Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
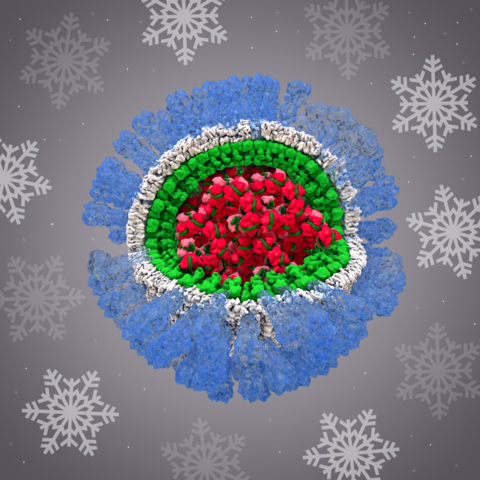

6356: H1N1 Influenza Virus
6356: H1N1 Influenza Virus
Related to image 6355.
Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego
View Media
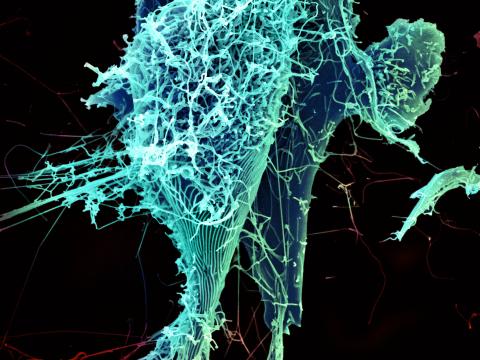
3619: String-like Ebola virus peeling off an infected cell
3619: String-like Ebola virus peeling off an infected cell
After multiplying inside a host cell, the stringlike Ebola virus is emerging to infect more cells. Ebola is a rare, often fatal disease that occurs primarily in tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. The virus is believed to spread to humans through contact with wild animals, especially fruit bats. It can be transmitted between one person and another through bodily fluids.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Heinz Feldmann, Peter Jahrling, Elizabeth Fischer and Anita Mora, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health
View Media
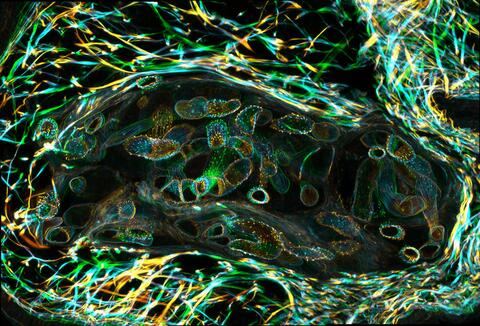
3627: Larvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
3627: Larvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Once mature, the worm swims back into the water, where it can infect people through skin contact. Initially, an infected person might have a rash, itchy skin, or flu-like symptoms, but the real damage is done over time to internal organs.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner
View Media
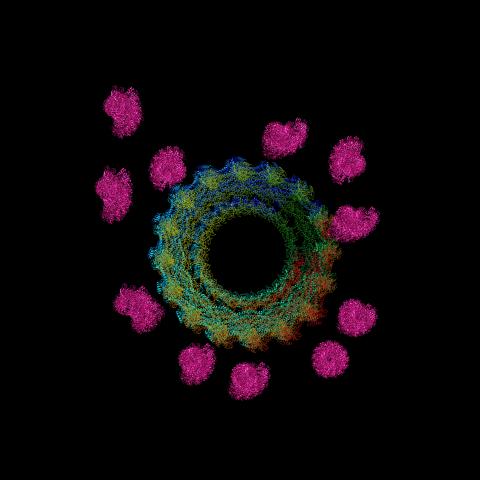
6571: Actin filaments bundled around the dynamin helical polymer
6571: Actin filaments bundled around the dynamin helical polymer
Multiple actin filaments (magenta) are organized around a dynamin helical polymer (rainbow colored) in this model derived from cryo-electron tomography. By bundling actin, dynamin increases the strength of a cell’s skeleton and plays a role in cell-cell fusion, a process involved in conception, development, and regeneration.
Elizabeth Chen, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
View Media
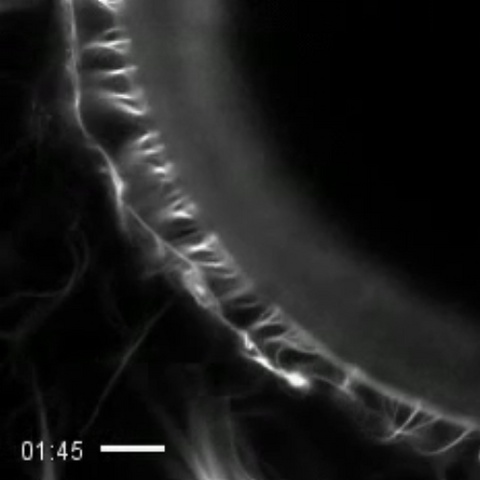
3494: How cilia do the wave
3494: How cilia do the wave
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Each one, made up of more than 600 different proteins, works together with hundreds of others in a tightly-packed layer to move like a crowd at a ball game doing "the wave." Their synchronized motion helps sweep mucus from the lungs and usher eggs from the ovaries into the uterus. By controlling how fluid flows around an embryo, cilia also help ensure that organs like the heart develop on the correct side of your body.
Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University
View Media
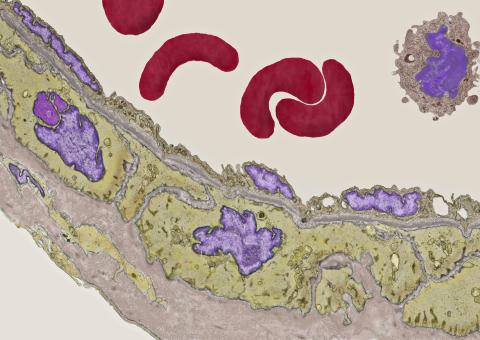
3738: Transmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
3738: Transmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Elastin fibers are at least five times stretchier than rubber bands of the same size. Tissues that expand, such as blood vessels and lungs, need to be both strong and elastic, so they contain both collagen (another ECM protein) and elastin. In this photo, the elastin-rich ECM is colored grayish brown and is most visible at the bottom of the photo. The curved red structures near the top of the image are red blood cells.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
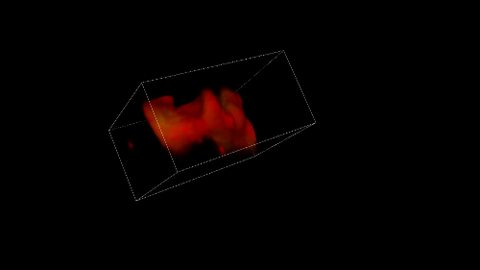
5877: Misfolded proteins in mitochondria, 3-D video
5877: Misfolded proteins in mitochondria, 3-D video
Three-dimensional image of misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to image 5878. Learn more in this press release by The American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Rong Li, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University
View Media
6597: Pathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597: Pathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. Discover more resources from NIGMS’ Pathways collaboration with Scholastic. View the video on YouTube for closed captioning.
National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
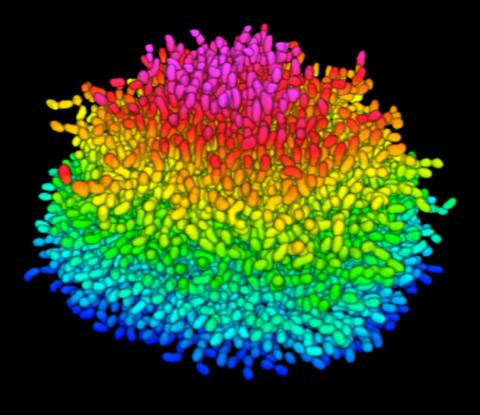
5825: A Growing Bacterial Biofilm
5825: A Growing Bacterial Biofilm
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth.
Each slightly curved comma shape represents an individual bacterium from assembled confocal microscopy images. Different colors show each bacterium’s position in the biofilm in relation to the surface on which the film is growing.
Each slightly curved comma shape represents an individual bacterium from assembled confocal microscopy images. Different colors show each bacterium’s position in the biofilm in relation to the surface on which the film is growing.
Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ.
View Media
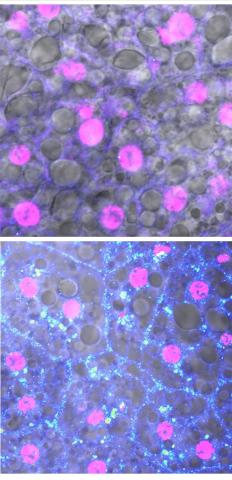
6984: Fruit fly starvation leads to adipokine accumulation
6984: Fruit fly starvation leads to adipokine accumulation
Adult Drosophila abdominal fat tissue showing cell nuclei labelled in magenta. The upper panel is from well-fed flies, and the lower panel is from flies that have been deprived of food for 4 hours. Starvation results in the accumulation of a key adipokine—a fat hormone (blue-green dots).
Related to images 6982, 6983, and 6985.
Related to images 6982, 6983, and 6985.
Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center
View Media

3728: Quorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
3728: Quorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
To simulate the consequences of disrupting bacterial cell-to-cell communication, called quorum sensing, in the crypts (small chambers within the colon), the researchers experimented with an inhibitor molecule (i.e., antagonist) to turn off quorum sensing in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), an antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria that often causes human infections. In this experiment, a medium promoting bacterial growth flows through experimental chambers mimicking the colon environment. The chambers on the right contained no antagonist. In the left chambers, after being added to the flowing medium, the quorum-sensing-inhibiting molecules quickly spread throughout the crevices, inactivating quorum sensing and reducing colonization. These results suggest a potential strategy for addressing MRSA virulence via inhibitors of bacterial communication. You can read more about this research here.
