Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
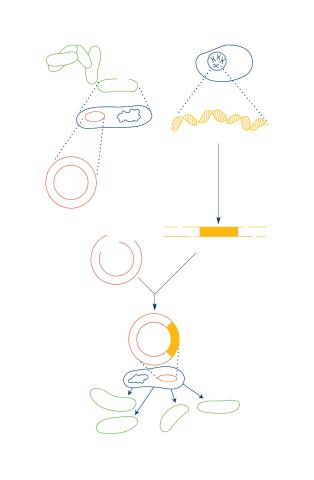
2564: Recombinant DNA
2564: Recombinant DNA
To splice a human gene into a plasmid, scientists take the plasmid out of an E. coli bacterium, cut the plasmid with a restriction enzyme, and splice in human DNA. The resulting hybrid plasmid can be inserted into another E. coli bacterium, where it multiplies along with the bacterium. There, it can produce large quantities of human protein. See image 2565 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media

2443: Mapping human genetic variation
2443: Mapping human genetic variation
This map paints a colorful portrait of human genetic variation around the world. Researchers analyzed the DNA of 485 people and tinted the genetic types in different colors to produce one of the most detailed maps of its kind ever made. The map shows that genetic variation decreases with increasing distance from Africa, which supports the idea that humans originated in Africa, spread to the Middle East, then to Asia and Europe, and finally to the Americas. The data also offers a rich resource that scientists could use to pinpoint the genetic basis of diseases prevalent in diverse populations. Featured in the March 19, 2008, issue of Biomedical Beat.
Noah Rosenberg and Martin Soave, University of Michigan
View Media

2543: DNA replication illustration
2543: DNA replication illustration
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. See image 2544 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
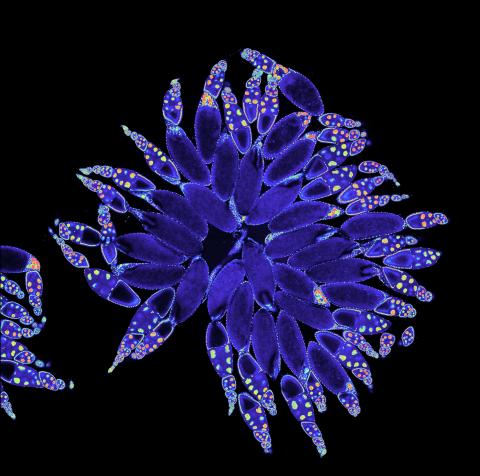
3607: Fruit fly ovary
3607: Fruit fly ovary
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Research on the flies has shed light on many aspects of human biology, including biological rhythms, learning, memory, and neurodegenerative diseases. Another reason fruit flies are so useful in a lab (and so successful in fruit bowls) is that they reproduce rapidly. About three generations can be studied in a single month.
Related to image 3656. This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Related to image 3656. This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara
View Media
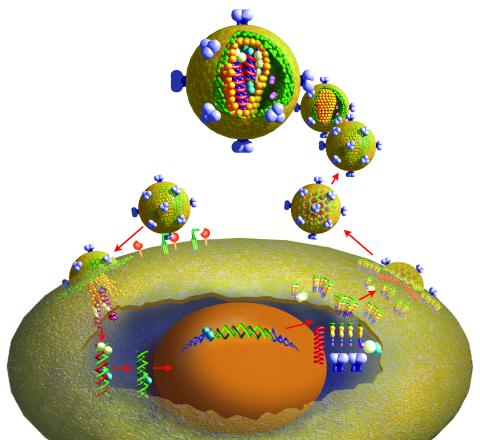
2513: Life of an AIDS virus
2513: Life of an AIDS virus
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Long before anyone had heard of HIV, researchers in labs all over the world studied retroviruses, tracing out their life cycle and identifying the key proteins the viruses use to infect cells. When HIV was identified as a retrovirus, these studies gave AIDS researchers an immediate jump-start. The previously identified viral proteins became initial drug targets. See images 2514 and 2515 for labeled versions of this illustration. Featured in The Structures of Life.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
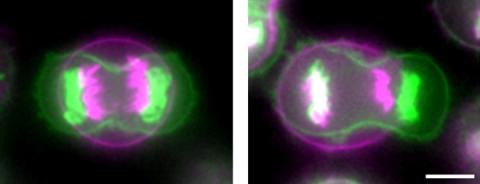
3648: Symmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
3648: Symmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
Merged fluorescent images of symmetrically (left) or asymmetrically (right) elongating HeLa cells at the end of early anaphase (magenta) and late anaphase (green). Chromosomes and cortical actin are visualized by expressing mCherry-histone H2B and Lifeact-mCherry. Scale bar, 10µm. See the PubMed abstract of this research.
Tomomi Kiyomitsu and Iain M. Cheeseman, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
View Media
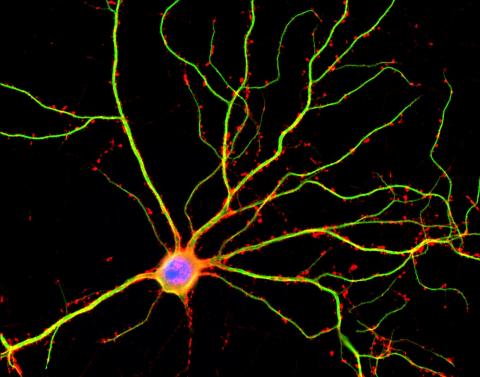
3687: Hippocampal neuron in culture
3687: Hippocampal neuron in culture
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Anesthesia and Brain Cells: A Temporary Disruption?
Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego
View Media
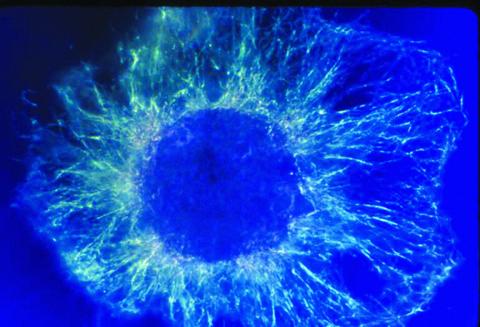
1058: Lily mitosis 01
1058: Lily mitosis 01
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
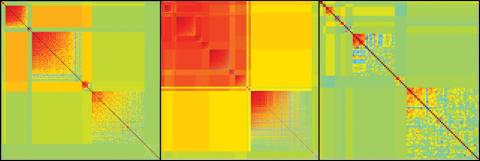
2588: Genetic patchworks
2588: Genetic patchworks
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Vibrant reds and oranges represent high and intermediate degrees of association between the genes, respectively. Genes in these areas show similar activity patterns in different fly lines. Cool blues represent gene pairs where one partner's activity is high and the other's is low. The green areas show pairs with activities that are not correlated. These quilt-like depictions help illustrate a recent finding that genes act in teams to influence sleep patterns.
Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University
View Media
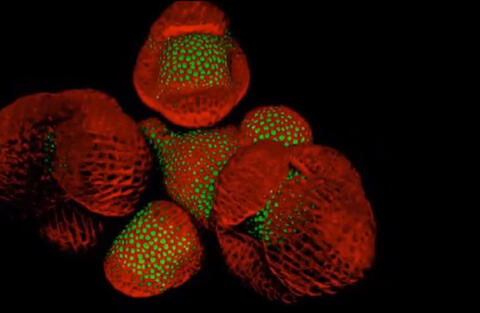
6503: Arabidopsis Thaliana: Flowers Spring to Life
6503: Arabidopsis Thaliana: Flowers Spring to Life
This image capture shows how a single gene, STM, plays a starring role in plant development. This gene acts like a molecular fountain of youth, keeping cells ever-young until it’s time to grow up and commit to making flowers and other plant parts. Because of its ease of use and low cost, Arabidopsis is a favorite model for scientists to learn the basic principles driving tissue growth and regrowth for humans as well as the beautiful plants outside your window. Image captured from video Watch Flowers Spring to Life, featured in the NIH Director's Blog: Watch Flowers Spring to Life.
Nathanaёl Prunet NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
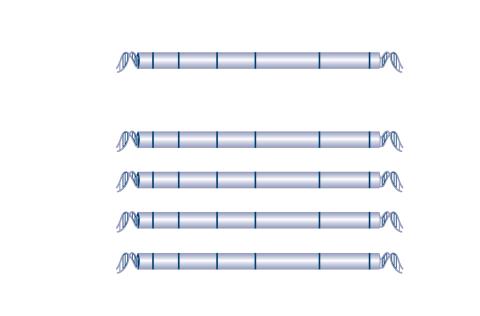
2566: Haplotypes
2566: Haplotypes
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. In this example, an original haplotype (top) evolved over time to create three newer haplotypes that each differ by a few nucleotides (red). See image 2567 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
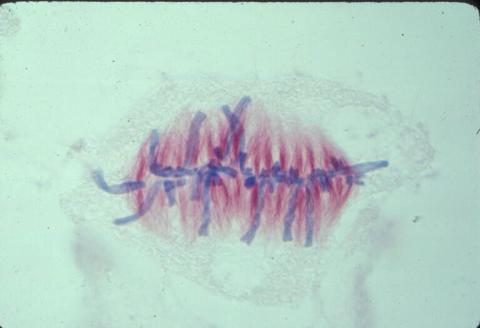
1017: Lily mitosis 07
1017: Lily mitosis 07
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue. Here, condensed chromosomes are clearly visible and have lined up in the middle of the dividing cell.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
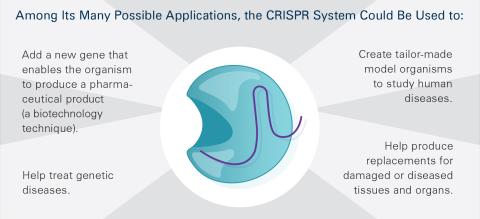
6489: CRISPR Illustration Frame 5
6489: CRISPR Illustration Frame 5
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. This is the fifthframe in a series of five. The CRISPR system has two components joined together: a finely tuned targeting device (a small strand of RNA programmed to look for a specific DNA sequence) and a strong cutting device (an enzyme called Cas9 that can cut through a double strand of DNA). For an explanation and overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 system, see the NIGMS Biomedical Beat blog entry, Field Focus: Precision Gene Editing with CRISPR and the iBiology video, Genome Engineering with CRISPR-Cas9: Birth of a Breakthrough Technology.
View Media
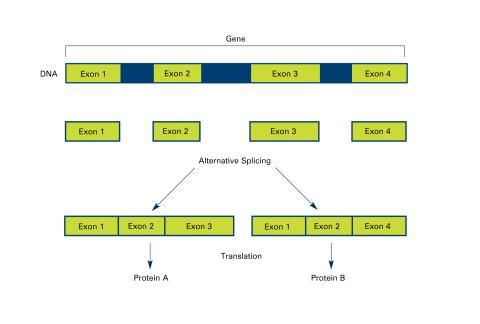
2553: Alternative splicing (with labels)
2553: Alternative splicing (with labels)
Arranging exons in different patterns, called alternative splicing, enables cells to make different proteins from a single gene. Featured in The New Genetics.
