Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
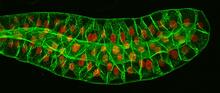
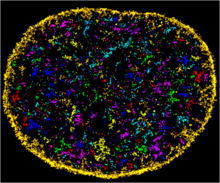
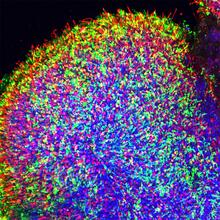
Salivary gland in the developing fruit fly
3603
For fruit flies, the salivary gland is used to secrete materials for making the pupal case, the protective enclosure in which a larva transforms into an adult fly. Richard Fehon, University of Chicago View MediaNano-rainbow
2326
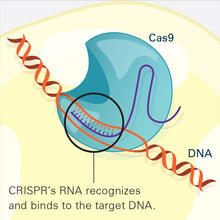
These vials may look like they're filled with colored water, but they really contain nanocrystals reflecting different colors under ultraviolet light. Shuming Nie, Emory University View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 2
6486
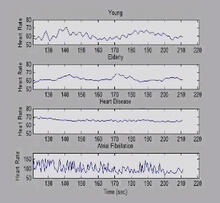
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaHeart rates time series image
3596
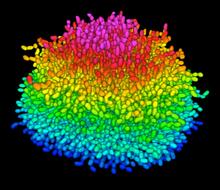
These time series show the heart rates of four different individuals. Madalena Costa and Ary Goldberger, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center View MediaA Growing Bacterial Biofilm
5825
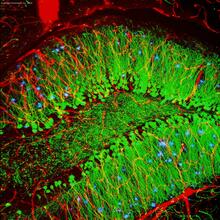
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth. Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
3742
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaZinc levels in a plant leaf
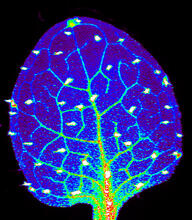
3727
Zinc is required for the function of more than 300 enzymes, including those that help regulate gene expression, in various organisms including humans. Suzana Car, Dartmouth College View MediaHigh-throughput protein structure determination pipeline
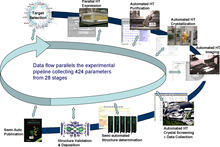
2364
This slide shows the technologies that the Joint Center for Structural Genomics developed for going from gene to structure and how the technologies have been integrated into a high-throughput pipeline Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaRibbon diagram of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
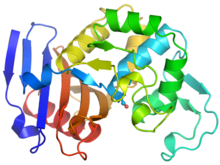
6766
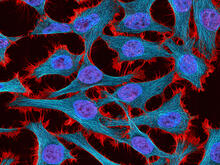
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaHeLa cells
3521
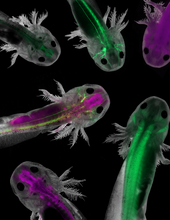
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAxolotls showing nervous system components
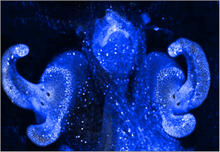
6928
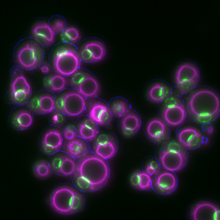
Axolotls—a type of salamander—that have been genetically modified so that various parts of their nervous systems glow purple and green. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaYeast cells responding to a glucose shortage
6772
These yeast cells were exposed to a glucose (sugar) shortage. Mike Henne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. View MediaColorful communication
2313
The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi glows when near its kind. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaMulticolor STORM
2325
In 2006, scientists developed an optical microscopy technique enabling them to clearly see individual molecules within cells. In 2007, they took the technique, abbreviated STORM, a step further. Xiaowei Zhuang, Harvard University View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
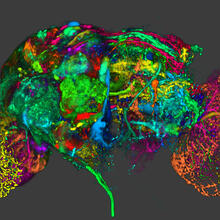
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaATP Synthase
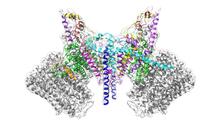
6353
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaCrawling cell
6964
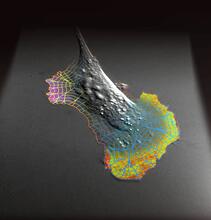
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaPores on the surface of the Hawaiian bobtail squid light organ
7016
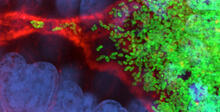
The light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, stained blue. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaBacterial cells migrating through the tissues of the squid light organ
7015
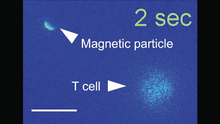
Vibrio fischeri cells (~ 2 mm), labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), passing through a very narrow bottleneck in the tissues (red) of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolope Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaMagnetic Janus particle activating a T cell
6800
A Janus particle being used to activate a T cell, a type of immune cell. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaRelapsing fever bacterium (gray) and red blood cells
3585
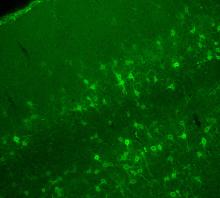
