Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
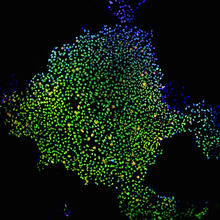
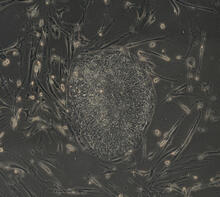
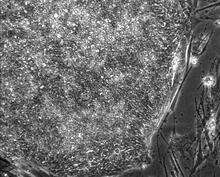
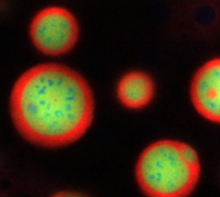
Induced stem cells from adult skin 02
2604
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaEpigenetic code (with labels)
2563
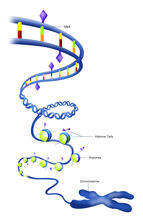
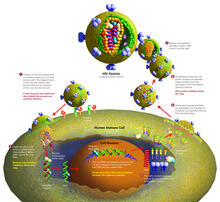
The "epigenetic code" controls gene activity with chemical tags that mark DNA (purple diamonds) and the "tails" of histone proteins (purple triangles). Crabtree + Company View MediaLife of an AIDS virus
2513
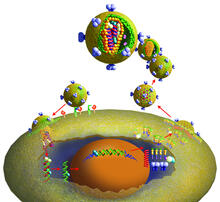
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaNucleotides make up DNA (with labels)
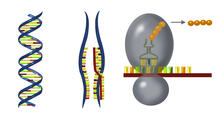
2542
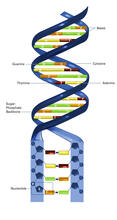
DNA consists of two long, twisted chains made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains one base, one phosphate molecule, and the sugar molecule deoxyribose. Crabtree + Company View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
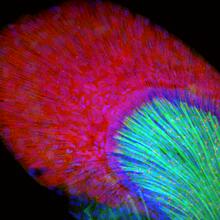
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
3443
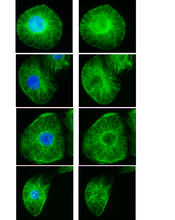
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaAlternative splicing
2552
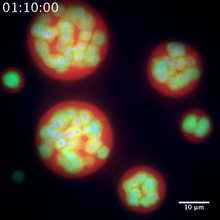
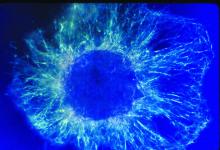
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Crabtree + Company View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaHIV enzyme
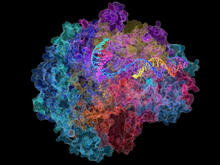
6999
These images model the molecular structures of three enzymes with critical roles in the life cycle of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
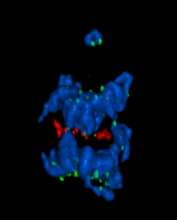
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaMitotic cell awaits chromosome alignment
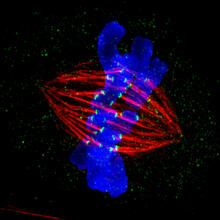
5765
During mitosis, spindle microtubules (red) attach to chromosome pairs (blue), directing them to the spindle equator. View MediaGlowing bacteria make a pretty postcard
3492
This tropical scene, reminiscent of a postcard from Key West, is actually a petri dish containing an artistic arrangement of genetically engineered bacteria. Nathan C. Shaner, The Scintillon Institute View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 3
3792
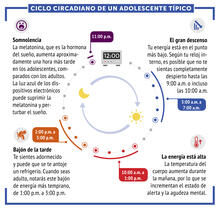
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaCiclo circadiano de un adolescente típico
6612
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y conductuales que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. NIGMS View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
3445
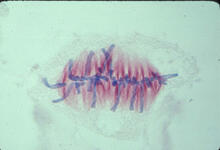
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaLily mitosis 01
1058
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
2759
In the absence of the engulfment receptor Draper, salivary gland cells (light blue) persist in the thorax of a developing Drosophila melanogaster pupa. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaRNA strand
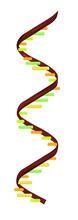
2554
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) has a sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Crabtree + Company View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaAverage teen circadian cycle
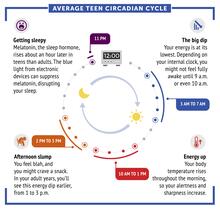
6611
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. Typical circadian rhythms lead to high energy during the middle of the day (10 a.m. NIGMS View MediaRNA Polymerase II