See image 2552 for an unlabeled version of this illustration.
See image 2552 for an unlabeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
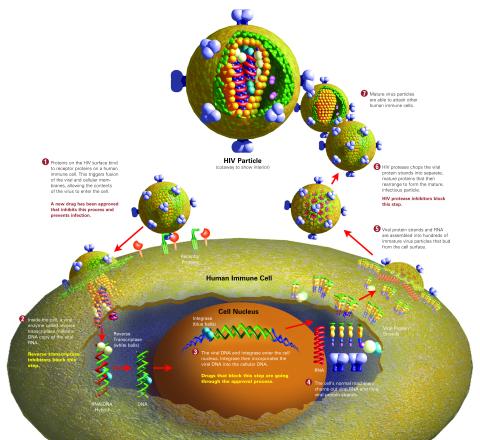
2515: Life of an AIDS virus (with labels and stages)
2515: Life of an AIDS virus (with labels and stages)
HIV is a retrovirus, a type of virus that carries its genetic material not as DNA but as RNA. Long before anyone had heard of HIV, researchers in labs all over the world studied retroviruses, tracing out their life cycle and identifying the key proteins the viruses use to infect cells. When HIV was identified as a retrovirus, these studies gave AIDS researchers an immediate jump-start. The previously identified viral proteins became initial drug targets. See images 2513 and 2514 for other versions of this illustration. Featured in The Structures of Life.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
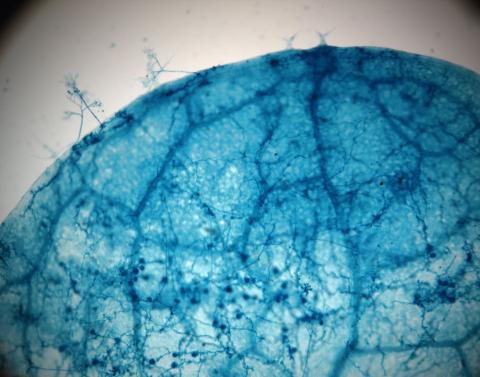
2782: Disease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
2782: Disease-susceptible Arabidopsis leaf
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf after several days of infection with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. The pathogen's blue hyphae grow throughout the leaf. On the leaf's edges, stalk-like structures called sporangiophores are beginning to mature and will release the pathogen's spores. Inside the leaf, the large, deep blue spots are structures called oopsorangia, also full of spores. Compare this response to that shown in Image 2781. Jeff Dangl has been funded by NIGMS to study the interactions between pathogens and hosts that allow or suppress infection.
Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
View Media
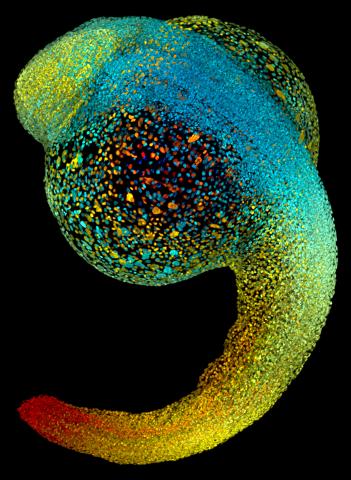
3644: Zebrafish embryo
3644: Zebrafish embryo
Just 22 hours after fertilization, this zebrafish embryo is already taking shape. By 36 hours, all of the major organs will have started to form. The zebrafish's rapid growth and see-through embryo make it ideal for scientists studying how organs develop.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Philipp Keller, Bill Lemon, Yinan Wan, and Kristin Branson, Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Va.
View Media
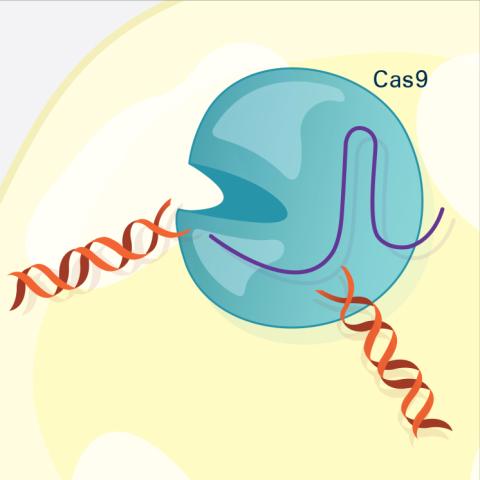
6487: CRISPR Illustration Frame 3
6487: CRISPR Illustration Frame 3
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. The CRISPR system has two components joined together: a finely tuned targeting device (a small strand of RNA programmed to look for a specific DNA sequence) and a strong cutting device (an enzyme called Cas9 that can cut through a double strand of DNA). In this frame (3 of 4), the Cas9 enzyme cuts both strands of the DNA.
For an explanation and overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 system, see the iBiology video, and find the full CRIPSR illustration here.
For an explanation and overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 system, see the iBiology video, and find the full CRIPSR illustration here.
National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
View Media
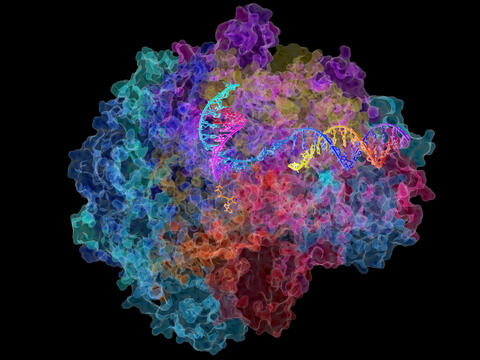
2484: RNA Polymerase II
2484: RNA Polymerase II
NIGMS-funded researchers led by Roger Kornberg solved the structure of RNA polymerase II. This is the enzyme in mammalian cells that catalyzes the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA, the molecule that in turn dictates the order of amino acids in proteins. For his work on the mechanisms of mammalian transcription, Kornberg received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2006.
