Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
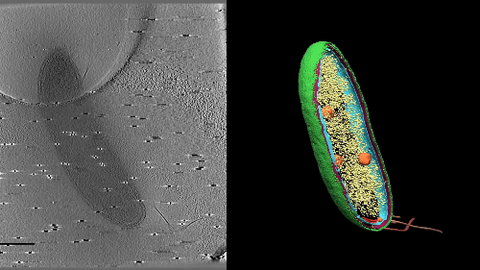
6569: Cryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
6569: Cryo-electron tomography of a Caulobacter bacterium
3D image of Caulobacter bacterium with various components highlighted: cell membranes (red and blue), protein shell (green), protein factories known as ribosomes (yellow), and storage granules (orange).
Peter Dahlberg, Stanford University.
View Media
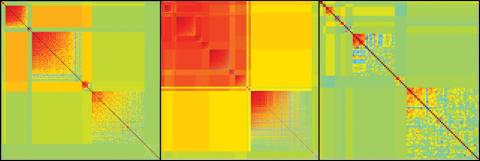
2588: Genetic patchworks
2588: Genetic patchworks
Each point in these colorful patchworks represents the correlation between two sleep-associated genes in fruit flies. Vibrant reds and oranges represent high and intermediate degrees of association between the genes, respectively. Genes in these areas show similar activity patterns in different fly lines. Cool blues represent gene pairs where one partner's activity is high and the other's is low. The green areas show pairs with activities that are not correlated. These quilt-like depictions help illustrate a recent finding that genes act in teams to influence sleep patterns.
Susan Harbison and Trudy Mackay, North Carolina State University
View Media
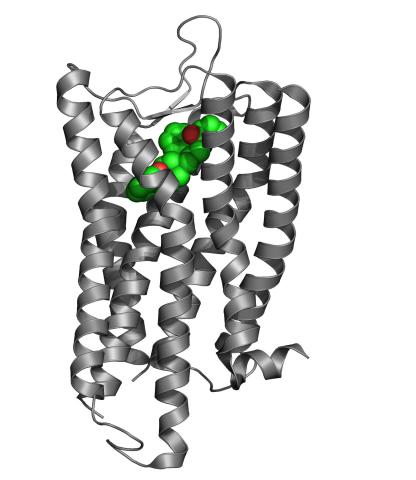
3364: Nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide opioid receptor
3364: Nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide opioid receptor
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, compound-24
Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute
View Media
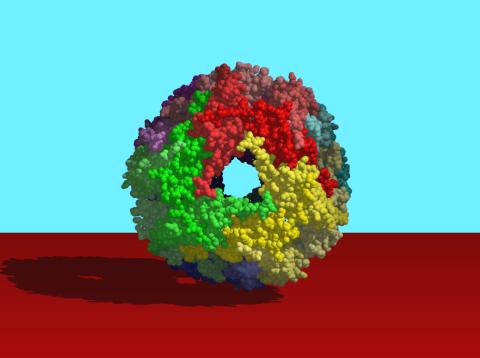
2385: Heat shock protein complex from Methanococcus jannaschii
2385: Heat shock protein complex from Methanococcus jannaschii
Model based on X-ray crystallography of the structure of a small heat shock protein complex from the bacteria, Methanococcus jannaschii. Methanococcus jannaschii is an organism that lives at near boiling temperature, and this protein complex helps it cope with the stress of high temperature. Similar complexes are produced in human cells when they are "stressed" by events such as burns, heart attacks, or strokes. The complexes help cells recover from the stressful event.
Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI-1
View Media
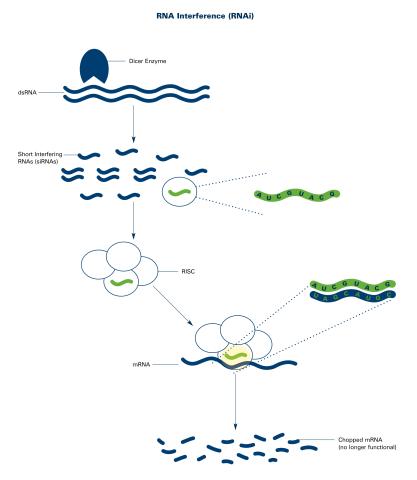
2559: RNA interference (with labels)
2559: RNA interference (with labels)
RNA interference or RNAi is a gene-silencing process in which double-stranded RNAs trigger the destruction of specific RNAs. See 2558 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
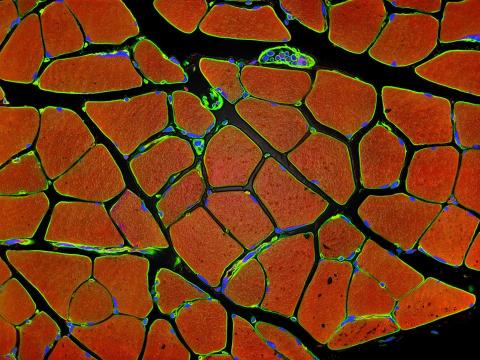
3677: Human skeletal muscle
3677: Human skeletal muscle
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media

3475: Automated Worm Sorter - 4
3475: Automated Worm Sorter - 4
Georgia Tech associate professor Hang Lu holds a microfluidic chip that is part of a system that uses artificial intelligence and cutting-edge image processing to automatically examine large number of nematodes used for genetic research.
Georgia Tech/Gary Meek
View Media
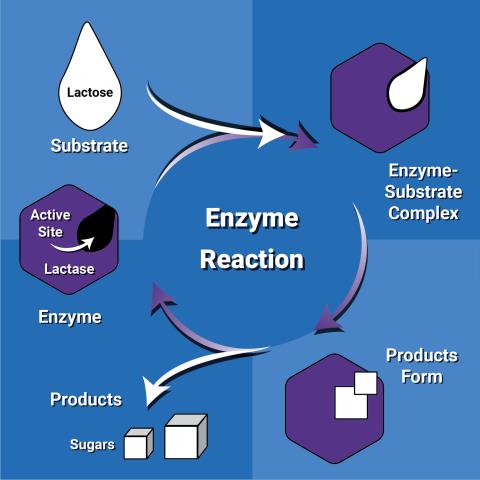
6604: Enzyme reaction
6604: Enzyme reaction
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by reducing the amount of energy needed for the reactions. The substrate (lactose) binds to the active site of the enzyme (lactase) and is converted into products (sugars).
NIGMS
View Media
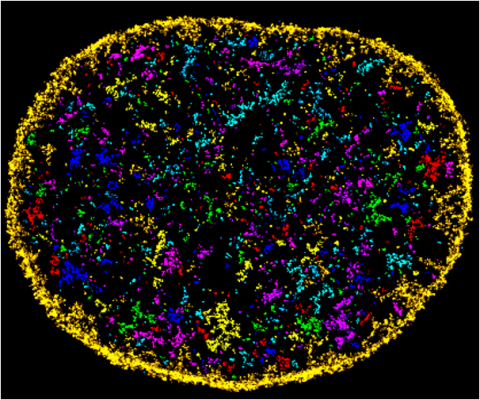
6888: Chromatin in human fibroblast
6888: Chromatin in human fibroblast
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Fibroblasts are one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue, and they play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6887 and 6893.
Related to images 6887 and 6893.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
3597: DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
3597: DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC)
A study published in March 2012 used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of the DNA replication origin recognition complex (ORC), a semi-circular, protein complex (yellow) that recognizes and binds DNA to start the replication process. The ORC appears to wrap around and bend approximately 70 base pairs of double stranded DNA (red and blue). Also shown is the protein Cdc6 (green), which is also involved in the initiation of DNA replication. Related to video 3307 that shows the structure from different angles. From a Brookhaven National Laboratory news release, "Study Reveals How Protein Machinery Binds and Wraps DNA to Start Replication."
