Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
Anti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743) with hydrogens 02
2791
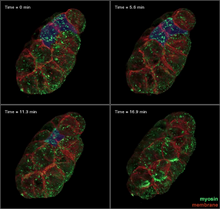
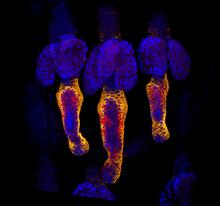
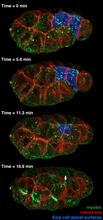
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3334
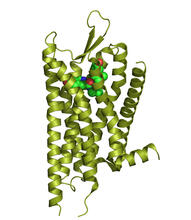
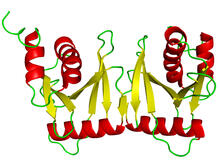
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaKappa opioid receptor
3359
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, JDTic. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaLily mitosis 09
1022
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaHuman opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
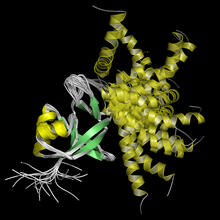
3314
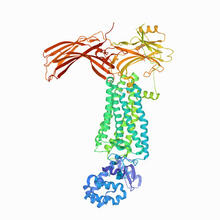
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute View MediaRhodopsin bound to visual arrestin
6768
Rhodopsin is a pigment in the rod cells of the retina (back of the eye). It is extremely light-sensitive, supporting vision in low-light conditions. Protein Data Bank. View MediaJack bean concanavalin A
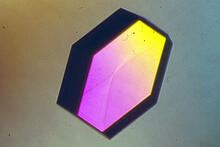
2407
Crystals of jack bean concanavalin A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaGrowing hair follicle stem cells
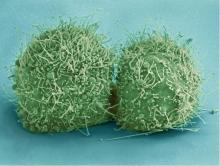
3499
Wound healing requires the action of stem cells. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaAutofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
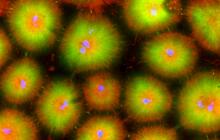
5755
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaCells lining the blood vessel walls
3633
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School. View MediaRibbon diagram of a cefotaxime-CCD-1 complex
6766
CCD-1 is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile that helps it resist antibiotics. Keith Hodgson, Stanford University. View MediaHydra 06
2442
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaLily mitosis 07
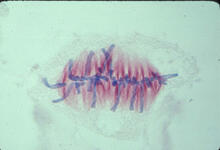
1017
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaA chromosome goes missing in anaphase
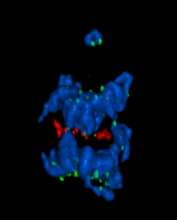
5766
Anaphase is the critical step during mitosis when sister chromosomes are disjoined and directed to opposite spindle poles, ensuring equal distribution of the genome during cell division. View MediaWorm sperm
3489
To develop a system for studying cell motility in unnatrual conditions -- a microscope slide instead of the body -- Tom Roberts and Katsuya Shimabukuro at Florida State University disassembled and rec Tom Roberts, Florida State University View MediaHeLa cells
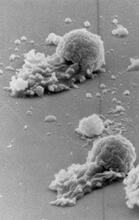
3518
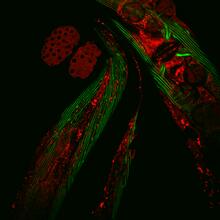
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaCloseup of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
6583
Closeup of C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory. View MediaYeast art depicting the New York City skyline
6521
This skyline of New York City was created by “printing” nanodroplets containing yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) onto a large plate. Each dot is a separate yeast colony. Michael Shen, Ph.D., Jasmine Temple, Leslie Mitchell, Ph.D., and Jef Boeke, Ph.D., New York University School of Medicine; and Nick Phillips, James Chuang, Ph.D., and Jiarui Wang, Johns Hopkins University. View MediaHen egg lysozyme (2)
2406
A crystal of hen egg lysozyme protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
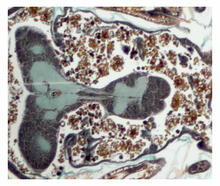
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaVesicular shuttle model
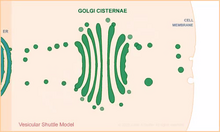
1306
Animation for the vesicular shuttle model of Golgi transport. Judith Stoffer View MediaCircadian rhythm
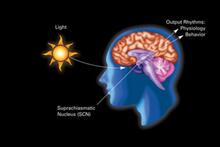
2841
The human body keeps time with a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. Crabtree + Company View MediaDisrupted and restored vasculature development in frog embryos
3405
Disassembly of vasculature and reassembly after addition and then washout of 250 µM TBZ in kdr:GFP frogs. Hye Ji Cha, University of Texas at Austin View MediaCrawling cell
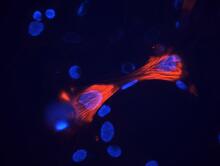
6964
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaMeiosis illustration (with labels)
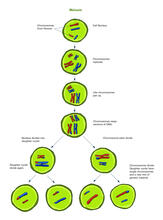
2546
Meiosis is the process whereby a cell reduces its chromosomes from diploid to haploid in creating eggs or sperm. Crabtree + Company View MediaSmooth muscle from mouse stem cells
3289
These smooth muscle cells were derived from mouse neural crest stem cells. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, blue indicates nuclei. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institutes, via CIRM View MediaBone cancer cell
