Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
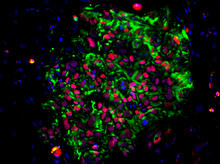
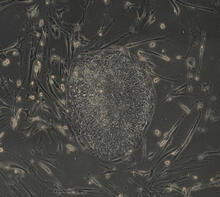
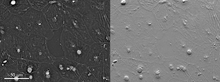
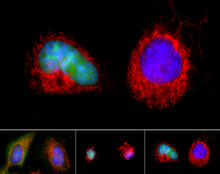
Induced pluripotent stem cells from skin
3278
These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) were derived from a woman's skin. Green and red indicate proteins found in reprogrammed cells but not in skin cells (TRA1-62 and NANOG). Kathrin Plath lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
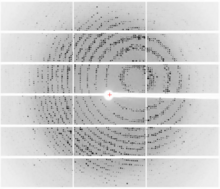
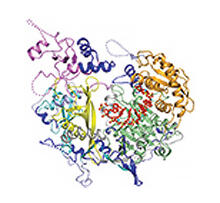
6765
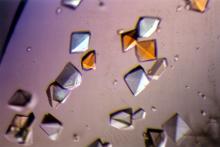
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (1)
2397
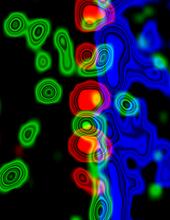
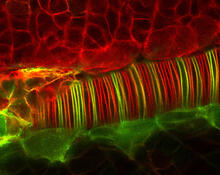
A crystal of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaMolecular interactions at the astrocyte nuclear membrane
3734
These ripples of color represent the outer membrane of the nucleus inside an astrocyte, a star-shaped cell inside the brain. Katerina Akassoglou, Gladstone Institute for Neurological Disease & UCSF View MediaBiofilm formed by a pathogen
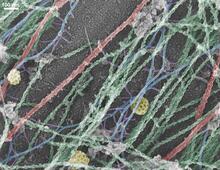
6518
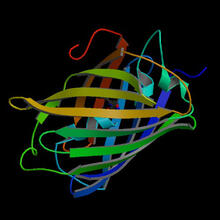
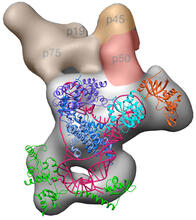
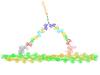
A biofilm is a highly organized community of microorganisms that develops naturally on certain surfaces. Scott Chimileski, Ph.D., and Roberto Kolter, Ph.D., Harvard Medical School. View MediaWreath-shaped protein from X. campestris
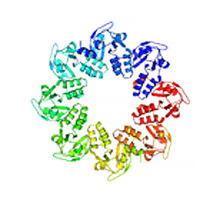
2372
Crystal structure of a protein with unknown function from Xanthomonas campestris, a plant pathogen. Eight copies of the protein crystallized to form a ring. Ken Schwinn and Sonia Espejon-Reynes, New York SGX Research Center for Structural Genomics View MediaCells use bubble-like structures called vesicles to transport cargo
3634
Cells use bubble-like structures called vesicles (yellow) to import, transport, and export cargo and in cellular communication. A single cell may be filled with thousands of moving vesicles.Tatyana Svitkina, University of Pennsylvania View Media
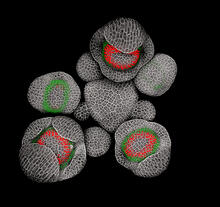
Developing Arabidopsis flower buds
3743
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flowe Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech View MediaElectrode probe on mouse Huntington's muscle cell
3479
Using an electrode, researchers apply an electrical pulse onto a piece of muscle tissue affected by Huntington's disease. Grigor Varuzhanyan and Andrew A. Voss, California State Polytechnic University View MediaHaplotypes
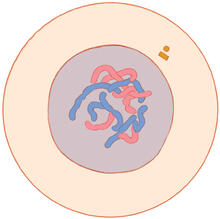
2566
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. Crabtree + Company View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 6
6593
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaIon channel
3487
A special "messy" region of a potassium ion channel is important in its function. Yu Zhoi, Christopher Lingle Laboratory, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaCell division with late aligning chromosomes
2747
This video shows an instance of abnormal mitosis where chromosomes are late to align. Gary Gorbsky, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation View MediaNeural tube development
2328
Proteins in the neural tissues of this zebrafish embryo direct cells to line up and form the neural tube, which will become the spinal cord and brain. Alexander Schier, Harvard University View MediaSea urchin embryo 05
1051
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaWhite Poppy
3424
A white poppy. View cropped image of a poppy here 3423. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaIon channels
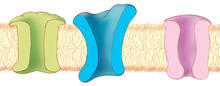
1284
The body uses a variety of ion channels to transport small molecules across cell membranes. Judith Stoffer View MediaMouse brain 3
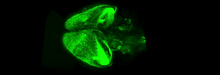
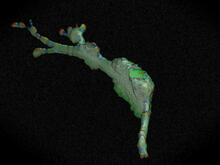
6931
Various views of a mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaFruitful dyes
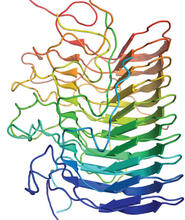
2317
These colorful, computer-generated ribbons show the backbone of a molecule that glows a fluorescent red. Roger Y. Tsien, University of California, San Diego View MediaHIV Infected Cell
3386
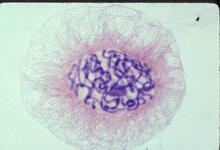
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaLily mitosis 04
1014
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaStructure of amyloid-forming prion protein
3542
This structure from an amyloid-forming prion protein shows one way beta sheets can stack. Douglas Fowler, University of Washington View MediaKluyveromyces polysporus Argonaute bound to guide RNA
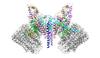
3408