Huilin Li, Brookhaven National Laboratory
View Media
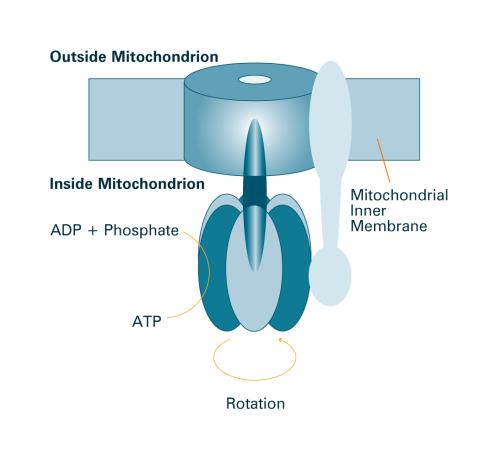
2518: ATP synthase (with labels)
2518: ATP synthase (with labels)
The world's smallest motor, ATP synthase, generates energy for the cell. See image 2517 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
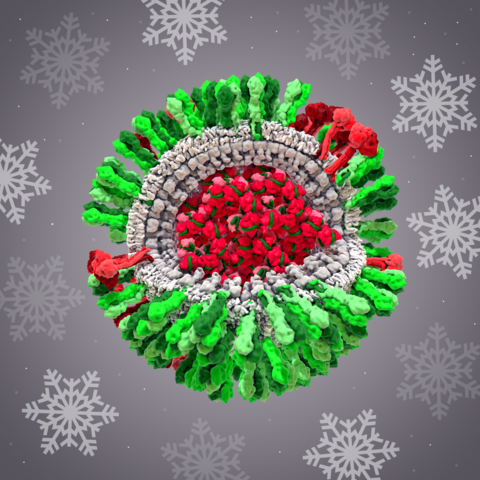

6355: H1N1 Influenza Virus
6355: H1N1 Influenza Virus
CellPack image of the H1N1 influenza virus, with hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins in green and red, respectively, on the outer envelope (white); matrix protein in gray, and ribonucleoprotein particles inside the virus in red and green. Related to image 6356.
Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego
View Media
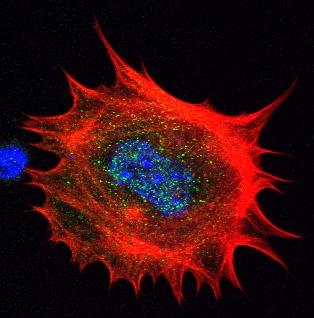
3329: Spreading Cells- 02
3329: Spreading Cells- 02
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Recent research has shown that an actin-polymerizing factor called the Arp2/3 complex is the key component of the actin polymerization engine that drives amoeboid cell motility. ARPC3, a component of the Arp2/3 complex, plays a critical role in actin nucleation. In this photo, the ARPC3-/- fibroblast cells were fixed and stained with Alexa 546 phalloidin for F-actin (red), Arp2 (green), and DAPI to visualize the nucleus (blue). Arp2, a subunit of the Arp2/3 complex, is absent in the filopodi-like structures based leading edge of ARPC3-/- fibroblasts cells. Related to images 3328, 3330, 3331, 3332, and 3333.
Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
View Media
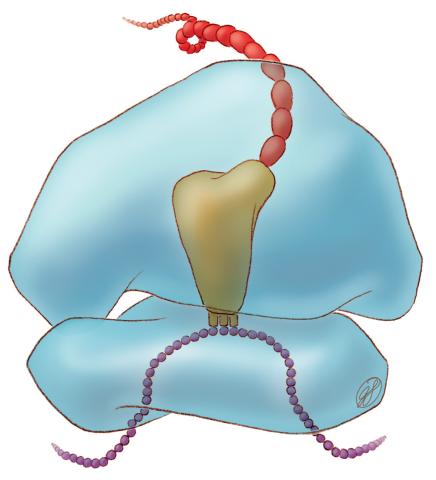
1281: Translation
1281: Translation
Ribosomes manufacture proteins based on mRNA instructions. Each ribosome reads mRNA, recruits tRNA molecules to fetch amino acids, and assembles the amino acids in the proper order.
Judith Stoffer
View Media

7014: Flagellated bacterial cells
7014: Flagellated bacterial cells
Vibrio fischeri (2 mm in length) is the exclusive symbiotic partner of the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes. After this bacterium uses its flagella to swim from the seawater into the light organ of a newly hatched juvenile, it colonizes the host and loses the appendages. This image was taken using a scanning electron microscope.
Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology.
View Media
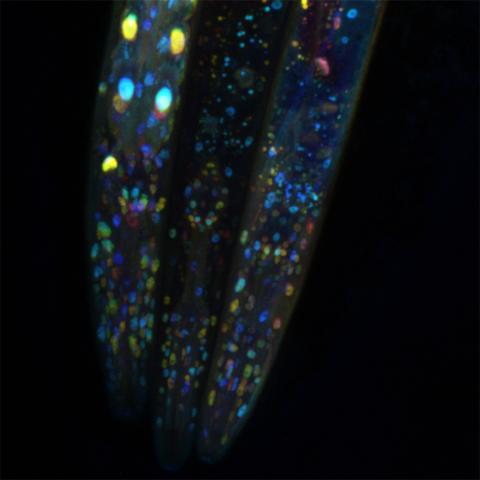
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. The head region of three worms that were genetically modified to express a fluorescent protein were imaged and the images were color-coded based on depth. The worm on the left lacks neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus every cell is fluorescent. In the middle worm, the expression of the fluorescent protein is silenced by neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus most cells are not fluorescent. The worm on the right lacks an enzyme that amplifies RNA for silencing. Surprisingly, the identities of the cells that depend on this enzyme for gene silencing are unpredictable. As a result, worms of identical genotype are nevertheless random mosaics for how the function of gene silencing is carried out. For more, see journal article and press release. Related to image 6534.
Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park
View Media
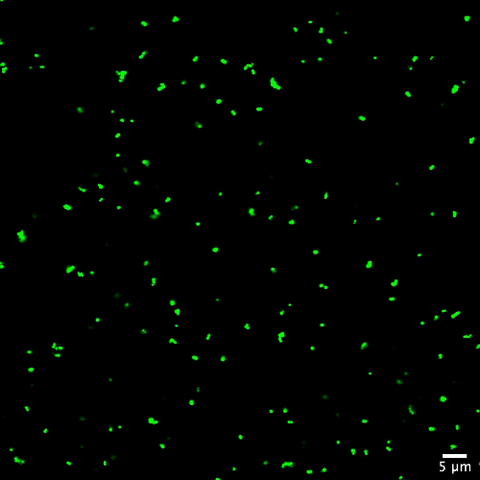
6805: Staphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
6805: Staphylococcus aureus aggregating upon contact with synovial fluid
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (green) grouping together upon contact with synovial fluid—a viscous substance found in joints. The formation of groups can help protect the bacteria from immune system defenses and from antibiotics, increasing the likelihood of an infection. This video is a 1-hour time lapse and was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the Journal of Bacteriology paper "In Vitro Staphylococcal Aggregate Morphology and Protection from Antibiotics Are Dependent on Distinct Mechanisms Arising from Postsurgical Joint Components and Fluid Motion" by Staats et al.
Related to images 6803 and 6804.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the Journal of Bacteriology paper "In Vitro Staphylococcal Aggregate Morphology and Protection from Antibiotics Are Dependent on Distinct Mechanisms Arising from Postsurgical Joint Components and Fluid Motion" by Staats et al.
Related to images 6803 and 6804.
Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University.