Minyoung Kevin Kim and Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University
View Media
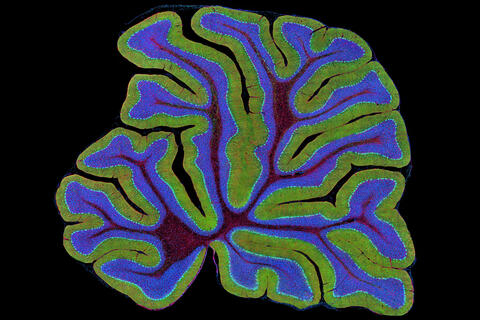
3639: Cerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
3639: Cerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
The cerebellum of a mouse is shown here in cross-section. The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. People with damage to this region of the brain often have difficulty with balance, coordination and fine motor skills. For a higher magnification, see image 3371.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Thomas Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego
View Media
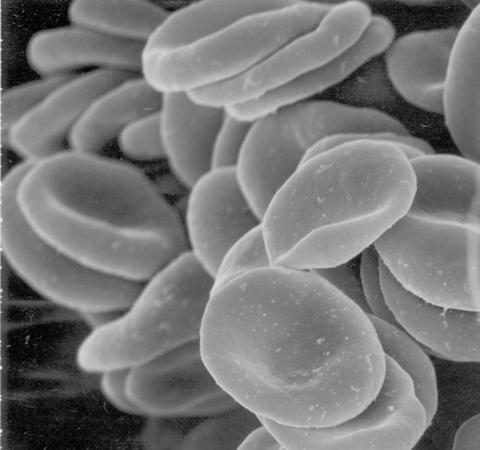
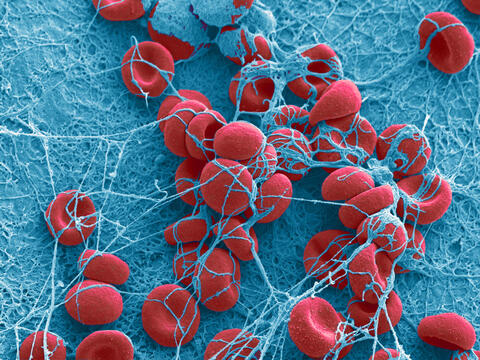
1101: Red blood cells
1101: Red blood cells
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sample.
Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa
View Media
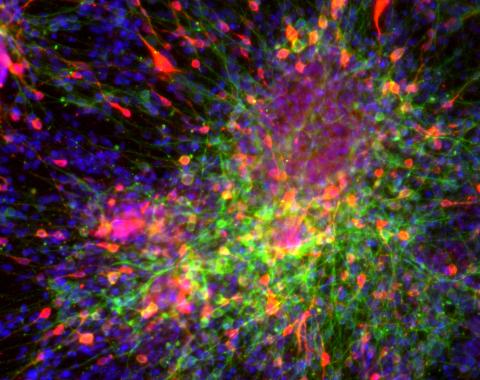
3271: Dopaminergic neurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
3271: Dopaminergic neurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
These neurons are derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. Red shows cells making a protein called TH that is characteristic of the neurons that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Green indicates a protein that's found in all neurons. Blue indicates the nuclei of all cells. Studying dopaminergic neurons can help researchers understand the origins of Parkinson's disease and could be used to screen potential new drugs. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Related to images 3270 and 3285.
Yaping Sun, lab of Su Guo, University of California, San Francisco, via CIRM
View Media

3272: Ear hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
3272: Ear hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
Mouse embryonic stem cells matured into this bundle of hair cells similar to the ones that transmit sound in the ear. These cells could one day be transplanted as a therapy for some forms of deafness, or they could be used to screen drugs to treat deafness. The hairs are shown at 23,000 times magnification via scanning electron microscopy. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Stefen Heller, Stanford University, via CIRM
View Media
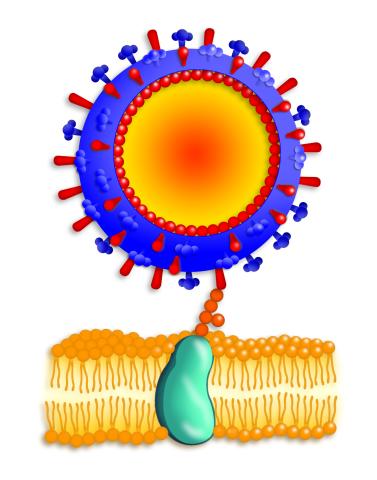
2425: Influenza virus attaches to host membrane
2425: Influenza virus attaches to host membrane
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Neuraminidase, an enzyme that chews sugars, helps newly made virus particles detach so they can infect other cells. Related to 213. Featured in the March 2006, issue of Findings in "Viral Voyages."
Crabtree + Company
View Media
6520: HeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
6520: HeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
Here, a human HeLa cell (a type of immortal cell line used in laboratory experiments) is undergoing cell division. They come from cervical cancer cells that were obtained in 1951 from Henrietta Lacks, a patient at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. The final stage of division, called cytokinesis, occurs after the genomes—shown in yellow—have split into two new daughter cells. The myosin II is a motor protein shown in blue, and the actin filaments, which are types of protein that support cell structure, are shown in red.
Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine.
View Media
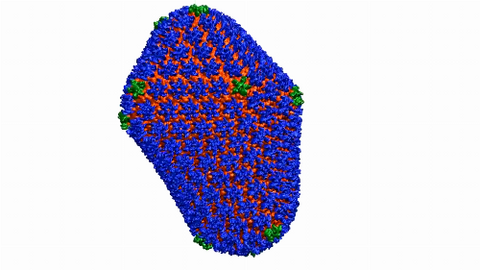
6601: Atomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
6601: Atomic-level structure of the HIV capsid
This animation shows atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that encloses the virus's genetic material. Scientists determined the exact structure of the capsid using a variety of imaging techniques and analyses. They then entered this data into a supercomputer to produce this image. Related to image 3477.
Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
View Media
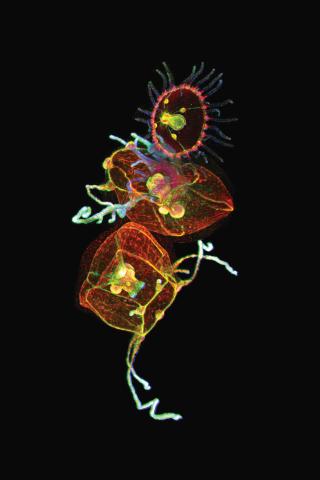
3636: Jellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
3636: Jellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
Jellyfish are especially good models for studying the evolution of embryonic tissue layers. Despite being primitive, jellyfish have a nervous system (stained green here) and musculature (red). Cell nuclei are stained blue. By studying how tissues are distributed in this simple organism, scientists can learn about the evolution of the shapes and features of diverse animals.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Helena Parra, Pompeu Fabra University, Spain
View Media
2434: Fruit fly retina 02
2434: Fruit fly retina 02
Section of a fruit fly retina showing the light-sensing molecules rhodopsin-5 (blue) and rhodopsin-6 (red).
Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University
View Media
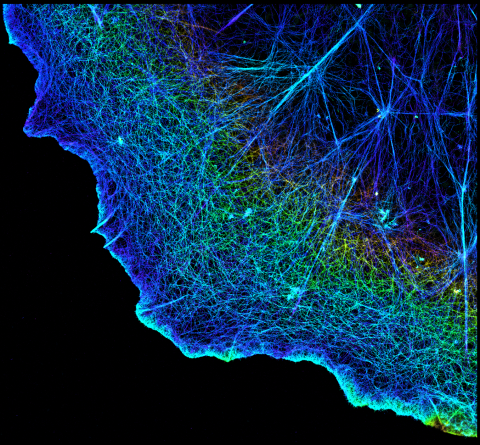
3749: 3D image of actin in a cell
3749: 3D image of actin in a cell
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Here, researchers have used a technique called stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) to visualize the actin network in a cell in three dimensions. The actin strands were labeled with a dye called Alexa Fluor 647-phalloidin. This image appears in a study published by Nature Methods, which reports how researchers use STORM to visualize the cytoskeleton.
Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University
View Media
2693: Fruit fly in the pink
2693: Fruit fly in the pink
Fruit flies are a common model organism for basic medical research.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
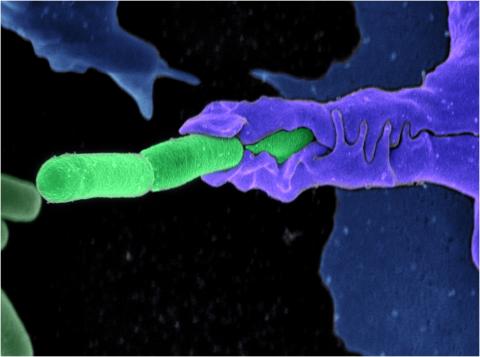
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
Multiple anthrax bacteria (green) being enveloped by an immune system cell (purple). Anthrax bacteria live in soil and form dormant spores that can survive for decades. When animals eat or inhale these spores, the bacteria activate and rapidly increase in number. Today, a highly effective and widely used vaccine has made the disease uncommon in domesticated animals and rare in humans.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Camenzind G. Robinson, Sarah Guilman, and Arthur Friedlander, United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases
View Media
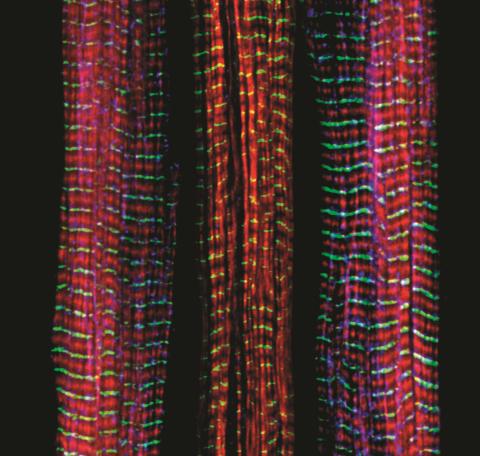
3630: Three muscle fibers; the middle has a defect found in some neuromuscular diseases
3630: Three muscle fibers; the middle has a defect found in some neuromuscular diseases
Of the three muscle fibers shown here, the one on the right and the one on the left are normal. The middle fiber is deficient a large protein called nebulin (blue). Nebulin plays a number of roles in the structure and function of muscles, and its absence is associated with certain neuromuscular disorders.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Christopher Pappas and Carol Gregorio, University of Arizona
View Media
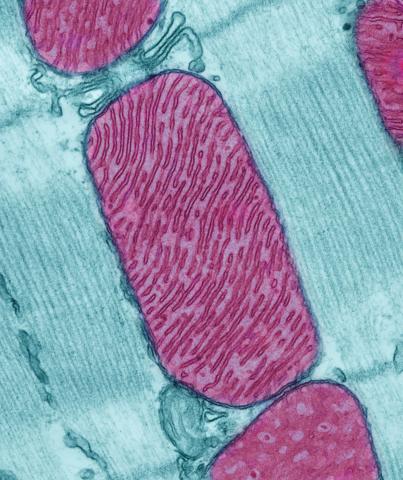
3661: Mitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
3661: Mitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
These mitochondria (red) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). This folding vastly increases the surface area for energy production. Nearly all our cells have mitochondria. Related to image 3664.