David Bushnell, Ken Westover and Roger Kornberg, Stanford University
View Media
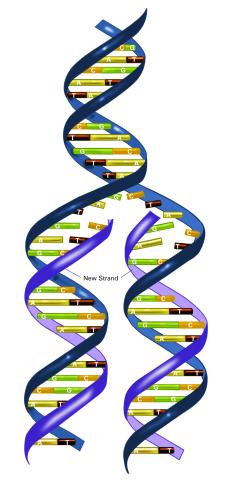
2544: DNA replication illustration (with labels)
2544: DNA replication illustration (with labels)
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. See image 2543 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media

6769: Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
6769: Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito larva
A mosquito larva with genes edited by CRISPR. The red-orange glow is a fluorescent protein used to track the edits. This species of mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus, can transmit West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and avian malaria, among other diseases. The researchers who took this image developed a gene-editing toolkit for Culex quinquefasciatus that could ultimately help stop the mosquitoes from spreading pathogens. The work is described in the Nature Communications paper "Optimized CRISPR tools and site-directed transgenesis towards gene drive development in Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitoes" by Feng et al. Related to image 6770 and video 6771.
Valentino Gantz, University of California, San Diego.
View Media
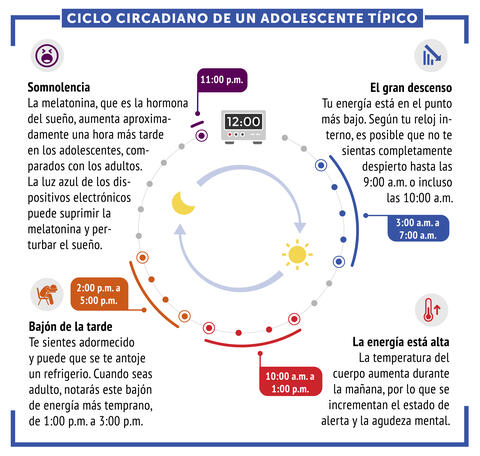
6612: Ciclo circadiano de un adolescente típico
6612: Ciclo circadiano de un adolescente típico
Los ritmos circadianos son cambios físicos, mentales y conductuales que siguen un ciclo de 24 horas. Los ritmos circadianos típicos conducen a un nivel alto de energía durante la mitad del día (de 10 a.m. a 1 p.m.) y un bajón por la tarde. De noche, los ritmos circadianos hacen que la hormona melatonina aumente, lo que hace que la persona se sienta somnolienta.
Vea 6611 para la versión en inglés de esta infografía.
Vea 6611 para la versión en inglés de esta infografía.
NIGMS
View Media
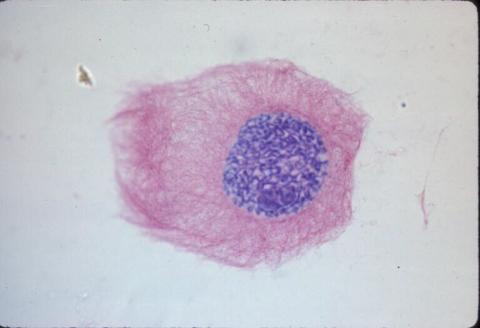
1013: Lily mitosis 03
1013: Lily mitosis 03
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
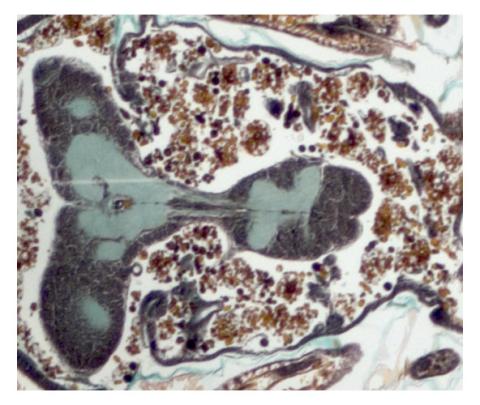
2758: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759.
Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School
View Media
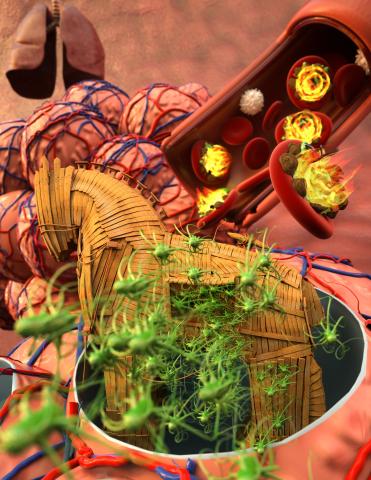
5764: Host infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764: Host infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. Salmonella are vulnerable to antibiotics while circulating in the blood (depicted by fire on red blood cell) but are highly resistant when residing within host macrophages. This leads to treatment failure with the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
This image was chosen as a winner of the 2016 NIH-funded research image call, and the research was funded in part by NIGMS.
View Media
This image was chosen as a winner of the 2016 NIH-funded research image call, and the research was funded in part by NIGMS.
