Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
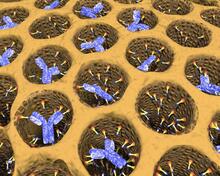
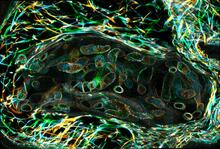
Antibodies in silica honeycomb
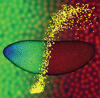
2750
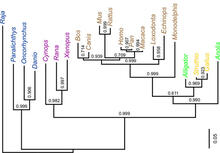
Antibodies are among the most promising therapies for certain forms of cancer, but patients must take them intravenously, exposing healthy tissues to the drug and increasing the risk of side effects. Chenghong Lei, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory & Karl Erik Hellstrom, University of Washington View MediaDinosaur evolutionary tree
2474
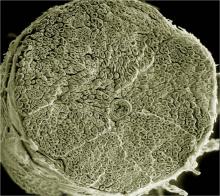
Analysis of 68 million-year-old collagen molecule fragments preserved in a T. Chris Organ, Harvard University View MediaNCMIR human spinal nerve
3387
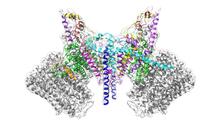
Spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. They run within the spinal column to carry nerve signals to and from all parts of the body. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaATP Synthase
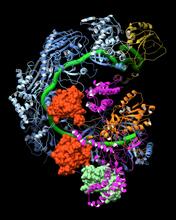
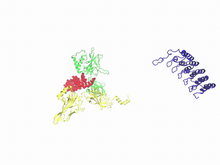
6353
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaLife in balance
1336
Mitosis creates cells, and apoptosis kills them. The processes often work together to keep us healthy. Judith Stoffer View MediaElectrostatic map of human spermine synthase
3658
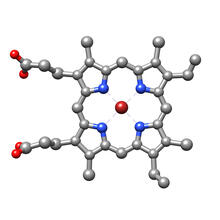
From PDB entry 3c6k, Crystal structure of human spermine synthase in complex with spermidine and 5-methylthioadenosine. Emil Alexov, Clemson University View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 04
2797
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaMyelinated axons 2
3397
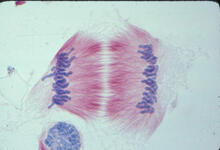
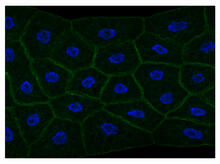
Top view of myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCentromeres on human chromosomes
3255
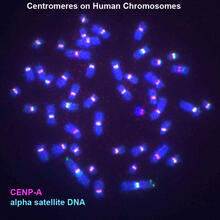
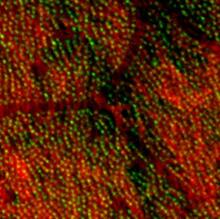
Human metaphase chromosomes are visible with fluorescence in vitro hybridization (FISH). Centromeric alpha satellite DNA (green) are found in the heterochromatin at each centromere. Peter Warburton, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaGenetic patchworks
2588
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University View MediaDynamin Fission
3448
Time lapse series shows short dynamin assemblies (not visible) constricting a lipid tube to make a "beads on a string" appearance, then cutting off one of the beads i.e., catalyzing membrane fission). Ramachandran, Pucadyil et al. , The Scripps Research Institute View MediaSynapses in culture
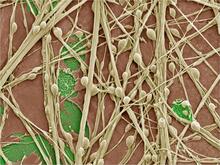
3399
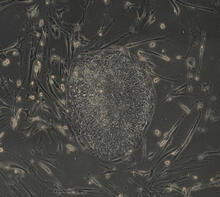
Cultured hippocampal neurons grown on a substrate of glial cells (astrocytes). The glial cells form the pink/brown underlayment in this image. The tan threads are the neurons. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaYeast cells entering mitosis
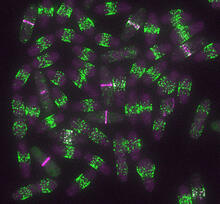
6791
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaTelomeres
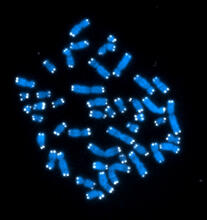
2626
The 46 human chromosomes are shown in blue, with the telomeres appearing as white pinpoints. Hesed Padilla-Nash and Thomas Ried, the National Cancer Institute, a part of NIH View MediaNCMIR mouse tail
3395
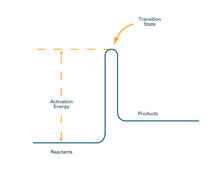
Stained cross section of a mouse tail. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaActivation energy (with labels)
2526
To become products, reactants must overcome an energy hill. See image 2525 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Crabtree + Company View MediaLily mitosis 11
1011
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaDisease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
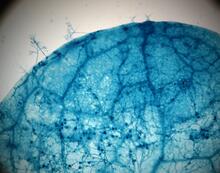
2782
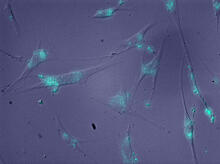
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaA molecular interaction network in yeast 3
3733
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. Keiichiro Ono, UCSD View MediaInduced stem cells from adult skin 03
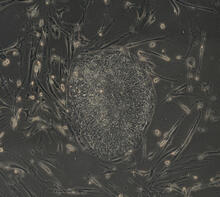
2605
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaX-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 5
3417
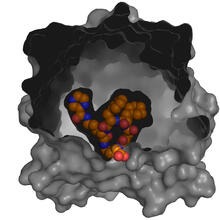
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
3488
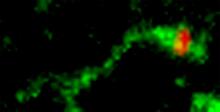
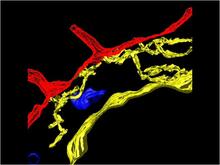
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaCentrioles anchor cilia in planaria
3292