2484
NIGMS-funded researchers led by Roger Kornberg solved the structure of RNA polymerase II. David Bushnell, Ken Westover and Roger Kornberg, Stanford University View MediaDicer generates microRNAs
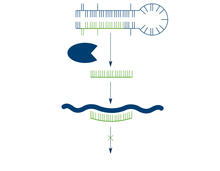
2556
The enzyme Dicer generates microRNAs by chopping larger RNA molecules into tiny Velcro®-like pieces. MicroRNAs stick to mRNA molecules and prevent the mRNAs from being made into proteins. Crabtree + Company View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaDicty fruit
2684
Dictyostelium discoideum is a microscopic amoeba. A group of 100,000 form a mound as big as a grain of sand. Featured in The New Genetics. View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
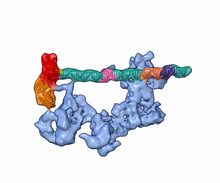
3597
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6771
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR swimming in water. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaLily mitosis 07
1017
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaA dynamic model of the DNA helicase protein complex
3750
This short video shows a model of the DNA helicase in yeast. This DNA helicase has 11 proteins that work together to unwind DNA during the process of copying it, called DNA replication. Huilin Li, Stony Brook University View MediaDNA replication illustration
2543
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. Crabtree + Company View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaPainted chromosomes
2764
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaArabidopsis leaf injected with a pathogen
2780
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf eight days after being infected with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, which is closely related to crop pathogens that Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaLife of an AIDS virus (with labels and stages)
2515
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaDeveloping Arabidopsis flower buds
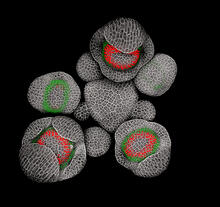
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaLily mitosis 06
1016
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
6774
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 01
2603
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaA chromosome goes missing in anaphase
5766
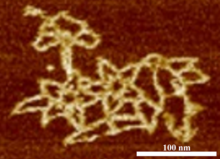
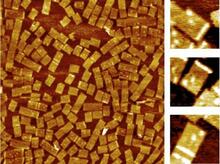
Anaphase is the critical step during mitosis when sister chromosomes are disjoined and directed to opposite spindle poles, ensuring equal distribution of the genome during cell division. View MediaMicroscopy image of bird-and-flower DNA origami
3690
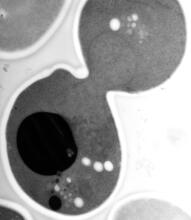
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 4
3793
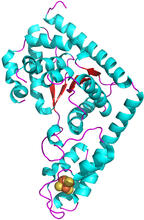
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaTrp_RS - tryptophanyl tRNA-synthetase family of enzymes
2483
This image represents the structure of TrpRS, a novel member of the tryptophanyl tRNA-synthetase family of enzymes. View MediaGolden gene chips
2455
A team of chemists and physicists used nanotechnology and DNA's ability to self-assemble with matching RNA to create a new kind of chip for measuring gene activity. Hao Yan and Yonggang Ke, Arizona State University View MediaZinc finger
2426
The structure of a gene-regulating zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Jeremy M. Berg, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 2
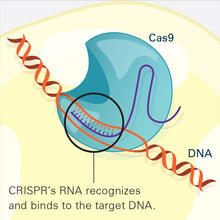
6486
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View Media