A segment of siRNA, shown in red, guides a "slicer" protein called Argonaute (multi-colored twists and corkscrews) to the target RNA molecules. Kotaro Nakanishi and David Weinberg, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaNormal vascular development in frog embryos
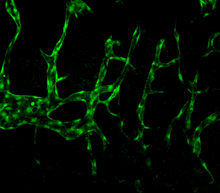
3404
In vivo vascular development in kdr:GFP frogs. Related to images 3403 and 3405. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaElectrostatic map of the adeno-associated virus
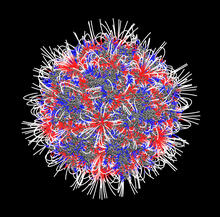
3374
The new highly efficient parallelized DelPhi software was used to calculate the potential map distribution of an entire virus, the adeno-associated virus, which is made up of more than 484,000 atoms. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaDNase
2410
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 03
2605
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaEpithelial cell migration
6899
High-resolution time lapse of epithelial (skin) cell migration and wound healing. It shows an image taken every 13 seconds over the course of almost 14 minutes. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaBiopixels
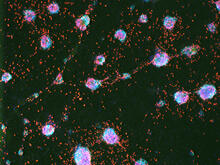
3266
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego View MediaHuman ES cells turn into insulin-producing cells
3277
Human embryonic stem cells were differentiated into cells like those found in the pancreas (blue), which give rise to insulin-producing cells (red). Eugene Brandon, ViaCyte, via CIRM View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
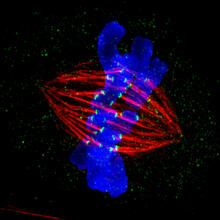
3445
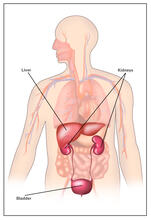
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaGenetic patchworks
2588
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University View MediaGroup of Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6770
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaATP synthase (with labels)
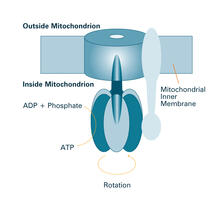
2518
The world's smallest motor, ATP synthase, generates energy for the cell. See image 2517 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaApoptosis reversed
3486
Two healthy cells (bottom, left) enter into apoptosis (bottom, center) but spring back to life after a fatal toxin is removed (bottom, right; top). Hogan Tang of the Denise Montell Lab, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaSea urchin embryo 04
1050
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaPig alpha amylase
2412
Crystals of porcine alpha amylase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaStructure of telomerase
3459
Scientists recently discovered the full molecular structure of telomerase, an enzyme important to aging and cancer. Jiansen Jiang, Edward J. Miracco, Z. Hong Zhou and Juli Feigon, University of California, Los Angeles; Kathleen Collins, University of California, Berkeley View MediaCell curvature
2803
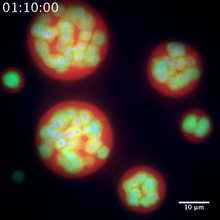
Rendering of the surface of an endothelial cell; membrane curvature is color coded. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaSnowflake yeast 1
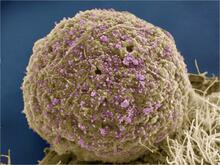
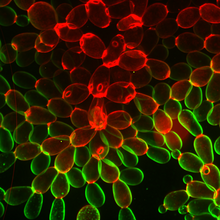
6969
Multicellular yeast called snowflake yeast that researchers created through many generations of directed evolution from unicellular yeast. William Ratcliff, Georgia Institute of Technology. View MediaHeLa cells
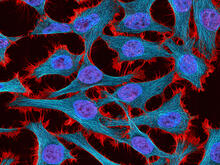
3521
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells stained with the actin binding toxin phalloidin (red), microtubules (cyan) and cell nuclei (blue). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaHistone deacetylases
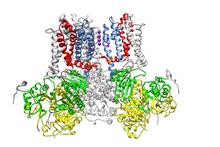
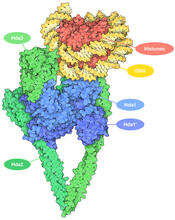
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaThymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime
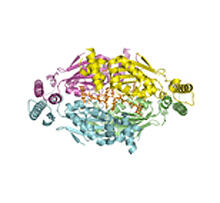
2387
A model of thymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime. Joint Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaProtein involved in cell division from Mycoplasma pneumoniae
2377
Model of a protein involved in cell division from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. This model, based on X-ray crystallography, revealed a structural domain not seen before. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaGroup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
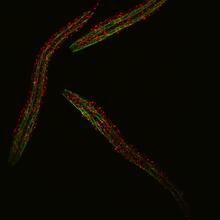
6582
Three C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaDividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
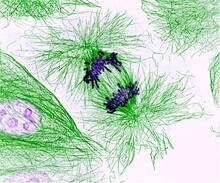
3631
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaStreptococcus bacteria
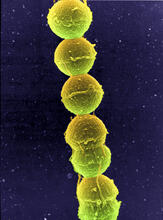
1157
Image of Streptococcus, a type (genus) of spherical bacteria that can colonize the throat and back of the mouth. Stroptococci often occur in pairs or in chains, as shown here. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View Media