Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
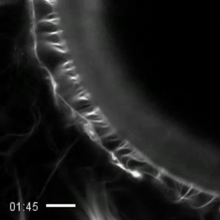
Sea urchin embryo 02
1048
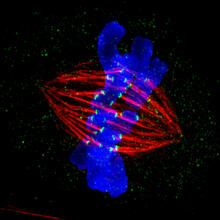
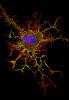
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaDividing cell in metaphase
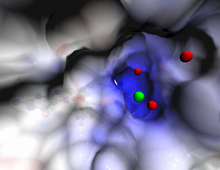
3445
This image of a mammalian epithelial cell, captured in metaphase, was the winning image in the high- and super-resolution microscopy category of the 2012 GE Healthcare Life Sciences Cell Imaging Compe Jane Stout in the laboratory of Claire Walczak, Indiana University, GE Healthcare 2012 Cell Imaging Competition View MediaQuartered torso
1280
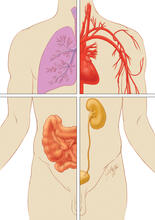
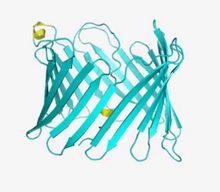
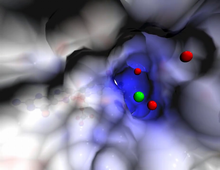
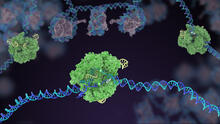
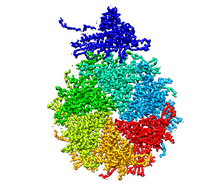
Cells function within organs and tissues, such as the lungs, heart, intestines, and kidney. Judith Stoffer View MediaDynamin structure
2744
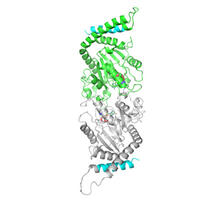
When a molecule arrives at a cell's outer membrane, the membrane creates a pouch around the molecule that protrudes inward. Josh Chappie, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH View MediaBacterial cells migrating through the tissues of the squid light organ
7015
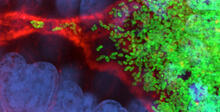
Vibrio fischeri cells (~ 2 mm), labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), passing through a very narrow bottleneck in the tissues (red) of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolope Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaHow cilia do the wave
3494
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University View MediaThe nascent juvenile light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7017
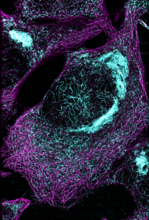
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, with different tissues are stained various colors. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaAntibiotic-surviving bacteria
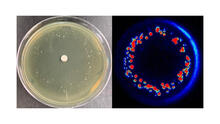
6802
Colonies of bacteria growing despite high concentrations of antibiotics. These colonies are visible both by eye, as seen on the left, and by bioluminescence imaging, as seen on the right. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaSee how immune cell acid destroys bacterial proteins
6602
This animation shows the effect of exposure to hypochlorous acid, which is found in certain types of immune cells, on bacterial proteins. American Chemistry Council View MediaQuorum-sensing inhibitor limits bacterial growth
3728
To simulate the consequences of disrupting bacterial cell-to-cell communication, called quorum sensing, in the crypts (small chambers within the colon), the researchers experimented with an inhibitor Minyoung Kevin Kim and Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaDengue virus membrane protein structure
3758
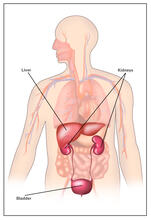
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne illness that infects millions of people in the tropics and subtropics each year. Like many viruses, dengue is enclosed by a protective membrane. Hong Zhou, UCLA View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaVDAC video 01
2570
This video shows the structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaA panorama view of cells
5761
This photograph shows a panoramic view of HeLa cells, a cell line many researchers use to study a large variety of important research questions. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaDNA replication illustration (with labels)
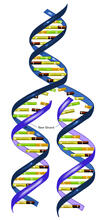
2544
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. Crabtree + Company View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 2
6588
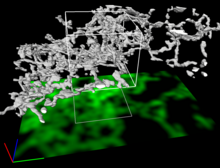
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 2
5856
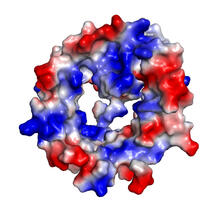
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaBovine trypsin
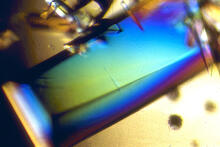
2408
A crystal of bovine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaWound healing in process
3498
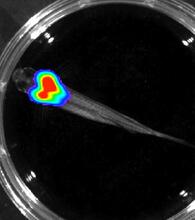
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
