Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
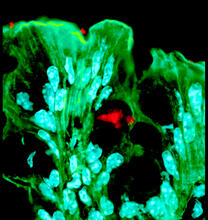
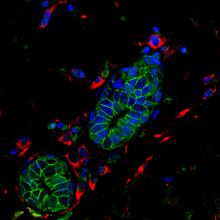
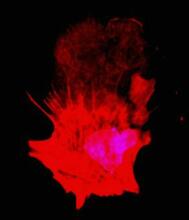
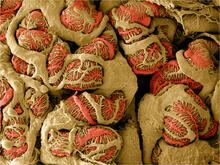
Bacteria in the mouse colon
3527
Image of the colon of a mouse mono-colonized with Bacteroides fragilis (red) residing within the crypt channel. The red staining is due to an antibody to B. Sarkis K. Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology View MediaG switch (with labels)
2537
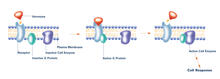
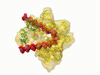
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. Crabtree + Company View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
3725
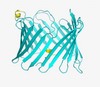
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
3286
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View MediaBicycling cell
1337
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaPigment cells in fish skin
5756
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaSynapses in culture
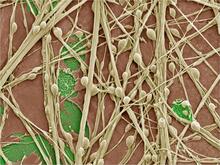
3399
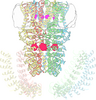
Cultured hippocampal neurons grown on a substrate of glial cells (astrocytes). The glial cells form the pink/brown underlayment in this image. The tan threads are the neurons. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of myelinated axons with ECM between the axons
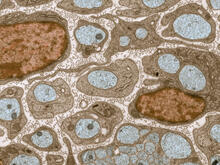
3736
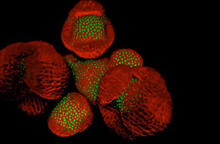
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells, as shown here. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaArabidopsis Thaliana: Flowers Spring to Life
6503
This image capture shows how a single gene, STM, plays a starring role in plant development. Nathanaёl Prunet NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaSticky stem cells
3457
Like a group of barnacles hanging onto a rock, these human cells hang onto a matrix coated glass slide. Ankur Singh and Andrés García, Georgia Institute of Technology View MediaMouse mammary cells lacking anti-cancer protein
3432
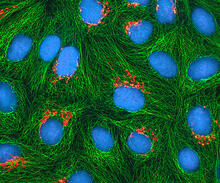
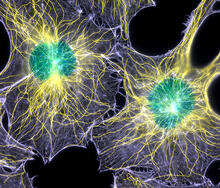
Shortly after a pregnant woman gives birth, her breasts start to secrete milk. This process is triggered by hormonal and genetic cues, including the protein Elf5. Nature Cell Biology, November 2012, Volume 14 No 11 pp1113-1231 View MediaHeLa cells
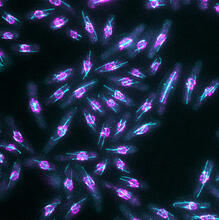
3522
Multiphoton fluorescence image of cultured HeLa cells with a fluorescent protein targeted to the Golgi apparatus (orange), microtubules (green) and counterstained for DNA (cyan). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaPolarized cells- 01
3332
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaSea urchin embryo 01
1047
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaDisease-resistant Arabidopsis leaf
2781
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf a few days after being exposed to the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaFruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
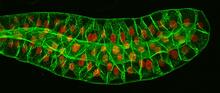
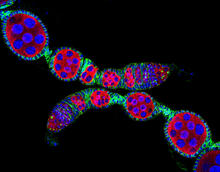
6754
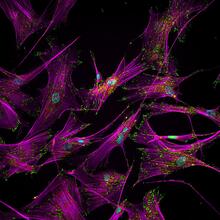
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaColorful cells
2428
Actin (purple), microtubules (yellow), and nuclei (green) are labeled in these cells by immunofluorescence. This image won first place in the Nikon 2003 Small World photo competition. Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute View MediaSimulation of leg muscles moving
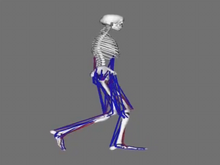
6598
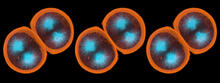
When we walk, muscles and nerves interact in intricate ways. This simulation, which is based on data from a six-foot-tall man, shows these interactions. Chand John and Eran Guendelman, Stanford University View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaMouse Brain Cross Section
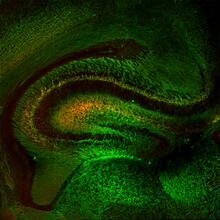
5886
The brain sections are treated with fluorescent antibodies specific to a particular protein and visualized using serial electron microscopy (SEM). Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaSkin cross-section