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research
View Media

1338: Nerve cell
1338: Nerve cell
Nerve cells have long, invisibly thin fibers that carry electrical impulses throughout the body. Some of these fibers extend about 3 feet from the spinal cord to the toes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
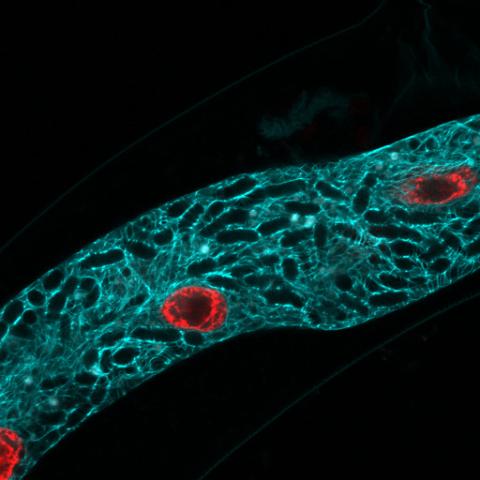
5778: Microsporidia in roundworm 2
5778: Microsporidia in roundworm 2
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Microsporidia—which are parasites closely related to fungi—infect and multiply inside animal cells, and take the rearranging of cells’ interiors to a new level. They reprogram animal cells such that the cells start to fuse, causing them to form long, continuous tubes. As shown in this image of the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans, microsporidia (dark oval shapes) invaded the worm’s gut cells (long tube; the cell nuclei are shown in red) and have instructed the cells to merge. The cell fusion enables the microsporidia to thrive and propagate in the expanded space. Scientists study microsporidia in worms to gain more insight into how these parasites manipulate their host cells. This knowledge might help researchers devise strategies to prevent or treat infections with microsporidia.
For more on the research into microsporidia, see this news release from the University of California San Diego. Related to images 5777 and 5779.
For more on the research into microsporidia, see this news release from the University of California San Diego. Related to images 5777 and 5779.
Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego
View Media

2667: Glowing fish
2667: Glowing fish
Professor Marc Zimmer's family pets, including these fish, glow in the dark in response to blue light. Featured in the September 2009 issue of Findings.
View Media
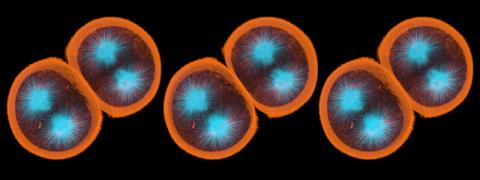
1047: Sea urchin embryo 01
1047: Sea urchin embryo 01
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). This image is part of a series of images: image 1048, image 1049, image 1050, image 1051 and image 1052.
George von Dassow, University of Washington
View Media
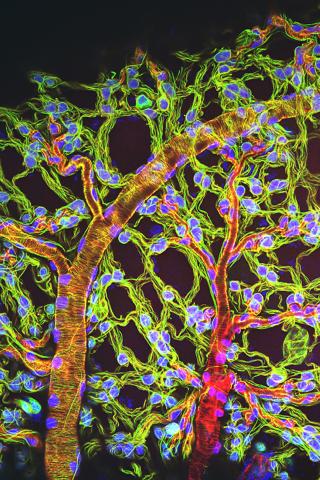
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Unlike mammals, which have red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body, insects have breathing tubes that carry air through their exoskeleton directly to where it's needed. This image shows the breathing tubes embedded in the weblike sheath cells that cover developing egg chambers.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University.
View Media

1283: Vesicle traffic
1283: Vesicle traffic
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. The double membrane that bounds the nucleus flows into the ribosome-studded rough endoplasmic reticulum (purple), where membrane-embedded proteins are manufactured. Proteins are processed and lipids are manufactured in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (blue) and Golgi apparatus (green). Vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane release their contents outside the cell. The cell can also take in material from outside by having vesicles pinch off from the cell membrane.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
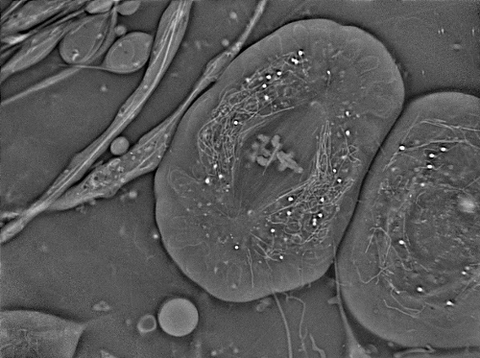
6898: Crane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
6898: Crane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
A crane fly spermatocyte during metaphase of meiosis-I, a step in the production of sperm. A meiotic spindle pulls apart three pairs of autosomal chromosomes, along with a sex chromosome on the right. Tubular mitochondria surround the spindle and chromosomes. This video was captured with quantitative orientation-independent differential interference contrast and is a time lapse showing a 1-second image taken every 30 seconds over the course of 30 minutes.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the J. Biomed Opt. paper “Orientation-Independent Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscopy and Its Combination with Orientation-Independent Polarization System” by Shribak et. al.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the J. Biomed Opt. paper “Orientation-Independent Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscopy and Its Combination with Orientation-Independent Polarization System” by Shribak et. al.
Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago.
View Media
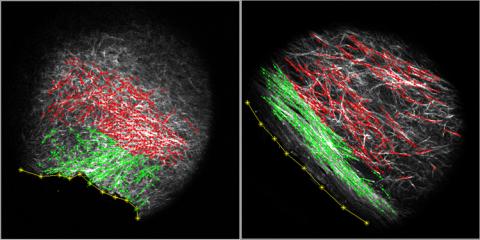
3478: DDR2 Receptors Attach to Collagen in Breast Tumor
3478: DDR2 Receptors Attach to Collagen in Breast Tumor
On the left, the boundary of a breast tumor (yellow) attaches to collagen fibers that are closest to it (green) using DDR2. On the right, a tumor without DDR2 remains disconnected from the collagen.