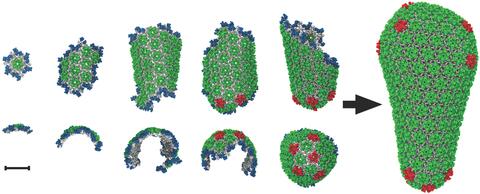
5729: Assembly of the HIV capsid
5729: Assembly of the HIV capsid
The HIV capsid is a pear-shaped structure that is made of proteins the virus needs to mature and become infective. The capsid is inside the virus and delivers the virus' genetic information into a human cell. To better understand how the HIV capsid does this feat, scientists have used computer programs to simulate its assembly. This image shows a series of snapshots of the steps that grow the HIV capsid. A model of a complete capsid is shown on the far right of the image for comparison; the green, blue and red colors indicate different configurations of the capsid protein that make up the capsid “shell.” The bar in the left corner represents a length of 20 nanometers, which is less than a tenth the size of the smallest bacterium. Computer models like this also may be used to reconstruct the assembly of the capsids of other important viruses, such as Ebola or the Zika virus. The studies reporting this research were published in Nature Communications and Nature. To learn more about how researchers used computer simulations to track the assembly of the HIV capsid, see this press release from the University of Chicago.
John Grime and Gregory Voth, The University of Chicago
View Media
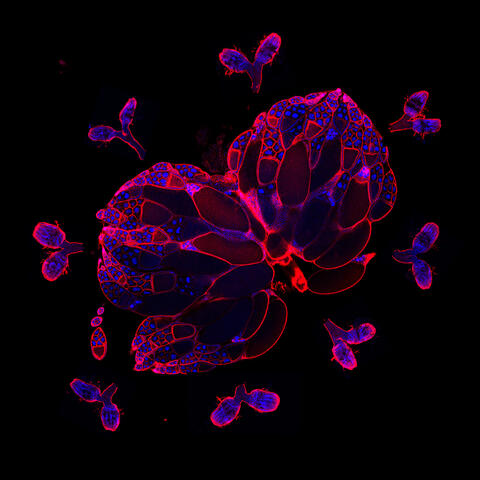
6806: Wild-type and mutant fruit fly ovaries
6806: Wild-type and mutant fruit fly ovaries
The two large, central, round shapes are ovaries from a typical fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). The small butterfly-like structures surrounding them are fruit fly ovaries where researchers suppressed the expression of a gene that controls microtubule polymerization and is necessary for normal development. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.
Related to image 6807.
Related to image 6807.
Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University.
View Media

2579: Bottles of warfarin
2579: Bottles of warfarin
In 2007, the FDA modified warfarin's label to indicate that genetic makeup may affect patient response to the drug. The widely used blood thinner is sold under the brand name Coumadin®. Scientists involved in the NIH Pharmacogenetics Research Network are investigating whether genetic information can be used to improve optimal dosage prediction for patients.
Alisa Machalek, NIGMS/NIH
View Media
2509: From DNA to Protein
2509: From DNA to Protein
Nucleotides in DNA are copied into RNA, where they are read three at a time to encode the amino acids in a protein. Many parts of a protein fold as the amino acids are strung together.
See image 2510 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Featured in The Structures of Life.
See image 2510 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Featured in The Structures of Life.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
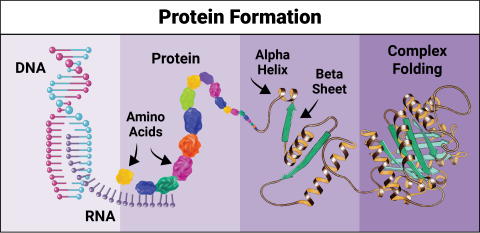
6603: Protein formation
6603: Protein formation
Proteins are 3D structures made up of smaller units. DNA is transcribed to RNA, which in turn is translated into amino acids. Amino acids form a protein strand, which has sections of corkscrew-like coils, called alpha helices, and other sections that fold flat, called beta sheets. The protein then goes through complex folding to produce the 3D structure.
NIGMS, with the folded protein illustration adapted from Jane Richardson, Duke University Medical Center
View Media
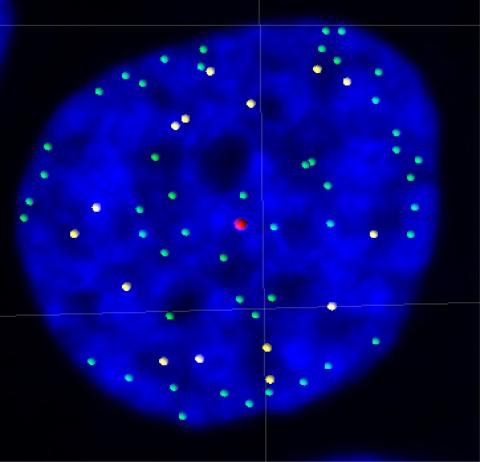
3484: Telomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
3484: Telomeres on outer edge of nucleus during cell division
New research shows telomeres moving to the outer edge of the nucleus after cell division, suggesting these caps that protect chromosomes also may play a role in organizing DNA.
Laure Crabbe, Jamie Kasuboski and James Fitzpatrick, Salk Institute for Biological Studies
View Media
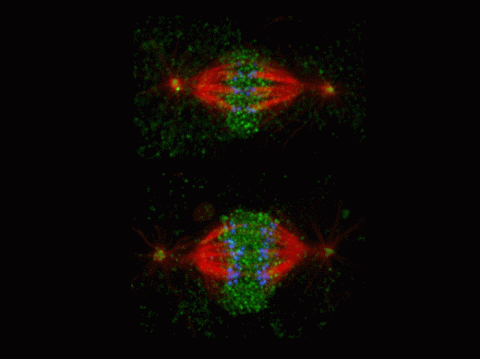
2594: Katanin protein regulates anaphase
2594: Katanin protein regulates anaphase
The microtubule severing protein, katanin, localizes to chromosomes and regulates anaphase A in mitosis. The movement of chromosomes on the mitotic spindle requires the depolymerization of microtubule ends. The figure shows the mitotic localization of the microtubule severing protein katanin (green) relative to spindle microtubules (red) and kinetochores/chromosomes (blue). Katanin targets to chromosomes during both metaphase (top) and anaphase (bottom) and is responsible for inducing the depolymerization of attached microtubule plus-ends. This image was a finalist in the 2008 Drosophila Image Award.
