Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Stem cell differentiation
1294
Undifferentiated embryonic stem cells cease to exist a few days after conception. In this image, ES cells are shown to differentiate into sperm, muscle fiber, hair cells, nerve cells, and cone cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
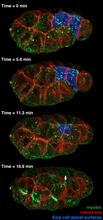
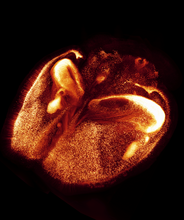
3297
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaA2A adenosine receptor
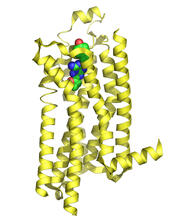
3361
The receptor is shown bound to an inverse agonist, ZM241385. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaC. elegans showing internal structures
6961
An image of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, showing internal structures including the intestine, pharynx, and body wall muscle. C. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated
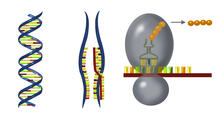
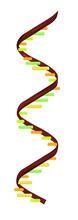
2547
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaNeurons from human ES cells
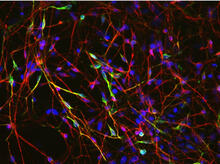
3284
These neural precursor cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies are stained red, and the nuclei are blue. Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM View MediaLab mice
1069
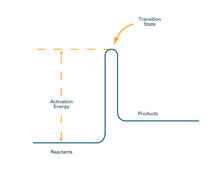
Many researchers use the mouse (Mus musculus) as a model organism to study mammalian biology. Bill Branson, National Institutes of Health View MediaActivation energy
2525
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2526 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaColorful cells
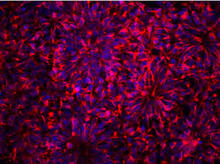
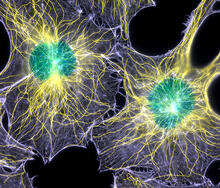
2428
Actin (purple), microtubules (yellow), and nuclei (green) are labeled in these cells by immunofluorescence. This image won first place in the Nikon 2003 Small World photo competition. Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute View MediaDrugs enter skin
2531
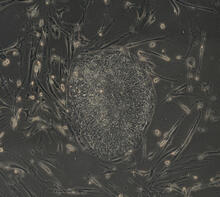
Drugs enter different layers of skin via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or transdermal delivery methods. See image 2532 for a labeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaHydra 04
2440
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaHeLa cells
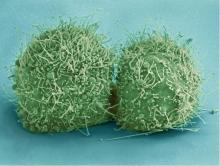
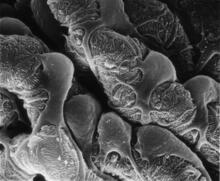
3518
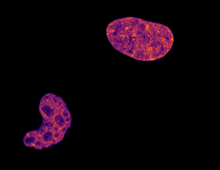
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
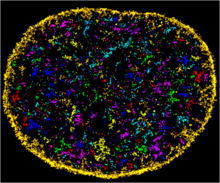
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaBacteriophage P22 capsid
5874
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer co Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine View MediaEndothelial cell
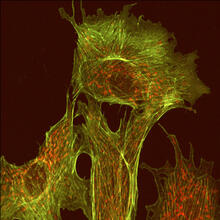
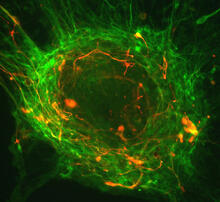
1102
This image shows two components of the cytoskeleton, microtubules (green) and actin filaments (red), in an endothelial cell derived from a cow lung. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
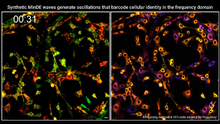
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaHydra 01
2437
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
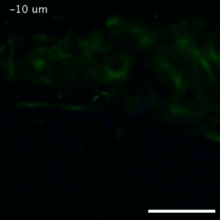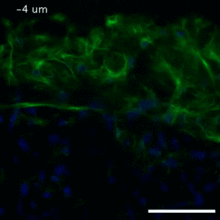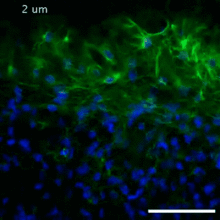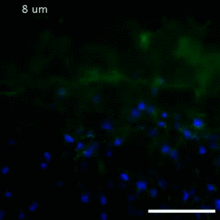
3725
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCell division and cell death
6790
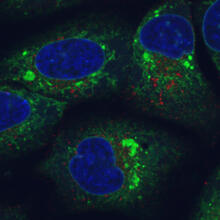
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaEndoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. Michel Becuwe, Harvard University. View MediadUTP pyrophosphatase from M. tuberculosis
2381
Model of an enzyme, dUTP pyrophosphatase, from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drugs targeted to this enzyme might inhibit the replication of the bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI View MediaRNA strand
2554
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) has a sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Crabtree + Company View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaDisrupted and restored vasculature development in frog embryos
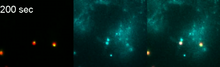
3405
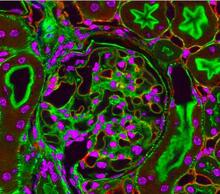
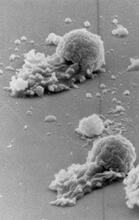
Disassembly of vasculature and reassembly after addition and then washout of 250 µM TBZ in kdr:GFP frogs. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaPodocytes from a chronically diseased kidney
