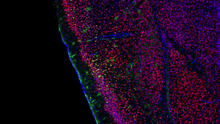
Brain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of myelinated axons with ECM between the axons
3736
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells, as shown here. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaZebrafish head vasculature video
6933
Various views of a zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaYeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
6798
Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes shown in magenta and tubulin shown in light blue. The nuclear envelope defines the borders of the nucleus, which houses DNA. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View Media