Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
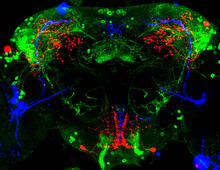
Circadian rhythm neurons in the fruit fly brain
3754
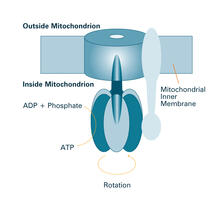
Some nerve cells (neurons) in the brain keep track of the daily cycle. This time-keeping mechanism, called the circadian clock, is found in all animals including us. Justin Blau, New York University View MediaATP synthase (with labels)
2518
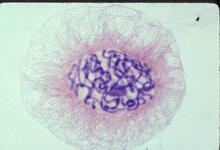
The world's smallest motor, ATP synthase, generates energy for the cell. See image 2517 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 04
1014
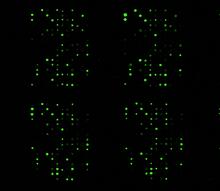
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaGlycan arrays
1265
The signal is obtained by allowing proteins in human serum to interact with glycan (polysaccharide) arrays. The arrays are shown in replicate so the pattern is clear. Ola Blixt, Scripps Research Institute View MediaChromosome inside nucleus (with labels)
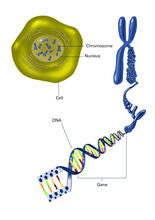
2540
The long, stringy DNA that makes up genes is spooled within chromosomes inside the nucleus of a cell. Crabtree + Company View MediaArabidopsis leaf injected with a pathogen
2780
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf eight days after being infected with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, which is closely related to crop pathogens that Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaPlasma membrane
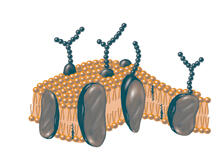
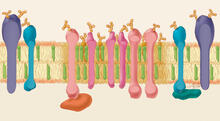
2523
The plasma membrane is a cell's protective barrier. See image 2524 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaEndothelial cell
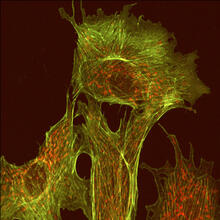
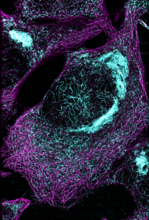
1102
This image shows two components of the cytoskeleton, microtubules (green) and actin filaments (red), in an endothelial cell derived from a cow lung. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaElectrostatic map of human spermine synthase
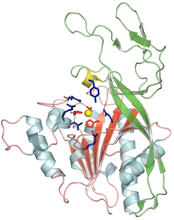
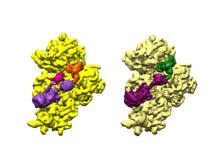
3658
From PDB entry 3c6k, Crystal structure of human spermine synthase in complex with spermidine and 5-methylthioadenosine. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaHydra 05
2441
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaOligoendopeptidase F from B. stearothermophilus
2373
Crystal structure of oligoendopeptidase F, a protein slicing enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus, a bacterium that can cause food products to spoil. Accelerated Technologies Center for Gene to 3D Structure/Midwest Center for Structural Genomics View MediaNMR spectrometer
2371
This photo shows a Varian Unity Inova 900 MHz, 21.1 T standard bore magnet Nuclear Magnetic Resonnance (NMR) spectrometer. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaMapping brain differences
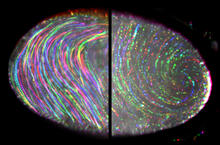
2419
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaHistones in chromatin
2560
Histone proteins loop together with double-stranded DNA to form a structure that resembles beads on a string. Crabtree + Company View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
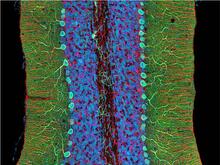
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMorphine Structure
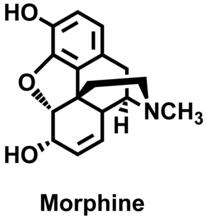
3438
The chemical structure of the morphine molecule Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center View MediaDDR2 Receptors Attach to Collagen in Breast Tumor
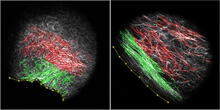
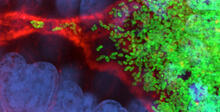
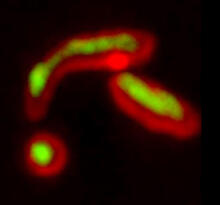
3478
On the left, the boundary of a breast tumor (yellow) attaches to collagen fibers that are closest to it (green) using DDR2. On the right, a tumor without DDR2 remains disconnected from the collagen. Callie Corsa and Suzanne Ponik, Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
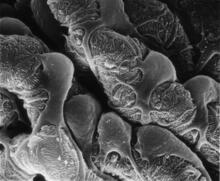
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View MediaHuman aspartoacylase
2352
Model of aspartoacylase, a human enzyme involved in brain metabolism. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaFruit fly brain responds to adipokines
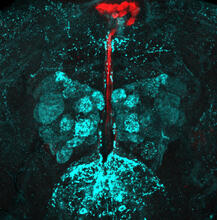
6985
Drosophila adult brain showing that an adipokine (fat hormone) generates a response from neurons (aqua) and regulates insulin-producing neurons (red).Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View Media
Dicer generates microRNAs
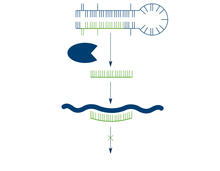
2556
The enzyme Dicer generates microRNAs by chopping larger RNA molecules into tiny Velcro®-like pieces. MicroRNAs stick to mRNA molecules and prevent the mRNAs from being made into proteins. Crabtree + Company View MediaYeast cells pack a punch
3788
Although they are tiny, microbes that are growing in confined spaces can generate a lot of pressure. In this video, yeast cells grow in a small chamber called a microfluidic bioreactor. Oskar Hallatschek, UC Berkeley View MediaRhodopsin bound to visual arrestin
6768
Rhodopsin is a pigment in the rod cells of the retina (back of the eye). It is extremely light-sensitive, supporting vision in low-light conditions. Protein Data Bank. View MediaFlagellated bacterial cells
