Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
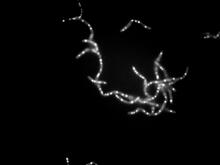
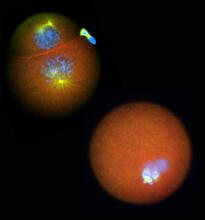
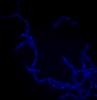
Bacillus anthracis being killed
3481
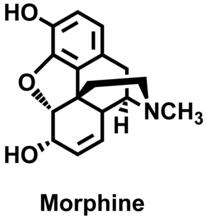
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. John Alumasa, Keiler Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University View MediaMorphine Structure
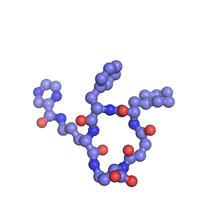
3438
The chemical structure of the morphine molecule Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaPig trypsin crystal
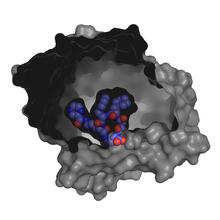
2403
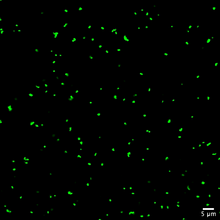
A crystal of pig trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805
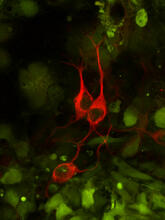
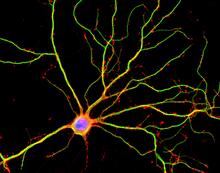
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaThree neurons and human ES cells
3290
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM View MediaDopaminergic neurons derived from mouse embryonic stem cells
3271
These neurons are derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. Red shows cells making a protein called TH that is characteristic of the neurons that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Yaping Sun, lab of Su Guo, University of California, San Francisco, via CIRM View MediaMost abundant protein in M. tuberculosis
2378
Model of a protein, antigen 85B, that is the most abundant protein exported by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 1
3789
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaNucleolinus
2762
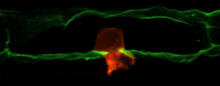
The nucleolinus is a cellular compartment that has been a lonely bystander in scientific endeavors. Mary Anne Alliegro, Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaAnchor cell in basement membrane
2707
An anchor cell (red) pushes through the basement membrane (green) that surrounds it. Elliott Hagedorn, Duke University. View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
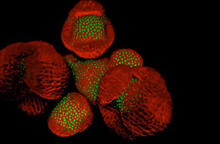
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaArabidopsis Thaliana: Flowers Spring to Life
6503
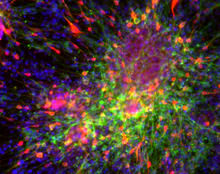
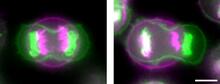
This image capture shows how a single gene, STM, plays a starring role in plant development. Nathanaёl Prunet NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaSymmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
3648
Merged fluorescent images of symmetrically (left) or asymmetrically (right) elongating HeLa cells at the end of early anaphase (magenta) and late anaphase (green). Tomomi Kiyomitsu and Iain M. Cheeseman, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research View MediaBeta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
3286
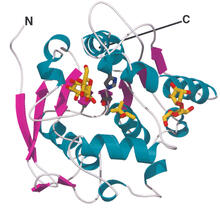
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View MediaOligoendopeptidase F from B. stearothermophilus
2373
Crystal structure of oligoendopeptidase F, a protein slicing enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus, a bacterium that can cause food products to spoil. Accelerated Technologies Center for Gene to 3D Structure/Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral view
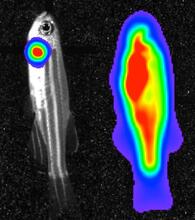
3558
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaCapillary protein crystallization robot
2357
This ACAPELLA robot for capillary protein crystallization grows protein crystals, freezes them, and centers them without manual intervention. Structural Genomics of Pathogenic Protozoa Consortium View MediaLily mitosis 03
1013
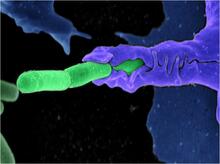
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaAnthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
3612
Multiple anthrax bacteria (green) being enveloped by an immune system cell (purple). Anthrax bacteria live in soil and form dormant spores that can survive for decades. Camenzind G. Robinson, Sarah Guilman, and Arthur Friedlander, United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases View MediaHigh-throughput protein structure determination pipeline
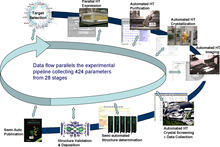
2364
This slide shows the technologies that the Joint Center for Structural Genomics developed for going from gene to structure and how the technologies have been integrated into a high-throughput pipeline Joint Center for Structural Genomics View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaCRISPR
6351
