Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
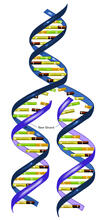
Repairing DNA
3493
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View MediaWild-type and mutant fruit fly ovaries
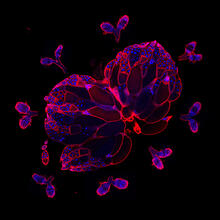
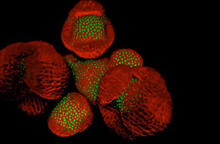
6806
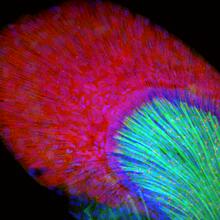
The two large, central, round shapes are ovaries from a typical fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaFruit fly ovaries
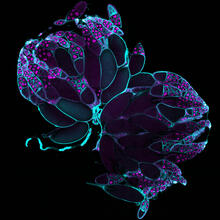
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
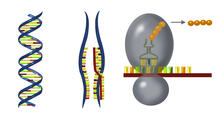
Nucleosome
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaPainted chromosomes
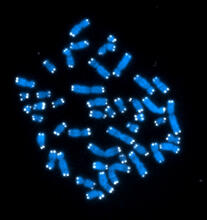
2764
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 12
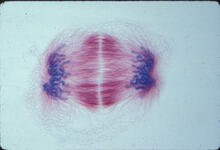
1018
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaCRISPR illustration
3719
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaLily mitosis 13
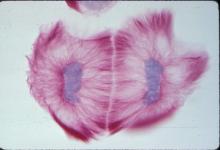
1019
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaMeiosis illustration (with labels)
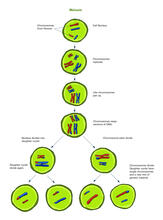
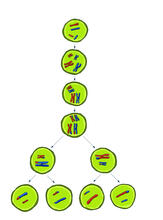
2546
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated (with labels and numbers for stages)
2549
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaGFP sperm
2683
Fruit fly sperm cells glow bright green when they express the gene for green fluorescent protein (GFP). View MediaPlanarian stem cell colony
3306
Planarians are freshwater flatworms that have powerful abilities to regenerate their bodies, which would seem to make them natural model organisms in which to study stem cells. Peter Reddien, Whitehead Institute View MediaDNA replication illustration (with labels)
2544
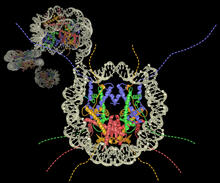
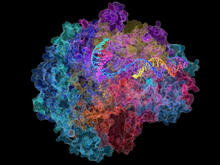
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. Crabtree + Company View MediaDynamic cryo-EM model of the human transcription preinitiation complex
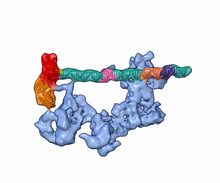
5730
Gene transcription is a process by which information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6771
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR swimming in water. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaFrom DNA to Protein
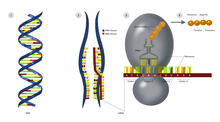
2509
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together. Crabtree + Company View MediaZinc finger
2426
The structure of a gene-regulating zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Jeremy M. Berg, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaMeiosis illustration
2545
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
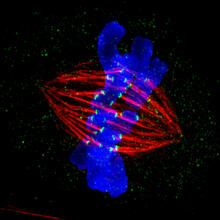
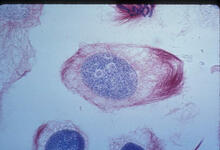
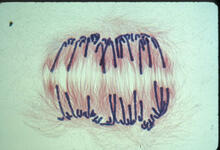
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaTelomeres
2626
The 46 human chromosomes are shown in blue, with the telomeres appearing as white pinpoints. Hesed Padilla-Nash and Thomas Ried, the National Cancer Institute, a part of NIH View MediaDNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
3597
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recogni Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory View MediaLily mitosis 06
1016
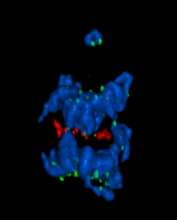
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaA chromosome goes missing in anaphase
5766
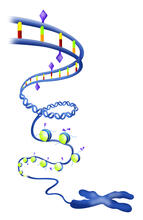
Anaphase is the critical step during mitosis when sister chromosomes are disjoined and directed to opposite spindle poles, ensuring equal distribution of the genome during cell division. View MediaEpigenetic code