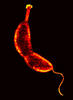
7014
Vibrio fischeri (2 mm in length) is the exclusive symbiotic partner of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaRotavirus structure
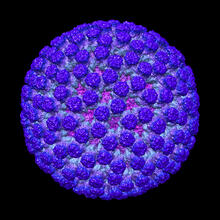
3584
This image shows a computer-generated, three-dimensional map of the rotavirus structure. This virus infects humans and other animals and causes severe diarrhea in infants and young children. Bridget Carragher, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaBacterial cells migrating through the tissues of the squid light organ
7015
Vibrio fischeri cells (~ 2 mm), labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP), passing through a very narrow bottleneck in the tissues (red) of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolope Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology. View MediaFruit fly egg ooplasmic streaming
6809
Two fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) egg cells, one on each side of the central black line. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaBacterial ribosome assembly
6578
3D reconstructions of two stages in the assembly of the bacterial ribosome created from time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy images. Ribosomes translate genetic instructions into proteins. Joachim Frank, Columbia University. View MediaMotion in the brain
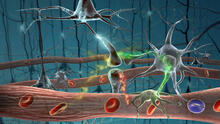
2323
Amid a network of blood vessels and star-shaped support cells, neurons in the brain signal each other. The mists of color show the flow of important molecules like glucose and oxygen. Kim Hager and Neal Prakash, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaDrugs enter skin
2531
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2532 for a labeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaZebrafish embryo
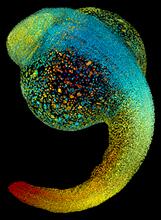
3644
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va. View MediaMotor neuron progenitors derived from human ES cells
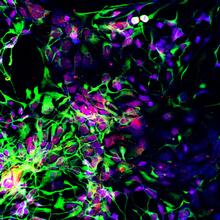
3280
Motor neuron progenitors (green) were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Hans Keirstead lab, University of California, Irvine, via CIRM View MediaBody toxins
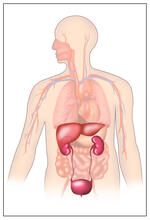
2496
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaHistone deacetylases
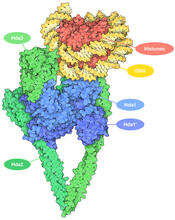
7001
The human genome contains much of the information needed for every cell in the body to function. However, different types of cells often need different types of information. Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaAutomated crystal screening system
2362
Automated crystal screening systems such as the one shown here are becoming a common feature at synchrotron and other facilities where high-throughput crystal structure determination is being carried Southeast Collaboratory for Structural Genomics View MediaRibonuclease P structure
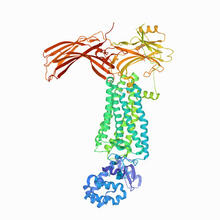
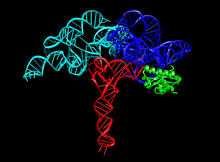
3660
Ribbon diagram showing the structure of Ribonuclease P with tRNA. PDB entry 3Q1Q, molecular modeling by Fred Friedman, NIGMS View MediaBiofilm blocking fluid flow
3446
This time-lapse movie shows that bacterial communities called biofilms can create blockages that prevent fluid flow in devices such as stents and catheters over a period of about 56 hours. Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University View MediaRecombinant DNA (with labels)
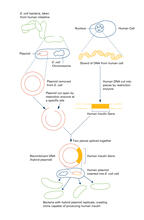
2565
To splice a human gene (in this case, the one for insulin) into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. Crabtree + Company View MediaLipid raft
1285
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. Judith Stoffer View MediaSpreading Cells- 02
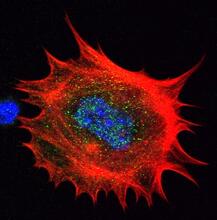
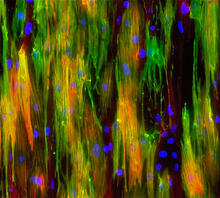
3329
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 02
2795
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaEarly life of a protein
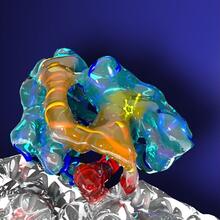
2740
This illustration represents the early life of a protein—specifically, apomyoglobin—as it is synthesized by a ribosome and emerges from the ribosomal tunnel, which contains the newly formed protein's Silvia Cavagnero, University of Wisconsin, Madison View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaMisfolded proteins within in the mitochondria
5878
Misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to video 5877. Rong Li rong@jhu.edu Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21218, USA. View MediaKinesin moves cellular cargo
3491
A protein called kinesin (blue) is in charge of moving cargo around inside cells and helping them divide. Charles Sindelar, Yale University View MediaSea urchin embryo 06
1052
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaMouse heart muscle cells 02
3283
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM View MediaChromosome fiber 01
2475
This microscopic image shows a chromatin fiber--a DNA molecule bound to naturally occurring proteins. Marc Green and Susan Forsburg, University of Southern California View Media