Callie Corsa and Suzanne Ponik, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
View Media
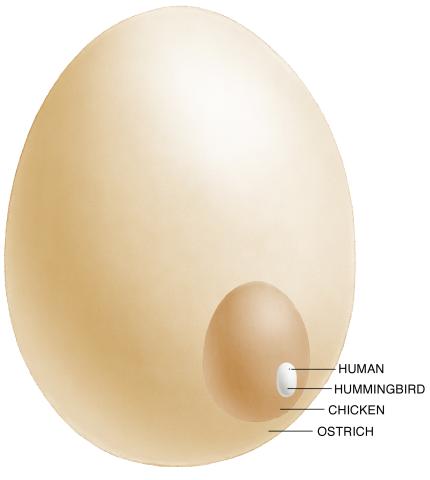
1339: Egg comparison
1339: Egg comparison
The largest human cell (by volume) is the egg. Human eggs are 150 micrometers in diameter and you can just barely see one with a naked eye. In comparison, consider the eggs of chickens...or ostriches!
Judith Stoffer
View Media
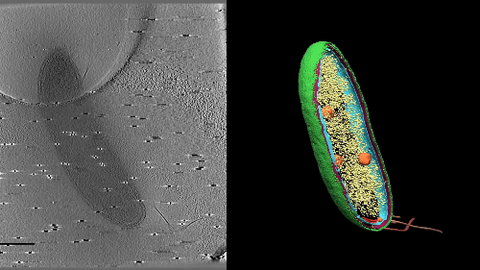
6569: Cryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
6569: Cryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules (orange).
Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University.
View Media
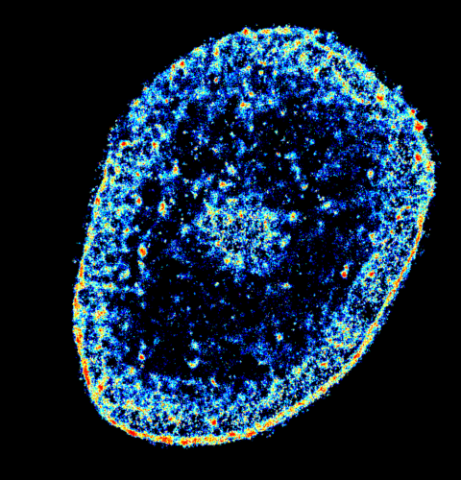
6893: Chromatin in human tenocyte
6893: Chromatin in human tenocyte
The nucleus of a degenerating human tendon cell, also known as a tenocyte. It has been color-coded based on the density of chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins. Areas of low chromatin density are shown in blue, and areas of high chromatin density are shown in red. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6887 and 6888.
Related to images 6887 and 6888.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
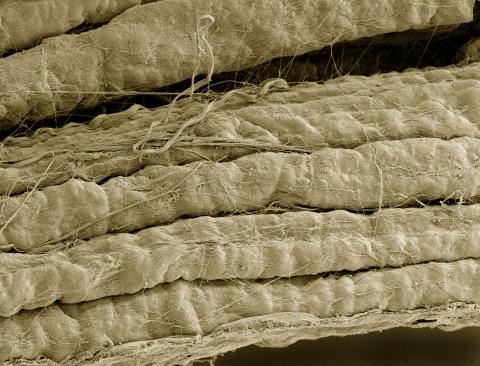
3737: A bundle of myelinated peripheral nerve cells (axons)
3737: A bundle of myelinated peripheral nerve cells (axons)
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells. The axons of nerve cells are surrounded by the ECM encasing myelin-supplying Schwann cells, which insulate the axons to help speed the transmission of electric nerve impulses along the axons.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
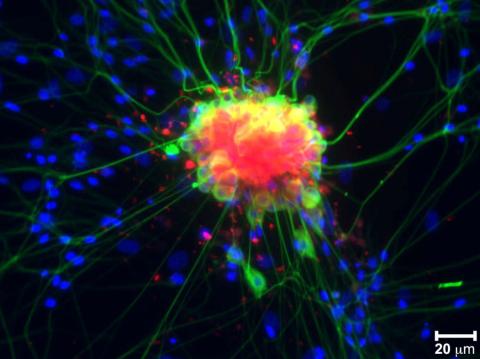
3251: Spinal nerve cells
3251: Spinal nerve cells
Neurons (green) and glial cells from isolated dorsal root ganglia express COX-2 (red) after exposure to an inflammatory stimulus (cell nuclei are blue). Lawrence Marnett and colleagues have demonstrated that certain drugs selectively block COX-2 metabolism of endocannabinoids -- naturally occurring analgesic molecules -- in stimulated dorsal root ganglia. Featured in the October 20, 2011 issue of Biomedical Beat.