David Sharp, Albert Einstein College of Medicine
View Media
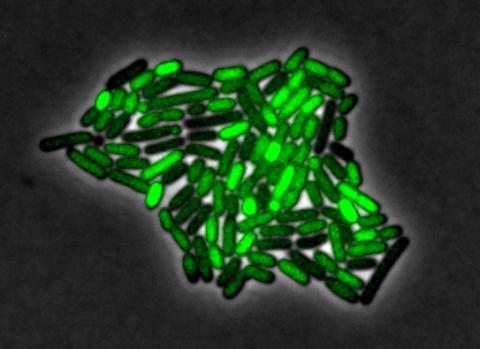
3253: Pulsating response to stress in bacteria
3253: Pulsating response to stress in bacteria
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. In response to a stressful environment like one lacking food, B. subtilis activates a large set of genes that help it respond to the hardship. Instead of leaving those genes on as previously thought, researchers discovered that the bacteria flip the genes on and off, increasing the frequency of these pulses with increasing stress. See entry 3254 for the related video.
Michael Elowitz, Caltech University
View Media
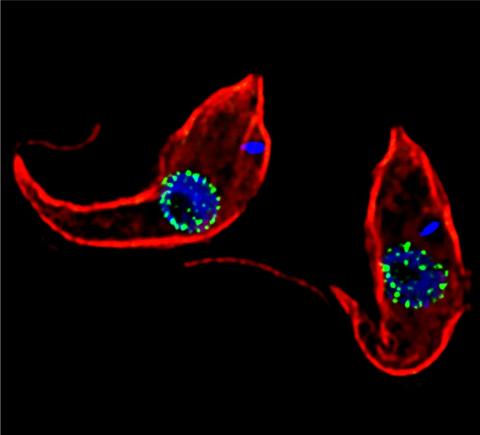
3765: Trypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
3765: Trypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
Trypanosoma brucei is a single-cell parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans. Scientists have been studying trypanosomes for some time because of their negative effects on human and also animal health, especially in sub-Saharan Africa. Moreover, because these organisms evolved on a separate path from those of animals and plants more than a billion years ago, researchers study trypanosomes to find out what traits they may harbor that are common to or different from those of other eukaryotes (i.e., those organisms having a nucleus and mitochondria). This image shows the T. brucei cell membrane in red, the DNA in the nucleus and kinetoplast (a structure unique to protozoans, including trypanosomes, which contains mitochondrial DNA) in blue and nuclear pore complexes (which allow molecules to pass into or out of the nucleus) in green. Scientists have found that the trypanosome nuclear pore complex has a unique mechanism by which it attaches to the nuclear envelope. In addition, the trypanosome nuclear pore complex differs from those of other eukaryotes because its components have a near-complete symmetry, and it lacks almost all of the proteins that in other eukaryotes studied so far are required to assemble the pore.
Michael Rout, Rockefeller University
View Media
2426: Zinc finger
2426: Zinc finger
The structure of a gene-regulating zinc finger protein bound to DNA.
Jeremy M. Berg, National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
2764: Painted chromosomes
2764: Painted chromosomes
Like a paint-by-numbers picture, painted probes tint individual human chromosomes by targeting specific DNA sequences. Chromosome 13 is colored green, chromosome 14 is in red and chromosome 15 is painted yellow. The image shows two examples of fused chromosomes—a pair of chromosomes 15 connected head-to-head (yellow dumbbell-shaped structure) and linked chromosomes 13 and 14 (green and red dumbbell). These fused chromosomes—called dicentric chromosomes—may cause fertility problems or other difficulties in people.
Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University
View Media
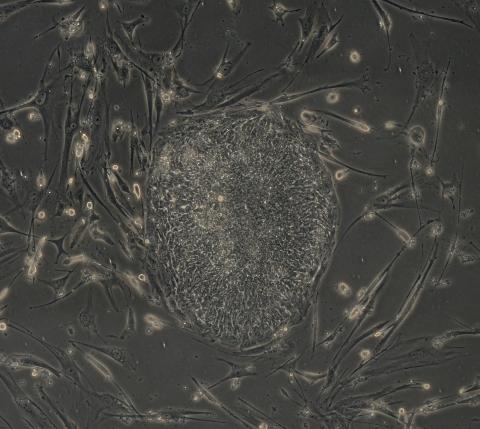
2605: Induced stem cells from adult skin 03
2605: Induced stem cells from adult skin 03
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. A scientific team from the University of Wisconsin-Madison including researchers Junying Yu, James Thomson, and their colleagues produced the transformation by introducing a set of four genes into human fibroblasts, skin cells that are easy to obtain and grow in culture.
James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison
View Media
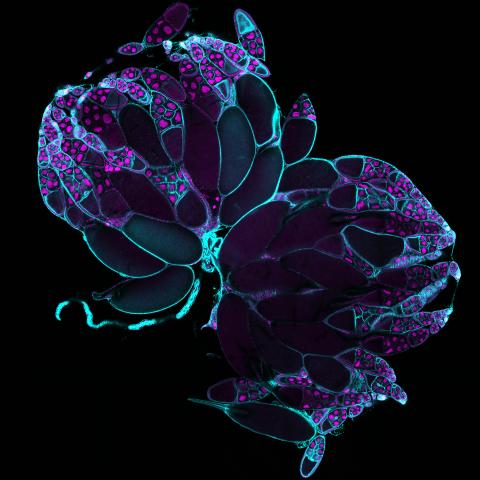
6807: Fruit fly ovaries
6807: Fruit fly ovaries
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.
