Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
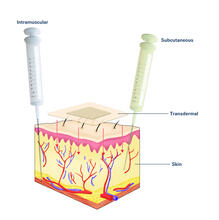
Drugs enter skin (with labels)
2532
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2531 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaMature, flowering Arabidopsis
2779
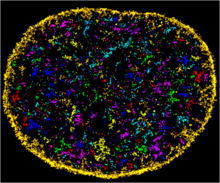
This is an adult flowering Arabidopsis thaliana plant with the inbred designation L-er. Arabidopsis is the most widely used model organism for researchers who study plant genetics. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
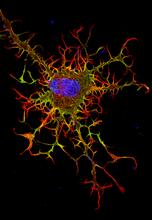
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaCysteine dioxygenase from mouse
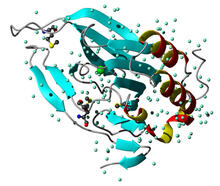
2347
Model of the mammalian iron enzyme cysteine dioxygenase from a mouse. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaHuman fibroblast undergoing cell division
6519
During cell division, cells physically divide after separating their genetic material to create two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nilay Taneja, Vanderbilt University, and Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaFrom DNA to Protein
2509
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together. Crabtree + Company View MediaActive site of sulfite oxidase
2746
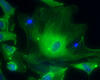
Sulfite oxidase is an enzyme that is essential for normal neurological development in children. John Enemark, University of Arizona View MediaJellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
3636
Jellyfish are especially good models for studying the evolution of embryonic tissue layers. Despite being primitive, jellyfish have a nervous system (stained green here) and musculature (red). Helena Parra, Pompeu Fabra University, Spain View MediaMicroarray 01
1070
Microarrays, also called gene chips, are tools that let scientists track the activity of hundreds or thousands of genes simultaneously. Maggie Werner-Washburne, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaColor-coded chromosomes
2312
By mixing fluorescent dyes like an artist mixes paints, scientists are able to color code individual chromosomes. Anna Jauch, Institute of Human Genetics, Heidelberg, Germany View MediaCulex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego. View MediaNicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase
2355
Model of the enzyme nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase. Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI View MediaCytoskeleton
1272
The three fibers of the cytoskeleton--microtubules in blue, intermediate filaments in red, and actin in green--play countless roles in the cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaSpreading Cells 01
3328
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaBacillus anthracis being killed
3525
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) cells being killed by a fluorescent trans-translation inhibitor, which disrupts bacterial protein synthesis. Kenneth Keiler, Penn State University View MediaGene silencing
2318
Pretty in pink, the enzyme histone deacetylase (HDA6) stands out against a background of blue-tinted DNA in the nucleus of an Arabidopsis plant cell. Olga Pontes and Craig Pikaard, Washington University View MediaBicycling cell
1337
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaZebrafish head vasculature video
6933
Various views of a zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaBottles of warfarin
2579
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH View MediaRat Hippocampus
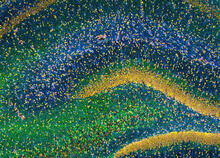
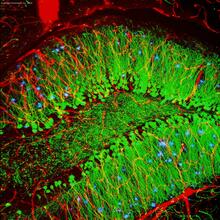
3308
This image of the hippocampus was taken with an ultra-widefield high-speed multiphoton laser microscope. Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaSupernova bacteria
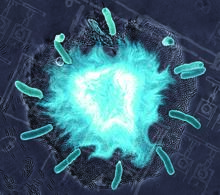
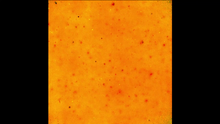
2725
Bacteria engineered to act as genetic clocks flash in synchrony. Here, a "supernova" burst in a colony of coupled genetic clocks just after reaching critical cell density. Jeff Hasty, UCSD View MediaElectrostatic map of human spermine synthase
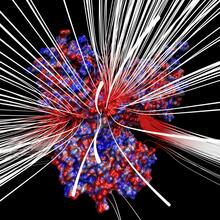
3658
From PDB entry 3c6k, Crystal structure of human spermine synthase in complex with spermidine and 5-methylthioadenosine. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaAbnormal, spiky fibroblast
3613
This is a fibroblast, a connective tissue cell that plays an important role in wound healing. Normal fibroblasts have smooth edges. Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research, Kansas City, Mo. View MediaX-ray diffraction pattern from a crystallized cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
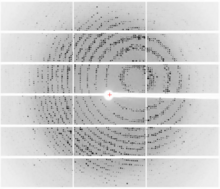
6765
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaCell-like compartments emerging from scrambled frog eggs 3
6589
Cell-like compartments spontaneously emerge from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Video created using epifluorescence microscopy. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaTime-lapse video of floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 24 hours
6550
This time-lapse video shows the emergence of a flower-like pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), that are gr L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaBrain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). Alvin Gogineni, Genentech View MediaMicroscopy image of bird-and-flower DNA origami
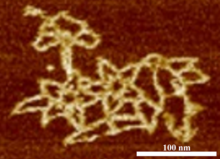
3690
An atomic force microscopy image shows DNA folded into an intricate, computer-designed structure. Hao Yan, Arizona State University View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaTonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaHuman Adenovirus
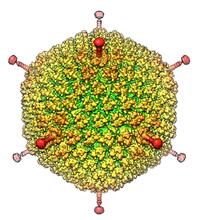
6347
The cryo-EM structure of human adenovirus D26 (HAdV-D26) at near atomic resolution (3.7 Å), determined in collaboration with the NRAMM facility*. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaStructure of Glutamate Dehydrogenase
3421
Some children are born with a mutation in a regulatory site on this enzyme that causes them to over-secrete insulin when they consume protein. Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaNatcher Building 09
1089
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus. Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaAntibodies in silica honeycomb
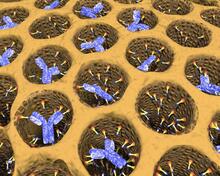
2750
Antibodies are among the most promising therapies for certain forms of cancer, but patients must take them intravenously, exposing healthy tissues to the drug and increasing the risk of side effects. Chenghong Lei, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory & Karl Erik Hellstrom, University of Washington View Media