1056
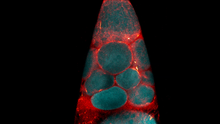
Cross-section of skin anatomy shows layers and different tissue types. National Institutes of Health Medical Arts View MediaSalivary gland in the developing fruit fly
3603
For fruit flies, the salivary gland is used to secrete materials for making the pupal case, the protective enclosure in which a larva transforms into an adult fly. Richard Fehon, University of Chicago View MediaVibrio bacteria
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaAnchor cell in basement membrane
2707
An anchor cell (red) pushes through the basement membrane (green) that surrounds it. Elliott Hagedorn, Duke University. View MediaYeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
6798
Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes shown in magenta and tubulin shown in light blue. The nuclear envelope defines the borders of the nucleus, which houses DNA. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
3306
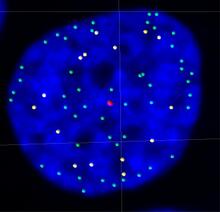
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaCultured cells
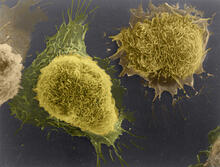
1178
This image of laboratory-grown cells was taken with the help of a scanning electron microscope, which yields detailed images of cell surfaces. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
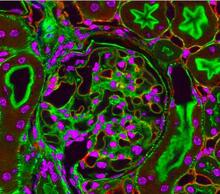
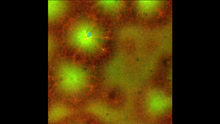
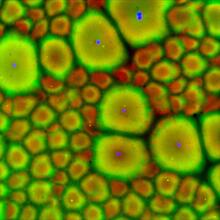
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaNCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
3392
Stained glomeruli in the kidney. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaLily mitosis 12
1018
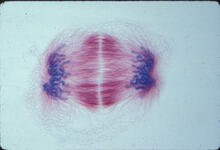
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMapping brain differences
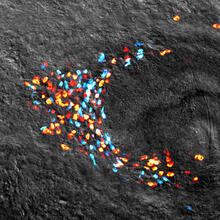
2419
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaTelomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
3484
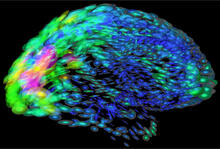
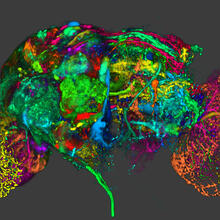
New research shows telomeres moving to the outer edge of the nucleus after cell division, suggesting these caps that protect chromosomes also may play a role in organizing DNA. Laure Crabbe, Jamie Kasuboski and James Fitzpatrick, Salk Institute for Biological Studies View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaCrawling cell
6964
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaStretch detectors
2714
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania View MediaYeast cells entering mitosis
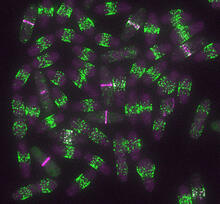
6791
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaAutofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
5755
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaThree muscle fibers; the middle has a defect found in some neuromuscular diseases
3630
Of the three muscle fibers shown here, the one on the right and the one on the left are normal. The middle fiber is deficient a large protein called nebulin (blue). Christopher Pappas and Carol Gregorio, University of Arizona View MediaConfocal microscopy image of two Drosophila ovarioles
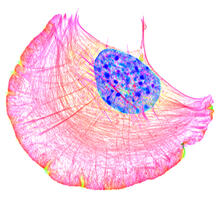
5772
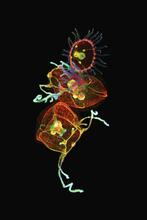
Ovarioles in female insects are tubes in which egg cells (called oocytes) form at one end and complete their development as they reach the other end of the tube. 2004 Olympus BioScapes Competition View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
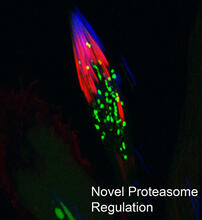
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaProteasome
3451
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaJellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
3636
Jellyfish are especially good models for studying the evolution of embryonic tissue layers. Despite being primitive, jellyfish have a nervous system (stained green here) and musculature (red). Helena Parra, Pompeu Fabra University, Spain View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
6585
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaMath from the heart
3592
Watch a cell ripple toward a beam of light that turns on a movement-related protein. View Media