Related to image 6806.
Related to image 6806.
Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University.
View Media
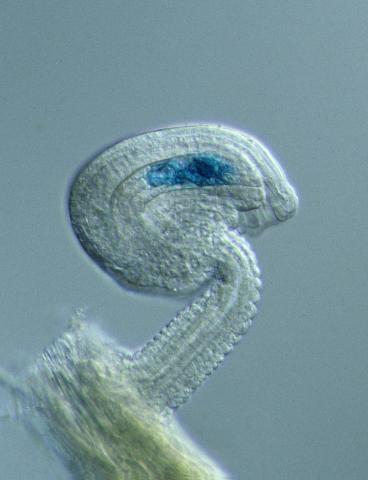
2418: Genetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
2418: Genetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. The cell is expressing only the maternal copy of a gene called MEDEA. This phenomenon, in which the activity of a gene can depend on the parent that contributed it, is called genetic imprinting. In Arabidopsis, the maternal copy of MEDEA makes a protein that keeps the paternal copy silent and reduces the size of the endosperm. In flowering plants and mammals, this sort of genetic imprinting is thought to be a way for the mother to protect herself by limiting the resources she gives to any one embryo. Featured in the May 16, 2006, issue of Biomedical Beat.
Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley
View Media
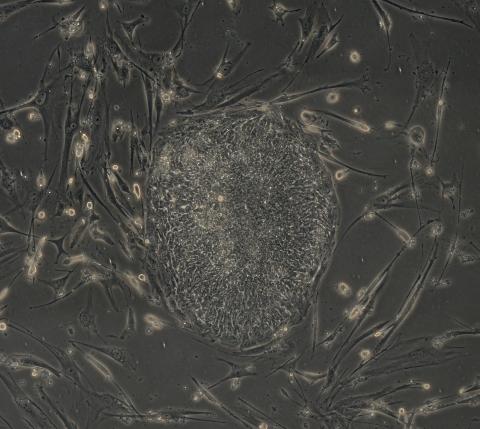
2606: Induced stem cells from adult skin 04
2606: Induced stem cells from adult skin 04
The human skin cells pictured contain genetic modifications that make them pluripotent, essentially equivalent to embryonic stem cells. A scientific team from the University of Wisconsin-Madison including researchers Junying Yu, James Thomson, and their colleagues produced the transformation by introducing a set of four genes into human fibroblasts, skin cells that are easy to obtain and grow in culture.
James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison
View Media
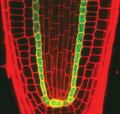
2329: Planting roots
2329: Planting roots
At the root tips of the mustard plant Arabidopsis thaliana (red), two proteins work together to control the uptake of water and nutrients. When the cell division-promoting protein called Short-root moves from the center of the tip outward, it triggers the production of another protein (green) that confines Short-root to the nutrient-filtering endodermis. The mechanism sheds light on how genes and proteins interact in a model organism and also could inform the engineering of plants.
Philip Benfey, Duke University
View Media
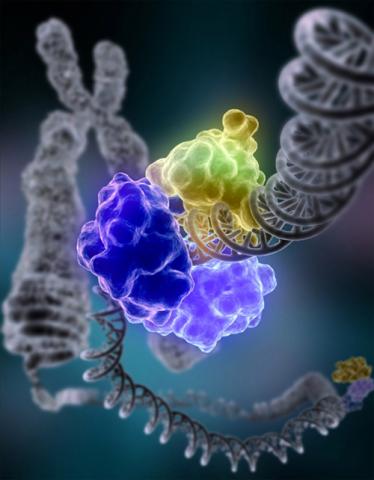
2330: Repairing DNA
2330: Repairing DNA
Like a watch wrapped around a wrist, a special enzyme encircles the double helix to repair a broken strand of DNA. Without molecules that can mend such breaks, cells can malfunction, die, or become cancerous. Related to image 3493.
Tom Ellenberger, Washington University School of Medicine
View Media
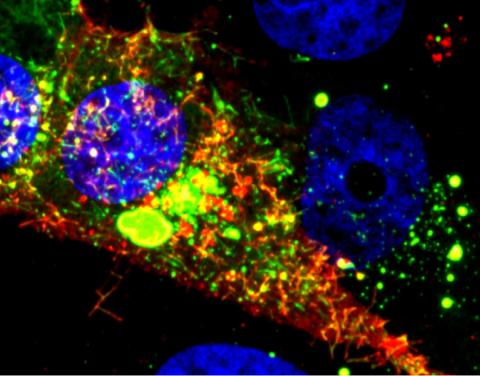
3567: RSV-Infected Cell
3567: RSV-Infected Cell
Viral RNA (red) in an RSV-infected cell. More information about the research behind this image can be found in a Biomedical Beat Blog posting from January 2014.
Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University
View Media
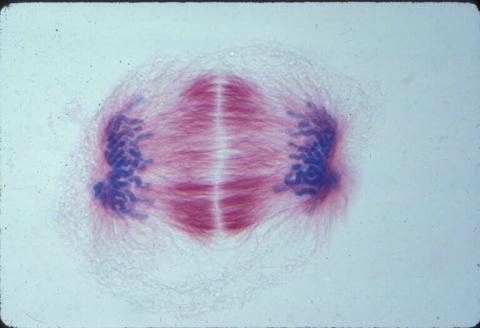
1018: Lily mitosis 12
1018: Lily mitosis 12
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue. Here, condensed chromosomes are clearly visible near the end of a round of mitosis.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1019, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1019, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
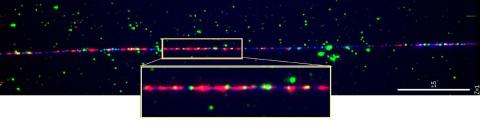
2475: Chromosome fiber 01
2475: Chromosome fiber 01
This microscopic image shows a chromatin fiber--a DNA molecule bound to naturally occurring proteins.
Marc Green and Susan Forsburg, University of Southern California
View Media
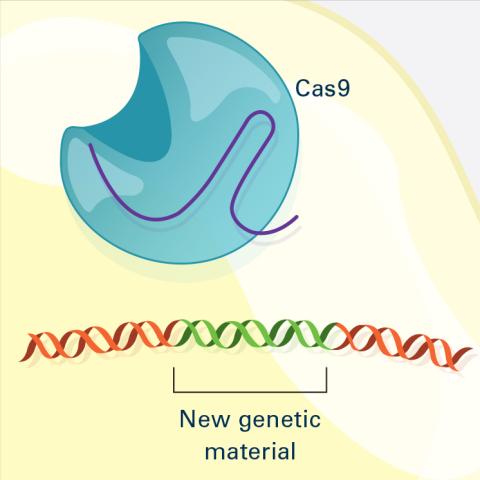
6488: CRISPR Illustration Frame 4
6488: CRISPR Illustration Frame 4
This illustration shows, in simplified terms, how the CRISPR-Cas9 system can be used as a gene-editing tool. The CRISPR system has two components joined together: a finely tuned targeting device (a small strand of RNA programmed to look for a specific DNA sequence) and a strong cutting device (an enzyme called Cas9 that can cut through a double strand of DNA). This frame (4 out of 4) shows a repaired DNA strand with new genetic material that researchers can introduce, which the cell automatically incorporates into the gap when it repairs the broken DNA.
For an explanation and overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 system, see the iBiology video, and find the full CRIPSR illustration here.
For an explanation and overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 system, see the iBiology video, and find the full CRIPSR illustration here.
National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
View Media
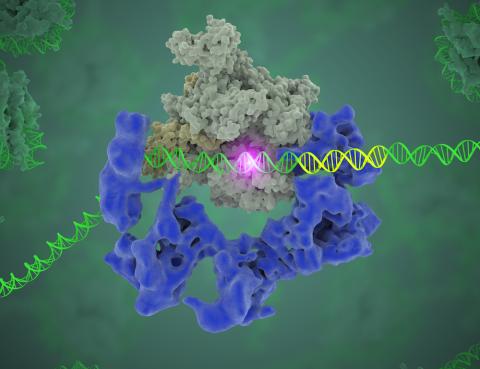
3766: TFIID complex binds DNA to start gene transcription
3766: TFIID complex binds DNA to start gene transcription
Gene transcription is a process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA. It's essential for all life and requires the activity of proteins, called transcription factors, that detect where in a DNA strand transcription should start. In eukaryotes (i.e., those that have a nucleus and mitochondria), a protein complex comprising 14 different proteins is responsible for sniffing out transcription start sites and starting the process. This complex, called TFIID, represents the core machinery to which an enzyme, named RNA polymerase, can bind to and read the DNA and transcribe it to RNA. Scientists have used cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to visualize the TFIID-RNA polymerase-DNA complex in unprecedented detail. In this illustration, TFIID (blue) contacts the DNA and recruits the RNA polymerase (gray) for gene transcription. The start of the transcribed gene is shown with a flash of light. To learn more about the research that has shed new light on gene transcription, see this news release from Berkeley Lab. Related to video 5730.
Eva Nogales, Berkeley Lab
View Media
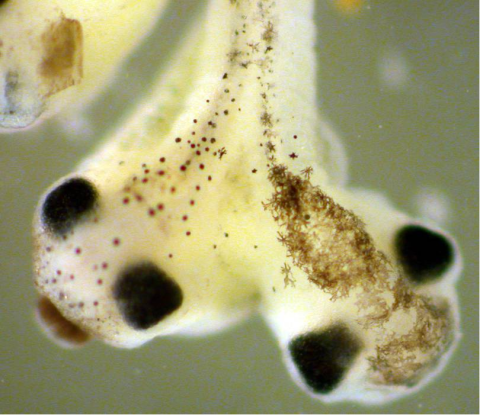
2755: Two-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
2755: Two-headed Xenopus laevis tadpole
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a research organism for studying embryonic development. The abnormal presence of RNA encoding the signaling molecule plakoglobin causes atypical signaling, giving rise to a two-headed tadpole.
Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder
View Media
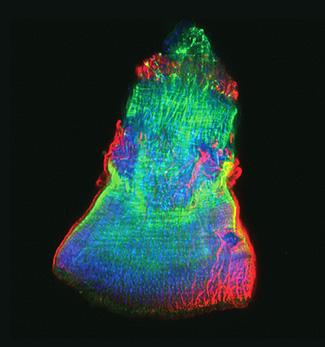
3593: Isolated Planarian Pharynx
3593: Isolated Planarian Pharynx
The feeding tube, or pharynx, of a planarian worm with cilia shown in red and muscle fibers shown in green
View Media

2683: GFP sperm
2683: GFP sperm
Fruit fly sperm cells glow bright green when they express the gene for green fluorescent protein (GFP).
View Media