Centrioles (green) anchor cilia (red), which project on the surface of pharynx cells of the freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea. Juliette Azimzadeh, University of California, San Francisco View MediaAlternative splicing
2552
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Crabtree + Company View MediaPetri dish
6752
The white circle in this image is a Petri dish, named for its inventor, Julius Richard Petri. H. Robert Horvitz and Dipon Ghosh, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. View MediaCell cycle (with labels)
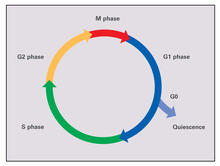
2499
Cells progress through a cycle that consists of phases for growth (G1, S, and G2) and division (M). Cells become quiescent when they exit this cycle (G0). Crabtree + Company View MediaSmooth muscle from mouse stem cells
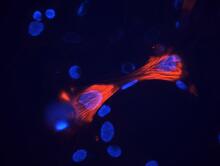
3289
These smooth muscle cells were derived from mouse neural crest stem cells. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, blue indicates nuclei. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institutes, via CIRM View MediaMolecular interactions
2743
This network map shows molecular interactions (yellow) associated with a congenital condition that causes heart arrhythmias and the targets for drugs that alter these interactions (red and blue). Ravi Iyengar, Mount Sinai School of Medicine View MediaCryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
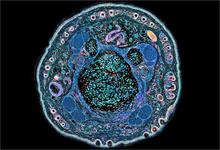
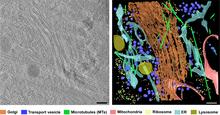
6606
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California. View MediaOptic nerve astrocytes
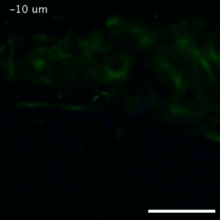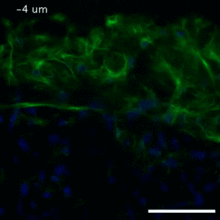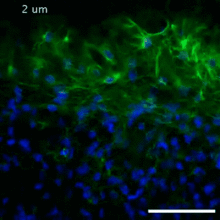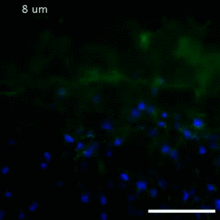
5852
Astrocytes in the cross section of a human optic nerve head Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaBiosensors illustration
2802
A rendering of an activity biosensor image overlaid with a cell-centered frame of reference used for image analysis of signal transduction. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaLily mitosis 08
1021
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaCRISPR surveillance complex
6352
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaStructure of heme, top view
3539
Molecular model of the struture of heme. Heme is a small, flat molecule with an iron ion (dark red) at its center. Rachel Kramer Green, RCSB Protein Data Bank View MediaComputer model of cell membrane
2636
A computer model of the cell membrane, where the plasma membrane is red, endoplasmic reticulum is yellow, and mitochondria are blue. Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico View MediaA molecular switch strips transcription factor from DNA
3729
In this video, Rice University scientists used molecular modeling with a mathematical algorithm called AWSEM (for associative memory, water-mediated, structure and energy model) and structural data to Davit Potoyan and Peter Wolynes View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3334
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaRNA strand
2554
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) has a sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). Crabtree + Company View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaTrypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
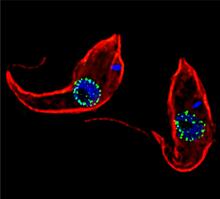
3765
Trypanosoma brucei is a single-cell parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans. Michael Rout, Rockefeller University View MediaSmooth muscle from human ES cells
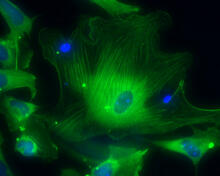
3288
These smooth muscle cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The nuclei are stained blue, and the proteins of the cytoskeleton are stained green. Alexey Terskikh lab, Burnham Institute for Medical Research, via CIRM View MediaLarvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
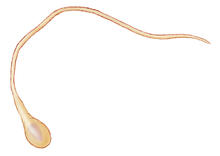
3627
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner View MediaMolecules blocking Huntington's protein production
2600
The molecules that glow blue in these cultured cells prevent the expression of the mutant proteins that cause Huntington's disease. Jiaxin Hu, David W. Dodd and Robert H. E. Hudson, UT Southwestern Medical Center View MediaDraper, shown in the fatbody of a Drosophila melanogaster larva
2757
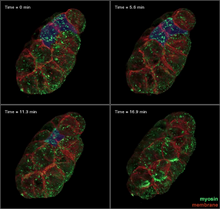
The fly fatbody is a nutrient storage and mobilization organ akin to the mammalian liver. The engulfment receptor Draper (green) is located at the cell surface of fatbody cells. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaMath from the heart
3592
Watch a cell ripple toward a beam of light that turns on a movement-related protein. View Media