Lawrence Marnett, Vanderbilt University
View Media
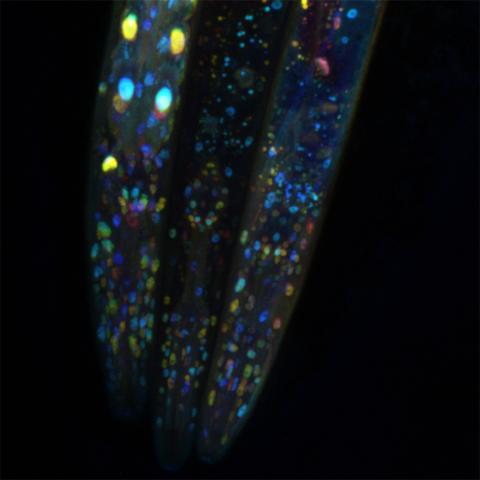
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. The head region of three worms that were genetically modified to express a fluorescent protein were imaged and the images were color-coded based on depth. The worm on the left lacks neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus every cell is fluorescent. In the middle worm, the expression of the fluorescent protein is silenced by neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus most cells are not fluorescent. The worm on the right lacks an enzyme that amplifies RNA for silencing. Surprisingly, the identities of the cells that depend on this enzyme for gene silencing are unpredictable. As a result, worms of identical genotype are nevertheless random mosaics for how the function of gene silencing is carried out. For more, see journal article and press release. Related to image 6534.
Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park
View Media
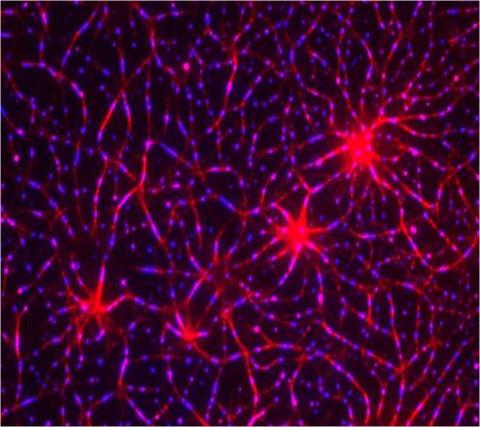
3787: In vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787: In vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Each T cell carries proteins, called T-cell receptors, on its surface that are activated when they come in contact with an invader. This activation sets in motion a cascade of biochemical changes inside the T cell to mount a defense against the invasion. Scientists have been interested for some time what happens after a T-cell receptor is activated. One obstacle has been to study how this signaling cascade, or pathway, proceeds inside T cells.
In this image, researchers have created a T-cell receptor pathway consisting of 12 proteins outside the cell on an artificial membrane. The image shows two key steps during the signaling process: clustering of a protein called linker for activation of T cells (LAT) (blue) and polymerization of the cytoskeleton protein actin (red). The findings show that the T-cell receptor signaling proteins self-organize into separate physical and biochemical compartments. This new system of studying molecular pathways outside the cells will enable scientists to better understand how the immune system combats microbes or other agents that cause infection.
To learn more how researchers assembled this T-cell receptor pathway, see this press release from HHMI's Marine Biological Laboratory Whitman Center. Related to video 3786.
In this image, researchers have created a T-cell receptor pathway consisting of 12 proteins outside the cell on an artificial membrane. The image shows two key steps during the signaling process: clustering of a protein called linker for activation of T cells (LAT) (blue) and polymerization of the cytoskeleton protein actin (red). The findings show that the T-cell receptor signaling proteins self-organize into separate physical and biochemical compartments. This new system of studying molecular pathways outside the cells will enable scientists to better understand how the immune system combats microbes or other agents that cause infection.
To learn more how researchers assembled this T-cell receptor pathway, see this press release from HHMI's Marine Biological Laboratory Whitman Center. Related to video 3786.
Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory
View Media
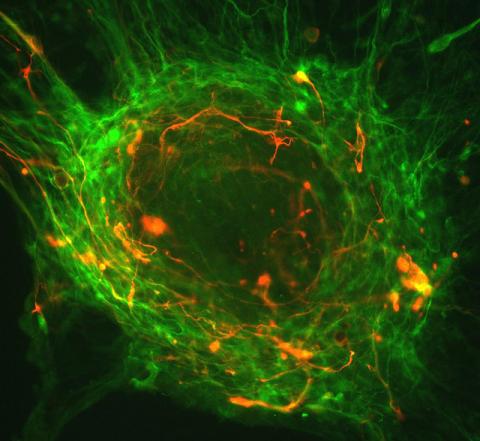
3276: Human ES cells differentiating into neurons
3276: Human ES cells differentiating into neurons
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Some cells have become neurons (red), while others are still precursors of nerve cells (green). The yellow is an imaging artifact resulting when cells in both stages are on top of each other. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM
View Media
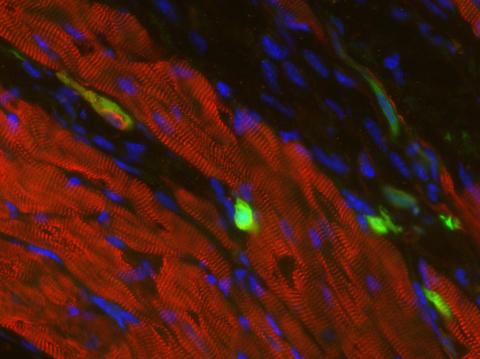
3273: Heart muscle with reprogrammed skin cells
3273: Heart muscle with reprogrammed skin cells
Skins cells were reprogrammed into heart muscle cells. The cells highlighted in green are remaining skin cells. Red indicates a protein that is unique to heart muscle. The technique used to reprogram the skin cells into heart cells could one day be used to mend heart muscle damaged by disease or heart attack. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, via CIRM
View Media
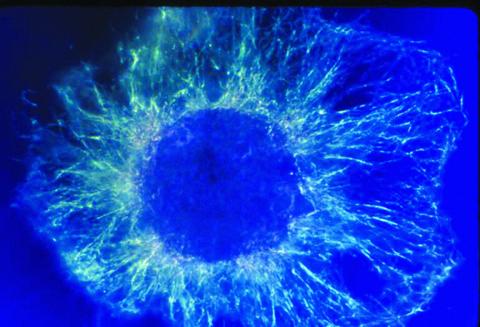
1058: Lily mitosis 01
1058: Lily mitosis 01
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
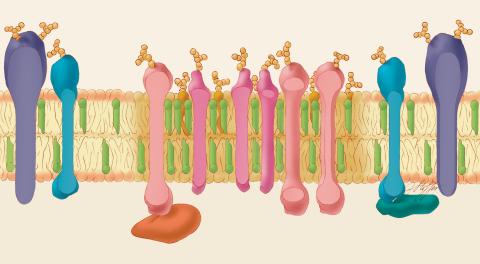
1285: Lipid raft
1285: Lipid raft
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. In artificial membranes, different lipids separate from each other based on their physical properties, forming small islands called lipid rafts.