RNA incorporated into the CRISPR surveillance complex is positioned to scan across foreign DNA. Cryo-EM density from a 3Å reconstruction is shown as a yellow mesh. NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaSection of an electron density map
2354
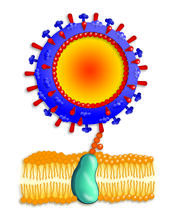
Electron density maps such as this one are generated from the diffraction patterns of X-rays passing through protein crystals. The Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaZika virus
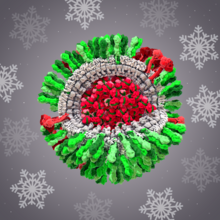
6998
Zika virus is shown in cross section at center left. On the outside, it includes envelope protein (red) and membrane protein (magenta) embedded in a lipid membrane (light purple). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaMouse retina
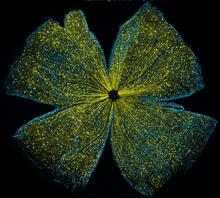
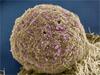
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaHuman retinal organoid
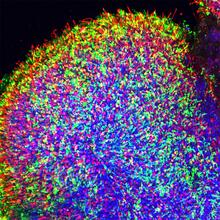
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaHippocampal neuron in culture
3687
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaStem cell differentiation
1294
Undifferentiated embryonic stem cells cease to exist a few days after conception. In this image, ES cells are shown to differentiate into sperm, muscle fiber, hair cells, nerve cells, and cone cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaInfluenza virus attaches to host membrane
2425
Influenza A infects a host cell when hemagglutinin grips onto glycans on its surface. Crabtree + Company View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 02
2791
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaCellular polarity
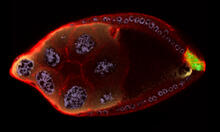
2309
As an egg cell develops, a process called polarization controls what parts ultimately become the embryo's head and tail. This picture shows an egg of the fruit fly Drosophila. Wu-Min Deng, Florida State University View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
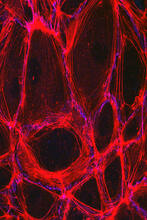
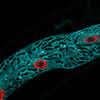
3633
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaStretch detectors
2714
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 3
3415
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaNetwork Map
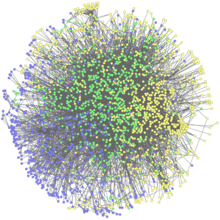
2735
This network map shows the overlap (green) between the long QT syndrome (yellow) and epilepsy (blue) protein-interaction neighborhoods located within the human interactome. Seth Berger, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaEarly ribbon drawing of a protein
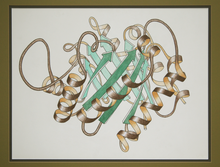
2748
This ribbon drawing of a protein hand drawn and colored by researcher Jane Richardson in 1981 helped originate the ribbon representation of proteins that is now ubiquitous in molecular graphics. Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 6
3418
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaAverage teen circadian cycle
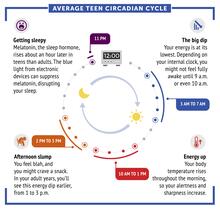
6611
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. Typical circadian rhythms lead to high energy during the middle of the day (10 a.m. NIGMS View MediaEnzyme transition states
3429
The molecule on the left is an electrostatic potential map of the van der Waals surface of the transition state for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Vern Schramm, Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaDrosophila (fruit fly) myosin 1D motility assay
6562
Actin gliding powered by myosin 1D. Note the counterclockwise motion of the gliding actin filaments. Serapion Pyrpassopoulos and E. Michael Ostap, University of Pennsylvania View MediaAspirin (with labels)
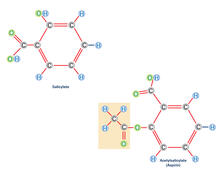
2530
Acetylsalicylate (bottom) is the aspirin of today. Crabtree + Company View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
6355
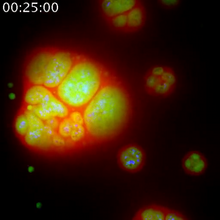
CellPack image of the H1N1 influenza virus, with hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins in green and red, respectively, on the outer envelope (white); matrix protein in gray, and ribonucleoprot Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaFinding one bug
2314
A nanometer-sized biosensor can detect a single deadly bacterium in tainted ground beef. How? Weihong Tan, University of Florida in Gainesville View MediaDicer generates microRNAs
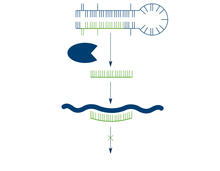
2556
The enzyme Dicer generates microRNAs by chopping larger RNA molecules into tiny Velcro®-like pieces. MicroRNAs stick to mRNA molecules and prevent the mRNAs from being made into proteins. Crabtree + Company View Media