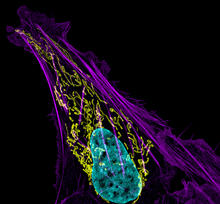
3626
This image shows an osteosarcoma cell with DNA in blue, energy factories (mitochondria) in yellow, and actin filaments—part of the cellular skeleton—in purple. Dylan Burnette and Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, NICHD View MediaNucleus and rough ER
1290
The nucleus contains the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Judith Stoffer View MediaHungry, hungry macrophages
7009
Macrophages (green) are the professional eaters of our immune system. Meghan Morrissey, University of California, Santa Barbara. View MediaStress Response in Cells
6570
Two highly stressed osteosarcoma cells are shown with a set of green droplet-like structures followed by a second set of magenta droplets. Julia F. Riley and Carlos A. Castañeda, Syracuse University View Media¿Qué es la sepsis? (Sepsis Infographic)
6551
La sepsis o septicemia es la respuesta fulminante y extrema del cuerpo a una infección. En los Estados Unidos, más de 1.7 millones de personas contraen sepsis cada año. Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas Generales View MediatRNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans
2351
An NMR solution structure model of the transfer RNA splicing enzyme endonuclease in humans (subunit Sen15). This represents the first structure of a eukaryotic tRNA splicing endonuclease subunit. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, PSI View MediaFour timepoints in gastrulation
3297
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaBlinking bacteria
2724
Like a pulsing blue shower, E. coli cells flash in synchrony. Genes inserted into each cell turn a fluorescent protein on and off at regular intervals. Jeff Hasty, University of California, San Diego View MediaHuman ES cells turn into insulin-producing cells
3277
Human embryonic stem cells were differentiated into cells like those found in the pancreas (blue), which give rise to insulin-producing cells (red). Eugene Brandon, ViaCyte, via CIRM View MediaProtein from Arabidopsis thaliana
2339
NMR solution structure of a plant protein that may function in host defense. This protein was expressed in a convenient and efficient wheat germ cell-free system. Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics View MediaBovine milk alpha-lactalbumin (1)
2397
A crystal of bovine milk alpha-lactalbumin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaFly cells
3594
If a picture is worth a thousand words, what's a movie worth? Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine View MediaAnti-tumor drug ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743), structure without hydrogens 02
2795
Ecteinascidin 743 (ET-743, brand name Yondelis), was discovered and isolated from a sea squirt, Ecteinascidia turbinata, by NIGMS grantee Kenneth Rinehart at the University of Illinois. Timothy Jamison, Massachusetts Institute of Technology View MediaCRISPR Illustration Frame 3
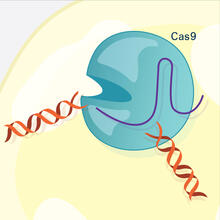
6487
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. National Institute of General Medical Sciences. View MediaRNase A (1)
2398
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures. Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
6591
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaNerve cell
1338
Nerve cells have long, invisibly thin fibers that carry electrical impulses throughout the body. Some of these fibers extend about 3 feet from the spinal cord to the toes. Judith Stoffer View MediaTwo-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
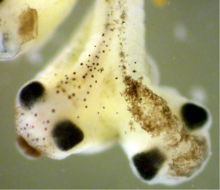
2755
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a research organism for studying embryonic development. Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder View MediaProtein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
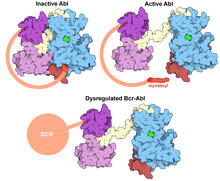
7004
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and co Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank. View MediaHippocampal neuron from rodent brain
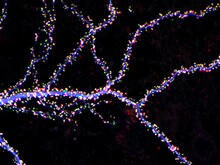
3686
Hippocampal neuron from rodent brain with dendrites shown in blue. The hundreds of tiny magenta, green and white dots are the dendritic spines of excitatory synapses. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 1
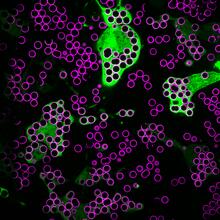
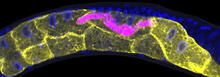
5777
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaVDAC-1 (2)
2491
The structure of the pore-forming protein VDAC-1 from humans. Gerhard Wagner, Harvard Medical School View Media