Judith Stoffer
View Media

5872: Mouse retina close-up
5872: Mouse retina close-up
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
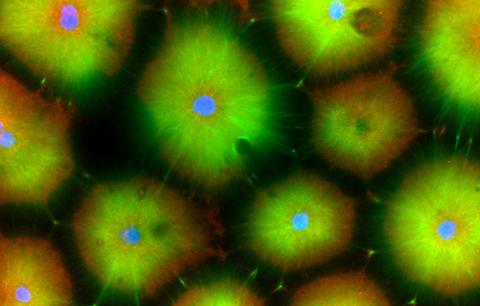
6593: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 6
6593: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 6
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Image created using confocal microscopy.
For more photos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6584, 6585, 6586, 6591, 6592.
For videos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6587, 6588, 6589, and 6590.
Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine.
View Media
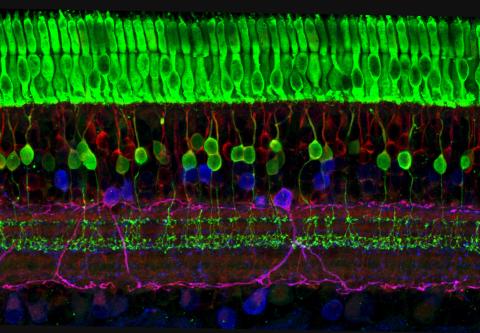
3635: The eye uses many layers of nerve cells to convert light into sight
3635: The eye uses many layers of nerve cells to convert light into sight
This image captures the many layers of nerve cells in the retina. The top layer (green) is made up of cells called photoreceptors that convert light into electrical signals to relay to the brain. The two best-known types of photoreceptor cells are rod- and cone-shaped. Rods help us see under low-light conditions but can't help us distinguish colors. Cones don't function well in the dark but allow us to see vibrant colors in daylight.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Wei Li, National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
View Media
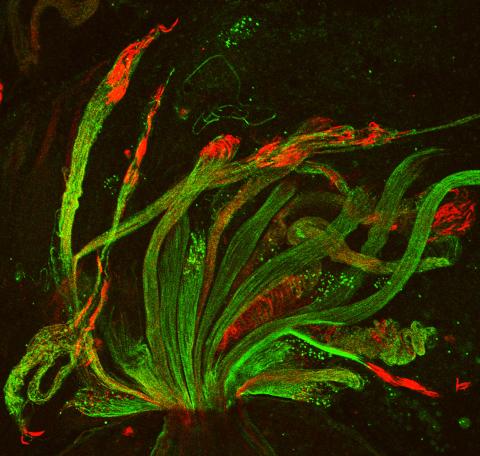
3590: Fruit fly spermatids
3590: Fruit fly spermatids
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. In the sperm cell's head is the cell nucleus; in its tail is the power to outswim thousands of competitors to fertilize an egg. As seen in this microscopy image, fruit fly spermatids start out as groups of interconnected cells. A small lipid molecule called PIP2 helps spermatids tell their heads from their tails. Here, PIP2 (red) marks the nuclei and a cell skeleton-building protein called tubulin (green) marks the tails. When PIP2 levels are too low, some spermatids get mixed up and grow with their heads at the wrong end. Because sperm development is similar across species, studies in fruit flies could help researchers understand male infertility in humans.
Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada
View Media
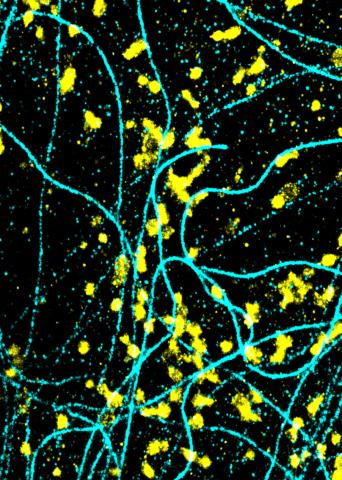
6889: Lysosomes and microtubules
6889: Lysosomes and microtubules
Lysosomes (yellow) and detyrosinated microtubules (light blue). Lysosomes are bubblelike organelles that take in molecules and use enzymes to break them down. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. The researchers who took this image found that in epithelial cells, detyrosinated microtubules are a small subset of fibers, and they concentrate lysosomes around themselves. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6890, 6891, and 6892.
Related to images 6890, 6891, and 6892.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media