3565
This scanning electron microscope (SEM) image shows podocytes--cells in the kidney that play a vital role in filtering waste from the bloodstream--from a patient with chronic kidney disease. Olga Troyanskaya, Princeton University and Matthias Kretzler, University of Michigan View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaFruit fly ovaries
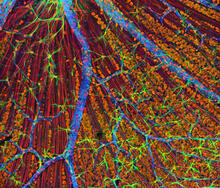
6807
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View Media
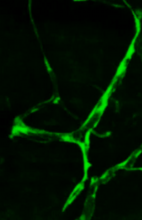
Neural circuits in worms similar to those in humans
3252
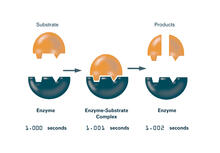
Green and yellow fluorescence mark the processes and cell bodies of some C. elegans neurons. Shawn Xu, University of Michigan View MediaEnzymes convert subtrates into products (with labels)
2522
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2521 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health. Crabtree + Company View MediaMouse Retina
3309
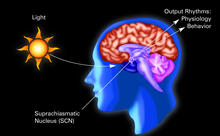
A genetic disorder of the nervous system, neurofibromatosis causes tumors to form on nerves throughout the body, including a type of tumor called an optic nerve glioma that can result in childhood bli Tom Deerinck, NCMIR View MediaCircadian rhythm (with labels)
2569
The human body keeps time with a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. Crabtree + Company View MediaSmooth ER
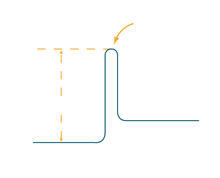
1292
The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two types: Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and prepares newly made proteins; smooth ER specializes in making lipids and breaking down toxic molecules. Judith Stoffer View MediaWorm sperm
3489
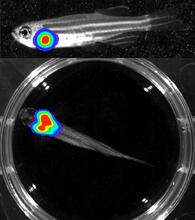
To develop a system for studying cell motility in unnatrual conditions -- a microscope slide instead of the body -- Tom Roberts and Katsuya Shimabukuro at Florida State University disassembled and rec Tom Roberts, Florida State University View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - lateral and overhead view
3556
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. Kenneth Poss, Duke University View MediaIn vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaNeurons from human ES cells 02
3285
These neurons were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies with axonal projections are visible in red, and the nuclei in blue. Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM View MediaMouse brain 2
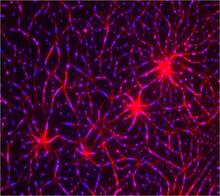
6930
A mouse brain that was genetically modified so that subpopulations of its neurons glow. Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School. View MediaHippocampal neuron from rodent brain
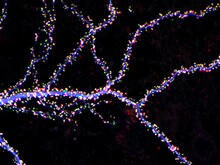
3686
Hippocampal neuron from rodent brain with dendrites shown in blue. The hundreds of tiny magenta, green and white dots are the dendritic spines of excitatory synapses. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaMyosin V binding to actin
2754
This simulation of myosin V binding to actin was created using the software tool Protein Mechanica. Simbios, NIH Center for Biomedical Computation at Stanford View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
6891
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaEM of yeast cell division
5770
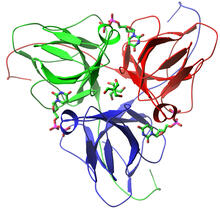
Cell division is an incredibly coordinated process. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaBacterial glucose isomerase
2409
A crystal of bacterial glucose isomerase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaA Growing Bacterial Biofilm
5825
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth. Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ. View MediaHIV enzyme
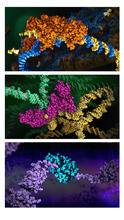
6999
These images model the molecular structures of three enzymes with critical roles in the life cycle of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHuman ES cells differentiating into neurons
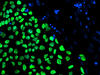
3276
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
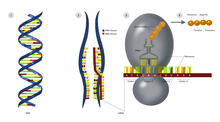
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaCentral dogma, illustrated (with labels and numbers for stages)
2549
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). Crabtree + Company View MediaRepairing DNA
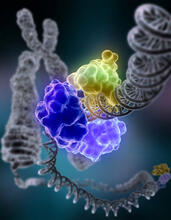
2330
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine View Media