View Media
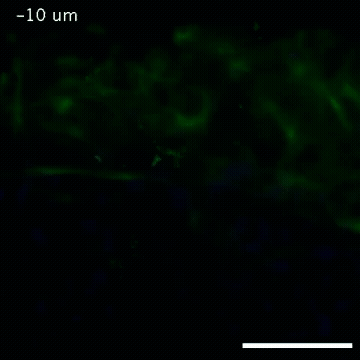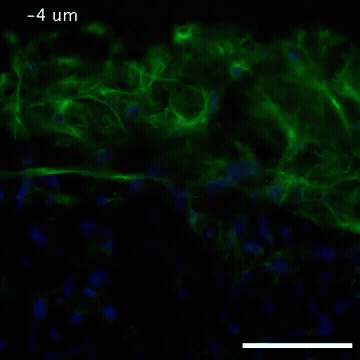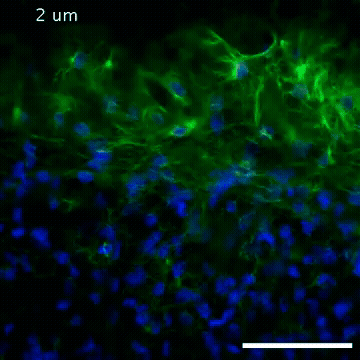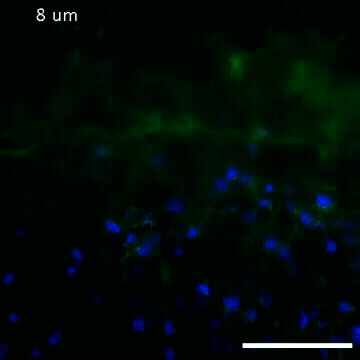
2809: Vimentin in a quail embryo
2809: Vimentin in a quail embryo
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. These images were obtained as part of a study to understand cell migration in embryos. An NIGMS grant to Professor Garcia was used to purchase the confocal microscope that collected these images. Related to images 2807 and 2808.
Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech
View Media

2743: Molecular interactions
2743: Molecular interactions
This network map shows molecular interactions (yellow) associated with a congenital condition that causes heart arrhythmias and the targets for drugs that alter these interactions (red and blue).
Ravi Iyengar, Mount Sinai School of Medicine
View Media
6983: Genetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983: Genetic mosaicism in fruit flies
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. This specific mosaicism results in accumulation of a critical fly adipokine (blue-green) within the fat tissue cells that have reduced expression a key nutrient sensing gene (in left panel). The dotted line shows the cells lacking the gene that is present and functioning in the rest of the cells. Nuclei are labelled in magenta. This image was captured using a confocal microscope and shows a maximum intensity projection of many slices.
Related to images 6982, 6984, and 6985.
Related to images 6982, 6984, and 6985.
Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center
View Media
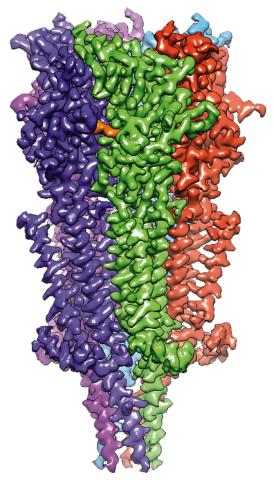
6579: Full-length serotonin receptor (ion channel)
6579: Full-length serotonin receptor (ion channel)
A 3D reconstruction, created using cryo-electron microscopy, of an ion channel known as the full-length serotonin receptor in complex with the antinausea drug granisetron (orange). Ion channels are proteins in cell membranes that help regulate many processes.
Sudha Chakrapani, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
View Media
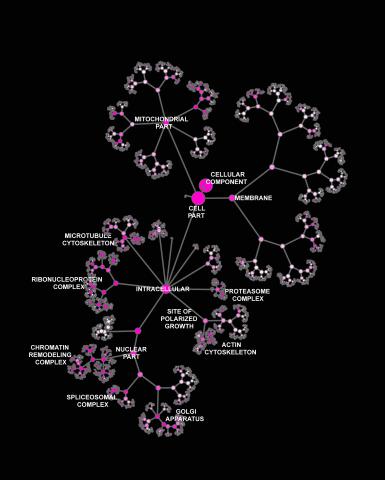
3437: Network diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
3437: Network diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. A gene ontology inferred from molecular networks Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;31(1):38-45. Related to 3436.
Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker, University of California, San Diego
View Media
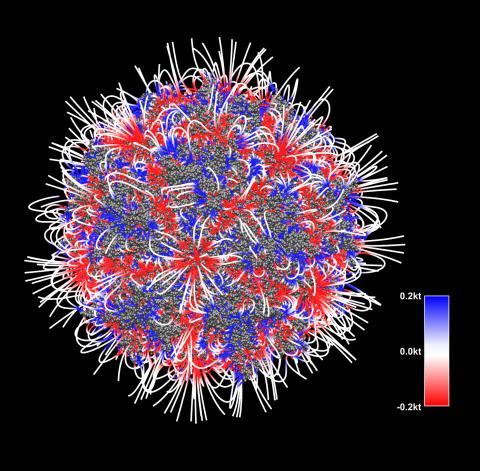
3375: Electrostatic map of the adeno-associated virus with scale
3375: Electrostatic map of the adeno-associated virus with scale
The new highly efficient parallelized DelPhi software was used to calculate the potential map distribution of an entire virus, the adeno-associated virus, which is made up of more than 484,000 atoms. Despite the relatively large dimension of this biological system, resulting in 815x815x815 mesh points, the parallelized DelPhi, utilizing 100 CPUs, completed the calculations within less than three minutes. Related to image 3374.
Emil Alexov, Clemson University
View Media
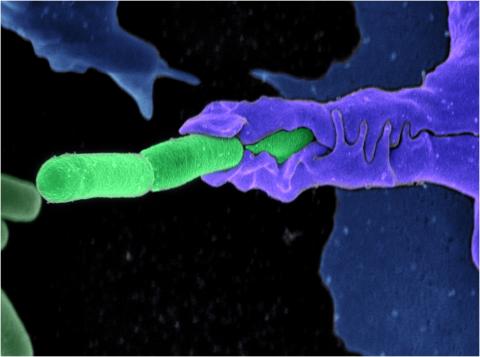
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
Multiple anthrax bacteria (green) being enveloped by an immune system cell (purple). Anthrax bacteria live in soil and form dormant spores that can survive for decades. When animals eat or inhale these spores, the bacteria activate and rapidly increase in number. Today, a highly effective and widely used vaccine has made the disease uncommon in domesticated animals and rare in humans.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Camenzind G. Robinson, Sarah Guilman, and Arthur Friedlander, United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases
View Media

1313: Cell eyes clock
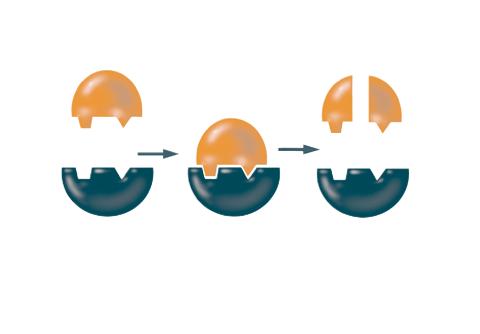
2521: Enzymes convert subtrates into products
2521: Enzymes convert subtrates into products
Enzymes convert substrates into products very quickly. See image 2522 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in The Chemistry of Health.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
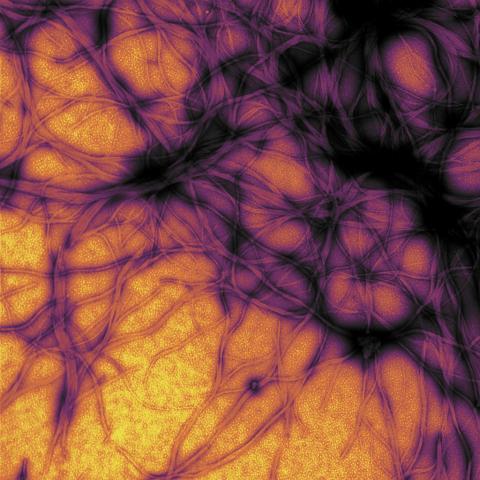
3460: Prion protein fibrils 1
3460: Prion protein fibrils 1
Recombinant proteins such as the prion protein shown here are often used to model how proteins misfold and sometimes polymerize in neurodegenerative disorders. This prion protein was expressed in E. coli, purified and fibrillized at pH 7. Image taken in 2004 for a research project by Roger Moore, Ph.D., at Rocky Mountain Laboratories that was published in 2007 in Biochemistry. This image was not used in the publication.
Ken Pekoc (public affairs officer) and Julie Marquardt, NIAID/ Rocky Mountain Laboratories
View Media

6751: Petri dish containing C. elegans
6751: Petri dish containing C. elegans
This Petri dish contains microscopic roundworms called Caenorhabditis elegans. Researchers used these particular worms to study how C. elegans senses the color of light in its environment.