3557
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaMouse retina
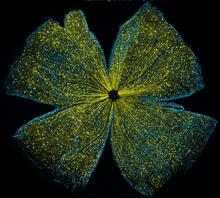
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
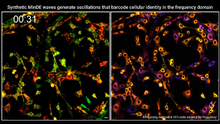
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaStaphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaZika virus
6998
Zika virus is shown in cross section at center left. On the outside, it includes envelope protein (red) and membrane protein (magenta) embedded in a lipid membrane (light purple). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaFused, dicentric chromosomes
2763
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University View MediaLeading cells with light
2708
A blue laser beam turns on a protein that helps this human cancer cell move. Responding to the stimulus, the protein, called Rac1, first creates ruffles at the edge of the cell. Yi Wu, University of North Carolina View MediaStructure of heme, side view
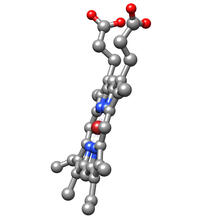
3540
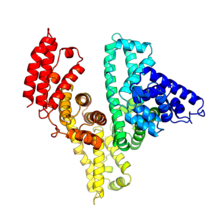
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
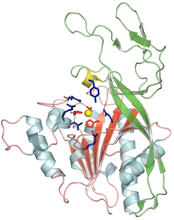
2746
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaVDAC-1 (4)
2495
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaSerum albumin structure 2
3745
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. Wladek Minor, University of Virginia View MediaHoneybee brain
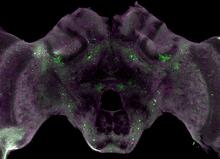
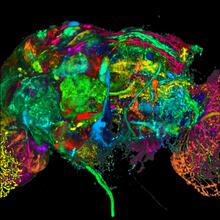
6755
Insect brains, like the honeybee brain shown here, are very different in shape from human brains. Gene Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. View MediaCas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
5816
In the gene-editing tool CRISPR, a small strand of RNA identifies a specific chunk of DNA. Janet Iwasa View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larvae
6771
Mosquito larvae with genes edited by CRISPR swimming in water. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaMouse heart muscle cells
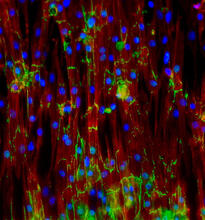
3282
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaBacteria working to eat
2304
Gram-negative bacteria perform molecular acrobatics just to eat. Because they're encased by two membranes, they must haul nutrients across both. Emad Tajkhorshid, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaCrab larva eye
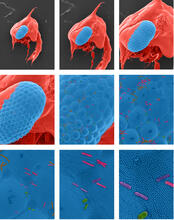
1251
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
5868
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaH1 histamine receptor
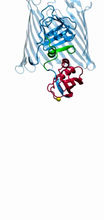
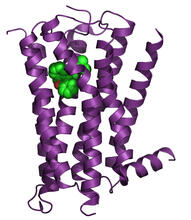
3360
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, doxepin. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaHuman aspartoacylase
2352
Model of aspartoacylase, a human enzyme involved in brain metabolism. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaZebrafish larva
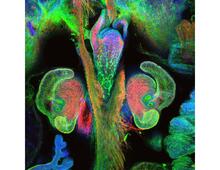
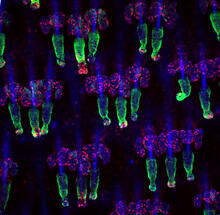
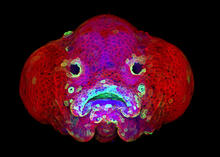
5881
You are face to face with a 6-day-old zebrafish larva. What look like eyes will become nostrils, and the bulges on either side will become eyes. Oscar Ruiz and George Eisenhoffer, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston View MediaFruit fly ovary_2
3656
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit--they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid, detail
5875
Detail of a subunit of the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaPlasma membrane (with labels)
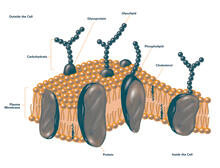
2524
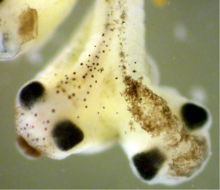
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2523 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaTwo-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
2755
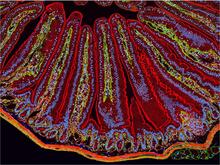
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a research organism for studying embryonic development. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaNCMIR Intestine-1
3389
The small intestine is where most of our nutrients from the food we eat are absorbed into the bloodstream. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View Media