Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Worms and human infertility
2333
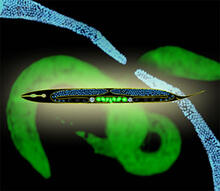
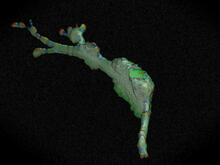
This montage of tiny, transparent C. elegans--or roundworms--may offer insight into understanding human infertility. Abby Dernburg, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaDynamin structure
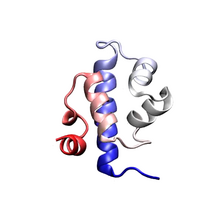
2744
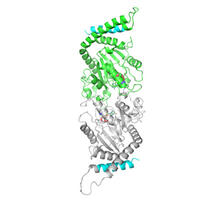
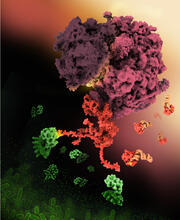
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaMitochondria
1287
Bean-shaped mitochondria are cells' power plants. These organelles have their own DNA and replicate independently. The highly folded inner membranes are the site of energy generation. Judith Stoffer View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 04
2793
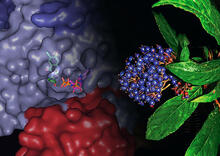
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaHuman blood cells with Borrelia hermsii, a bacterium that causes relapsing fever
3586
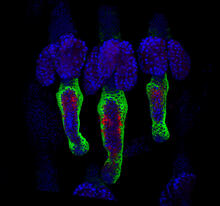
Relapsing fever is caused by a bacterium and transmitted by certain soft-bodied ticks or body lice. The disease is seldom fatal in humans, but it can be very serious and prolonged. NIAID View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
5868
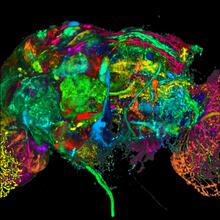
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaMouse Retina
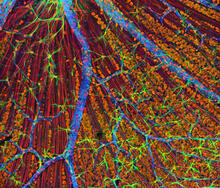
3309
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaWhite Poppy (cropped)
3423
A cropped image of a white poppy. View poppy uncropped here 3424. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaBicycling cell
1337
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaMicrotubule breakdown
2321
Like a building supported by a steel frame, a cell contains its own sturdy internal scaffolding made up of proteins, including microtubules. Eva Nogales, University of California, Berkeley View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
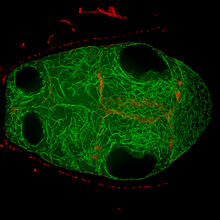
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaAn insect tracheal cell delivers air to muscles
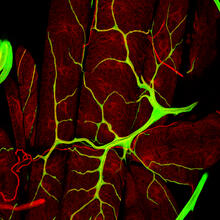
3615
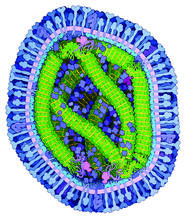
Insects like the fruit fly use an elaborate network of branching tubes called trachea (green) to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Jayan Nair and Maria Leptin, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany View MediaMeasles virus
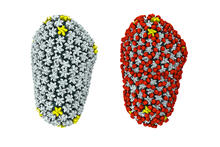
6995
A cross section of the measles virus in which six proteins work together to infect cells. The measles virus is extremely infectious; 9 out of 10 people exposed will contract the disease. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaWound healing in process
3497
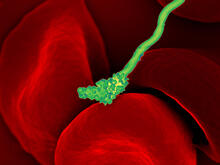
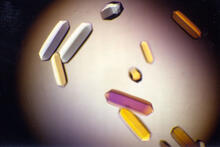
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaFungal lipase (1)
2395
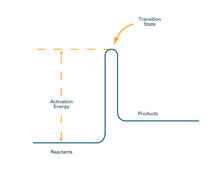
Crystals of fungal lipase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaBeaded bacteriophage
2305
This sculpture made of purple and clear glass beads depicts bacteriophage Phi174, a virus that infects bacteria. It rests on a surface that portrays an adaptive landscape, a conceptual visualization. Holly Wichman, University of Idaho. (Surface by A. Johnston; photo by J. Palmersheim) View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (White Background)
6534
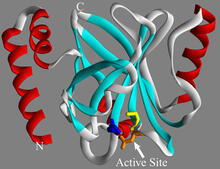
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaRibonuclease P structure
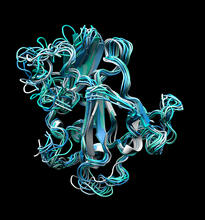
3660
Ribbon diagram showing the structure of Ribonuclease P with tRNA. PDB entry 3Q1Q, molecular modeling by Fred Friedman, NIGMS View MediaThymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime
2387
A model of thymidylate synthase complementing protein from Thermotoga maritime. Joint Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaFrom DNA to Protein
2509
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together. Crabtree + Company View MediaProtein folding video
3391
Proteins are long chains of amino acids. Each protein has a unique amino acid sequence. It is still a mystery how a protein folds into the proper shape based on its sequence. Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group View MediaCryo-EM reveals how the HIV capsid attaches to a human protein to evade immune detection
3755
The illustration shows the capsid of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) whose molecular features were resolved with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Juan R. Perilla, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaModeling disease spread
2322
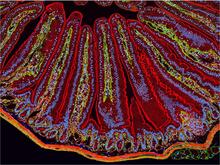
What looks like a Native American dream catcher is really a network of social interactions within a community. Stephen Eubank, University of Virginia Biocomplexity Institute (formerly Virginia Bioinformatics Institute) View MediaNCMIR Intestine-1