2562
The "epigenetic code" controls gene activity with chemical tags that mark DNA (purple diamonds) and the "tails" of histone proteins (purple triangles). Crabtree + Company View MediaKatanin protein regulates anaphase
2594
The microtubule severing protein, katanin, localizes to chromosomes and regulates anaphase A in mitosis. David Sharp, Albert Einstein College of Medicine View MediaArabidopsis Thaliana: Flowers Spring to Life
6503
This image capture shows how a single gene, STM, plays a starring role in plant development. Nathanaёl Prunet NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaRNA Polymerase II
2484
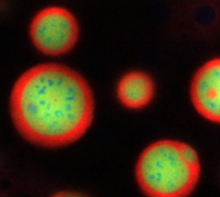
NIGMS-funded researchers led by Roger Kornberg solved the structure of RNA polymerase II. David Bushnell, Ken Westover and Roger Kornberg, Stanford University View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 4
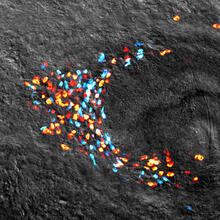
3793
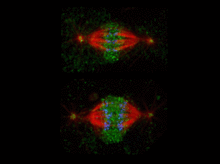
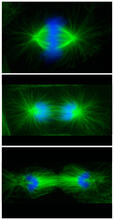
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaCell division phases in Xenopus frog cells
3442
These images show three stages of cell division in Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. They are (from top): metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison View MediaLily mitosis 02
1012
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaHost infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. View MediaAverage teen circadian cycle
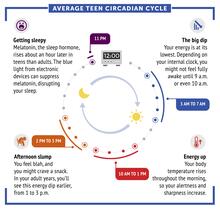
6611
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. Typical circadian rhythms lead to high energy during the middle of the day (10 a.m. NIGMS View MediaPollen grains: male germ cells in plants and a cause of seasonal allergies
3609
Those of us who get sneezy and itchy-eyed every spring or fall may have pollen grains, like those shown here, to blame. Edna, Gil, and Amit Cukierman, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pa. View MediaRNA interference
2558
RNA interference or RNAi is a gene-silencing process in which double-stranded RNAs trigger the destruction of specific RNAs. Crabtree + Company View MediaAssembly of the HIV capsid
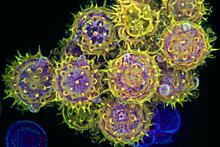
5729
The HIV capsid is a pear-shaped structure that is made of proteins the virus needs to mature and become infective. John Grime and Gregory Voth, The University of Chicago View MediaA dynamic model of the DNA helicase protein complex
3750
This short video shows a model of the DNA helicase in yeast. This DNA helicase has 11 proteins that work together to unwind DNA during the process of copying it, called DNA replication. Huilin Li, Stony Brook University View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
3443
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaChromosomes after crossing over
1314
Duplicated pair of chromosomes have exchanged material. Judith Stoffer View MediaProtein formation
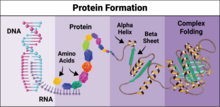
6603
Proteins are 3D structures made up of smaller units. DNA is transcribed to RNA, which in turn is translated into amino acids. NIGMS, with the folded protein illustration adapted from Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaRepairing DNA
2330
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
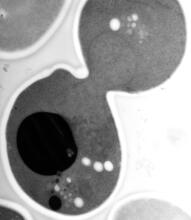
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaLily mitosis 10
1010
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 1
3730
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaHaplotypes (with labels)
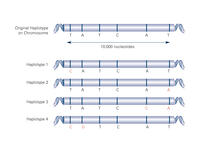
2567
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. Crabtree + Company View Media