Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Research mentor and student
2767
A research mentor (Lori Eidson) and student (Nina Waldron, on the microscope) were 2009 members of the BRAIN (Behavioral Research Advancements In Neuroscience) program at Georgia State University in A Elizabeth Weaver, Georgia State University View MediaIntroduction to Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
5815
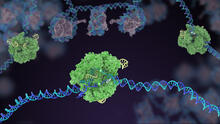
Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 is a rapidly expanding field of scientific research with emerging applications in disease treatment, medical therapeutics and bioenergy, just to name a few. Janet Iwasa View MediaSuperconducting magnet
1120
Superconducting magnet for NMR research, from the February 2003 profile of Dorothee Kern in Findings. Mike Lovett View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
3274
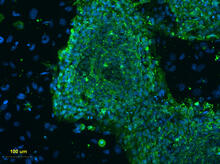
This fluorescent microscope image shows human embryonic stem cells whose nuclei are stained green. Blue staining shows the surrounding supportive feeder cells. Michael Longaker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
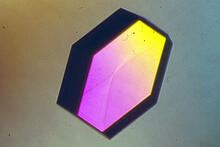
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCorrelative imaging by annotation with single molecules (CIASM) process
6568
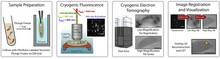
These images illustrate a technique combining cryo-electron tomography and super-resolution fluorescence microscopy called correlative imaging by annotation with single molecules (CIASM). Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University. View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaCas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
5816
In the gene-editing tool CRISPR, a small strand of RNA identifies a specific chunk of DNA. Janet Iwasa View MediaZebrafish head vasculature video
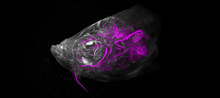
6933
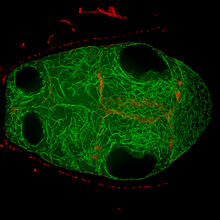
Various views of a zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaBacterial cells aggregated above a light-organ pore of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
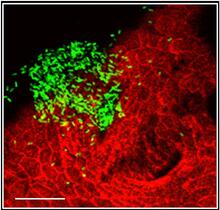
7019
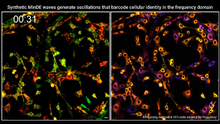
The beating of cilia on the outside of the Hawaiian bobtail squid’s light organ concentrates Vibrio fischeri cells (green) present in the seawater into aggregates near the pore-containing tis Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaSingle-cell “radios” image
7021
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
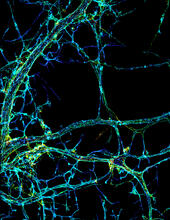
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaHuman retinal organoid
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaCRISPR
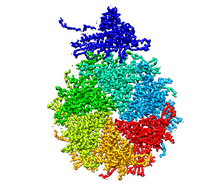
6351
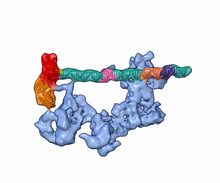
RNA incorporated into the CRISPR surveillance complex is positioned to scan across foreign DNA. Cryo-EM density from a 3Å reconstruction is shown as a yellow mesh. NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaMicrotubule breakdown
2321
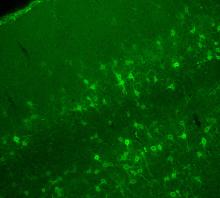
Like a building supported by a steel frame, a cell contains its own sturdy internal scaffolding made up of proteins, including microtubules. Eva Nogales, University of California, Berkeley View MediaCalling Cards in a mouse brain
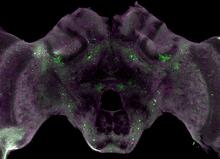
6780
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. Allen Yen, Lab of Joseph Dougherty, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
6774
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediaCryo-ET cross-section of a rat pancreas cell
6608
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaSmall blood vessels in a mouse retina
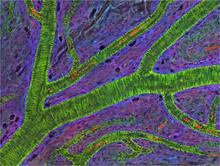
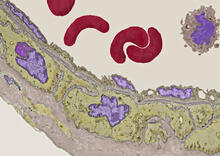
3400
Blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina) are used to diagnose glaucoma and diabetic eye disease. They also display characteristic changes in people with high blood pressure. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaFungal lipase (2)
2411
Crystals of fungal lipase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaHoneybees marked with paint
6756
Researchers doing behavioral experiments with honeybees sometimes use paint or enamel to give individual bees distinguishing marks. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaProtein purification robot
2375
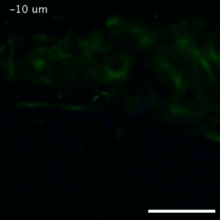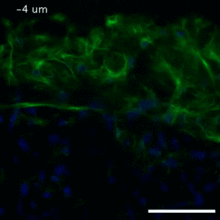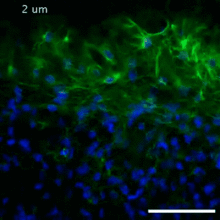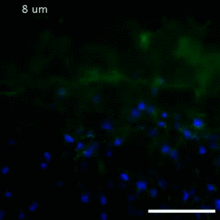
Irina Dementieva, a biochemist, and Youngchang Kim, a biophysicist and crystallographer, work with the first robot of its type in the U.S. to automate protein purification. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaRat Hippocampus
3308
This image of the hippocampus was taken with an ultra-widefield high-speed multiphoton laser microscope. Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
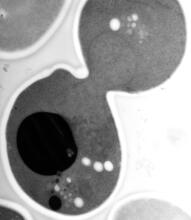
6591
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCryogenic storage tanks at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research
2722
Established in 1953, the Coriell Institute for Medical Research distributes cell lines and DNA samples to researchers around the world. Courtney Sill, Coriell Institute for Medical Research View MediaFluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
7022
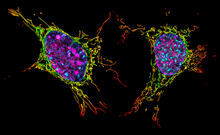
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
6789
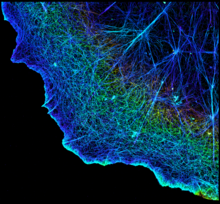
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaComputer algorithm
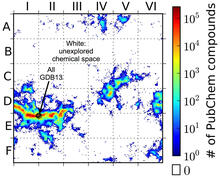
3458
This computer algorithm plots all feasible small carbon-based molecules as though they were cities on a map and identifies huge, unexplored spaces that may help fuel research into new drug therapies. Aaron Virshup, Julia Contreras-Garcia, Peter Wipf, Weitao Yang and David Beratan, University of Pittsburgh Center for Chemical Methodologies and Library Development View MediaCell division and cell death
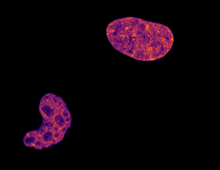
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaBovine trypsin
2408
A crystal of bovine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
5730
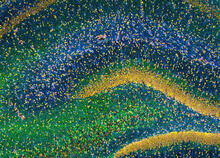
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
3742
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaYoung squids
6903
Real-time movie of young squids. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaColor-coded chromosomes
2312
By mixing fluorescent dyes like an artist mixes paints, scientists are able to color code individual chromosomes. Anna Jauch, Institute of Human Genetics, Heidelberg, Germany View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - image
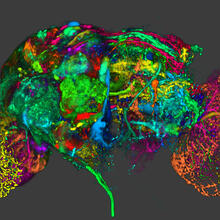
5838
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (1)
2397
A crystal of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaHoneybee brain
6755
Insect brains, like the honeybee brain shown here, are very different in shape from human brains. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaMouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
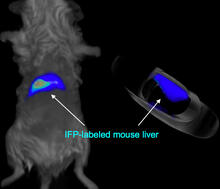
2601
A mouse liver glows after being tagged with specially designed infrared-fluorescent protein (IFP). Xiaokun Shu, University of California, San Diego View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
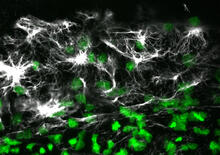
2807
Confocal image showing high levels of the protein vimentin (white) at the edge zone of a quail embryo. Cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View Media