3389
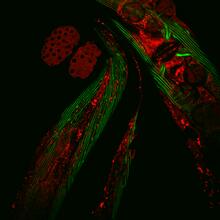
The small intestine is where most of our nutrients from the food we eat are absorbed into the bloodstream. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaFruit fly egg chamber
6811
A fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg chamber with microtubules shown in green and actin filaments shown in red. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaBacterial nanowire model
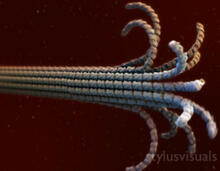
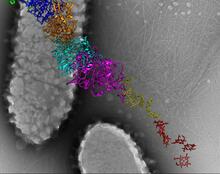
6580
A model of a Geobacter sulfurreducens nanowire created from cryo-electron microscopy images. Edward Egelman, University of Virginia. View MediaDose response curves
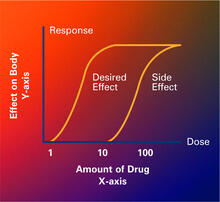
2533
Dose-response curves determine how much of a drug (X-axis) causes a particular effect, or a side effect, in the body (Y-axis). Featured in Medicines By Design. Crabtree + Company View MediaRNA polymerase
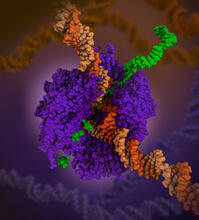
6993
RNA polymerase (purple) is a complex enzyme at the heart of transcription. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 4
6590
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaLily mitosis 04
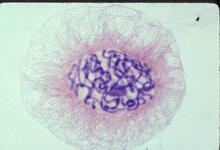
1014
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View Media2-D NMR
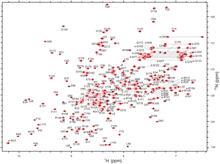
2299
A two-dimensional NMR spectrum of a protein, in this case a 2D 1H-15N HSQC NMR spectrum of a 228 amino acid DNA/RNA-binding protein. Dr. Xiaolian Gao's laboratory at the University of Houston View MediaChang Shan
3483
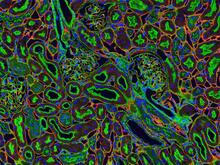
For thousands of years, Chinese herbalists have treated malaria using Chang Shan, a root extract from a type of hydrangea that grows in Tibet and Nepal. Paul Schimmel Lab, Scripps Research Institute View MediaNCMIR kidney-1
3675
Stained kidney tissue. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaSortase b from B. anthracis
2386
Structure of sortase b from the bacterium B. anthracis, which causes anthrax. Sortase b is an enzyme used to rob red blood cells of iron, which the bacteria need to survive. Midwest Center for Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaCloseup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
6583
Closeup of C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaCell curvature
2803
Rendering of the surface of an endothelial cell; membrane curvature is color coded. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaXenopus laevis embryos
2756
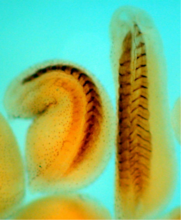
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a model organism for studying embryonic development. The frog embryo on the left lacks the developmental factor Sizzled. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaBacterial spore
2752
A spore from the bacterium Bacillus subtilis shows four outer layers that protect the cell from harsh environmental conditions. Patrick Eichenberger, New York University View MediaPig trypsin (3)
2414
Crystals of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaRecombinant DNA
2564
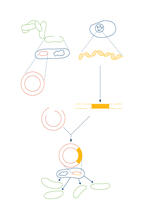
To splice a human gene into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. coli bacterium, cut the plasmid with a restriction enzyme, and splice in human DNA. Crabtree + Company View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
3633
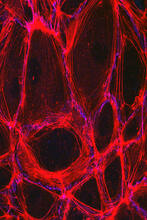
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaShiga toxin
6997
E. coli bacteria normally live harmlessly in our intestines, but some cause disease by making toxins. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaPigment cells in fish skin
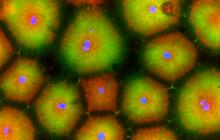
5756
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 03
2792
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaBacterial cells migrating through the tissues of the squid light organ
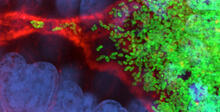
7015
Vibrio fischeri cells (~ 2 mm), labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), passing through a very narrow bottleneck in the tissues (red) of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolope Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaStructure of a key antigen protein involved with Hepatitis C Virus infection
5866
A three-dimensional representation of the structure of E2, a key antigen protein involved with hepatitis C virus infection. Mansun Law Associate Professor Department of Immunolgy and Microbial Science The Scripps Research Institute View MediaRetinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells
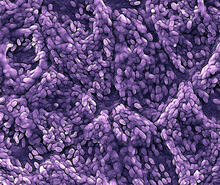
3286
This color-enhanced image is a scanning electron microscope image of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. David Hinton lab, University of Southern California, via CIRM View Media