Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
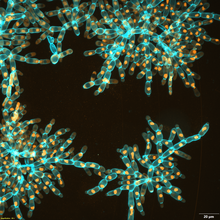
Trigonium diatom
6962
A Trigonium diatom imaged by a quantitative orientation-independent differential interference contrast (OI-DIC) microscope. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaLily mitosis 13
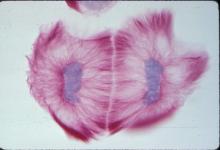
1019
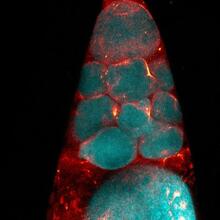
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
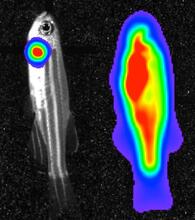
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaNerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
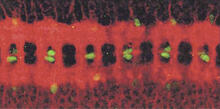
1091
Glial cells (stained green) in a fruit fly developing embryo have survived thanks to a signaling pathway initiated by neighboring nerve cells (stained red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaHeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
6520
Here, a human HeLa cell (a type of immortal cell line used in laboratory experiments) is undergoing cell division. Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaNCMIR Tongue 2
5811
Microscopy image of a tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5810 National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaDynein moving along microtubules
7023
Dynein (green) is a motor protein that “walks” along microtubules (red, part of the cytoskeleton) and carries its cargo along with it. This video was captured through fluorescence microscopy. Morgan DeSantis, University of Michigan. View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaDividing yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and spindle pole bodies
6795
Time-lapse video of yeast cells undergoing cell division. Nuclear envelopes are shown in green, and spindle pole bodies, which help pull apart copied genetic information, are shown in magenta. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaDisease-resistant Arabidopsis leaf
2781
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf a few days after being exposed to the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaFat cells (red) and blood vessels (green)
3600
A mouse's fat cells (red) are shown surrounded by a network of blood vessels (green). Daniela Malide, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaPlasma membrane
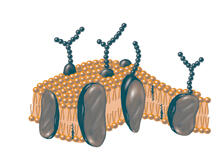
2523
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2524 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaVibrio bacteria
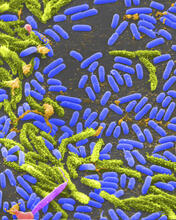
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaProteins related to myotonic dystrophy
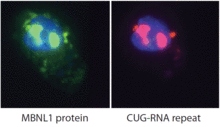
2727
Myotonic dystrophy is thought to be caused by the binding of a protein called Mbnl1 to abnormal RNA repeats. Manuel Ares, University of California, Santa Cruz View MediaA mammalian eye has approximately 70 different cell types
3641
The incredible complexity of a mammalian eye (in this case from a mouse) is captured here. Each color represents a different type of cell. Bryan William Jones and Robert E. Marc, University of Utah View MediaMigrating pigment cells
5758
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaNerve ending
1244
A scanning electron microscope picture of a nerve ending. It has been broken open to reveal vesicles (orange and blue) containing chemicals used to pass messages in the nervous system. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaCells lining the trachea
3646
In this image, viewed with a ZEISS ORION NanoFab microscope, the community of cells lining a mouse airway is magnified more than 10,000 times. Eva Mutunga and Kate Klein, University of the District of Columbia and National Institute of Standards and Technology View MediaFruit fly nurse cells during egg development
6753
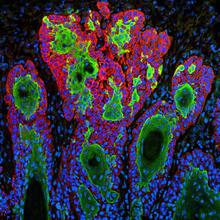
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
3661
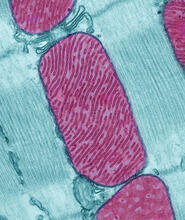
These mitochondria (red) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaMapping brain differences
2419
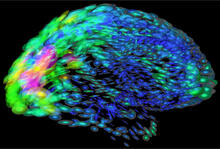
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaSkin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
3628
This image shows the uncontrolled growth of cells in squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is usually not life-threatening. Markus Schober and Elaine Fuchs, The Rockefeller University View MediaSnowflake yeast 3
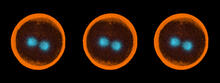
6971
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaSea urchin embryo 04
1050
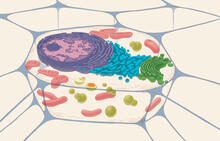
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaAnimal cell
1274
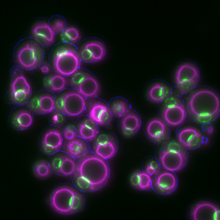
A typical animal cell, sliced open to reveal a cross-section of organelles. Judith Stoffer View MediaYeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaCrab larva eye
1251
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View Media3D reconstruction of the Golgi apparatus in a pancreas cell
6609
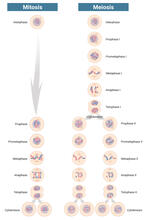
Researchers used cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) to capture images of a rat pancreas cell that were then compiled and color-coded to produce a 3D reconstruction. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared-labeled
6788
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaFocal adhesions
2502
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaCancer Cells Glowing from Luciferin
3480
The activator cancer cell culture, right, contains a chemical that causes the cells to emit light when in the presence of immune cells. Mark Sellmyer, Stanford University School of Medicine View MediaFruit fly sperm cells
2433
Developing fruit fly spermatids require caspase activity (green) for the elimination of unwanted organelles and cytoplasm via apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaSkin cross-section
1056
Cross-section of skin anatomy shows layers and different tissue types. National Institutes of Health Medical Arts View MediaHow cilia do the wave
3494
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaMouse retina
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaBacteria shapes
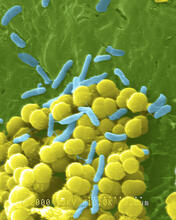
1158
A colorized scanning electron micrograph of bacteria. Scanning electron microscopes allow scientists to see the three-dimensional surface of their samples. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaBorrelia burgdorferi
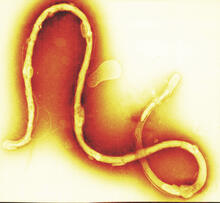
1241
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete, a class of long, slender bacteria that typically take on a coiled shape. Infection with this bacterium causes Lyme disease. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaActivated mast cell surface
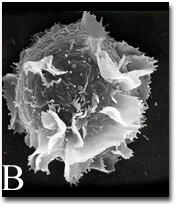
2637
A scanning electron microscope image of an activated mast cell. This image illustrates the interesting topography of the cell membrane, which is populated with receptors. Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico View MediaQuorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
3728
To simulate the consequences of disrupting bacterial cell-to-cell communication, called quorum sensing, in the crypts (small chambers within the colon), the researchers experimented with an inhibitor Minyoung Kevin Kim and Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View Media