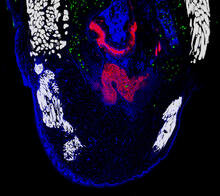
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
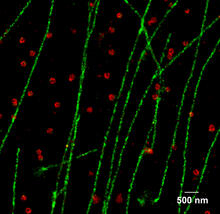
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaMicrotubules in hippocampal neurons
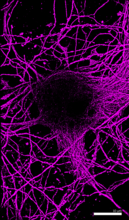
6890
Microtubules (magenta) in neurons of the hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 5
6489
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the fifthframe in a series of five. View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
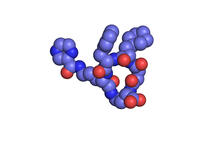
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 1
3413
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaScanning electron microscopy of collagen fibers
3735
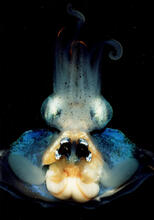
This image shows collagen, a fibrous protein that's the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen is a strong, ropelike molecule that forms stretch-resistant fibers. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaAn adult Hawaiian bobtail squid
7013
An adult female Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, with its mantle cavity exposed from the underside. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaSnowflake yeast 1
6969
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaAdult and juvenile Hawaiian bobtail squids
7010
An adult Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, (~4 cm) surrounded by newly hatched juveniles (~2 mm) in a bowl of seawater.Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View Media
Genetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaCryo-EM reveals how the HIV capsid attaches to a human protein to evade immune detection
3755
The illustration shows the capsid of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) whose molecular features were resolved with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Juan R. Perilla, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
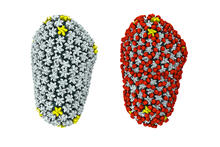
5874
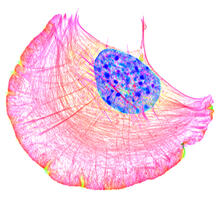
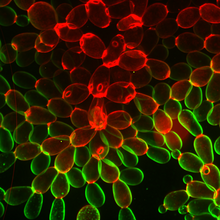
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaConfocal microscopy image of two Drosophila ovarioles
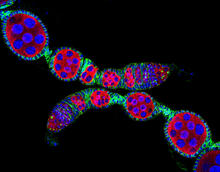
5772
Ovarioles in female insects are tubes in which egg cells (called oocytes) form at one end and complete their development as they reach the other end of the tube. 2004 Olympus BioScapes Competition View MediaAdult Hawaiian bobtail squid burying in the sand
7012
Each morning, the nocturnal Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, hides from predators by digging into the sand. At dusk, it leaves the sand again to hunt. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 2
6588
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
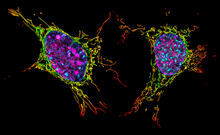
6789
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaHuman retinal organoid
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaRegenerating lizard tail
6968
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California. View MediaZebrafish embryo
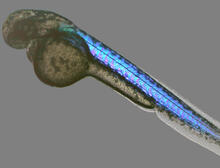
6897
A zebrafish embryo showing its natural colors. Zebrafish have see-through eggs and embryos, making them ideal research organisms for studying the earliest stages of development. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 6
6593
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaEnzyme transition states
3429
The molecule on the left is an electrostatic potential map of the van der Waals surface of the transition state for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Vern Schramm, Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University View MediaFruit fly ovarioles
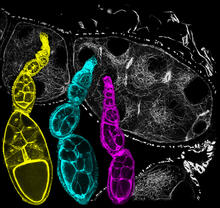
6810
Three fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovarioles (yellow, blue, and magenta) with egg cells visible inside them. Ovarioles are tubes in the reproductive systems of female insects. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaPig trypsin crystal
2403
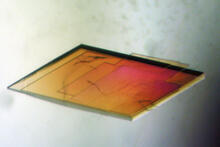
A crystal of pig trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (1)
2397
A crystal of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCrane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
6898
A crane fly spermatocyte during metaphase of meiosis-I, a step in the production of sperm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View Media