H. Robert Horvitz and Dipon Ghosh, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
View Media

5872: Mouse retina close-up
5872: Mouse retina close-up
Keunyoung ("Christine") Kim National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
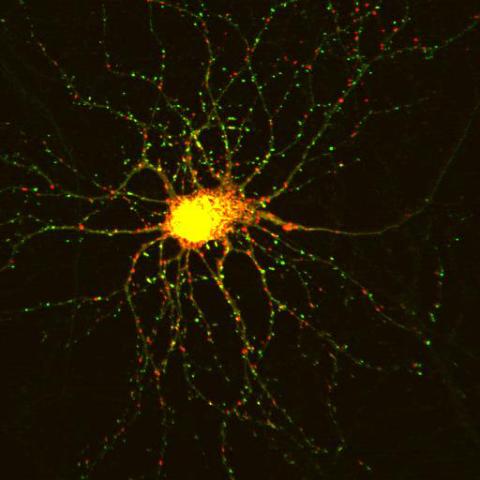
3509: Neuron with labeled synapses
3509: Neuron with labeled synapses
In this image, recombinant probes known as FingRs (Fibronectin Intrabodies Generated by mRNA display) were expressed in a cortical neuron, where they attached fluorescent proteins to either PSD95 (green) or Gephyrin (red). PSD-95 is a marker for synaptic strength at excitatory postsynaptic sites, and Gephyrin plays a similar role at inhibitory postsynaptic sites. Thus, using FingRs it is possible to obtain a map of synaptic connections onto a particular neuron in a living cell in real time.
Don Arnold and Richard Roberts, University of Southern California.
View Media
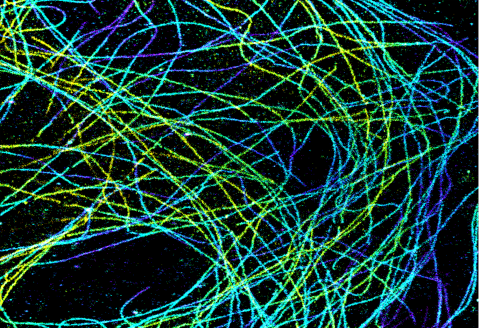
6891: Microtubules in African green monkey cells
6891: Microtubules in African green monkey cells
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Here, the microtubules have been color-coded based on their distance from the microscope lens: purple is closest to the lens, and yellow is farthest away. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6889, 6890, and 6892.
Related to images 6889, 6890, and 6892.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
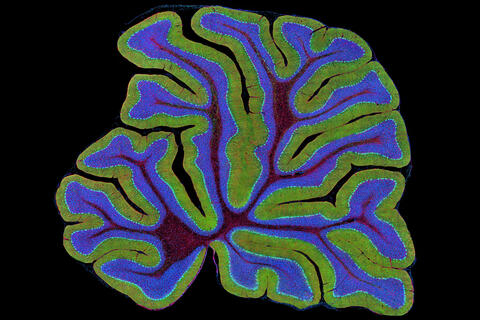
3723: Fluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue
3723: Fluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. It helps maintain normal water levels in our tissues and carries almost half of all calcium ions in human blood. SA also transports some hormones, nutrients and metals throughout the bloodstream. Despite being very similar to our own SA, those from other animals can cause some mild allergies in people. Therefore, some scientists study SAs from humans and other mammals to learn more about what subtle structural or other differences cause immune responses in the body.
Related to entries 3725 and 3675.
Related to entries 3725 and 3675.
Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research
View Media
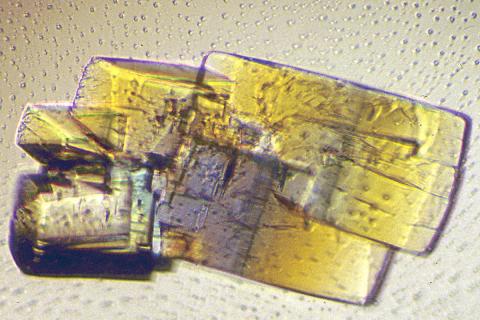
2402: RNase A (2)
2402: RNase A (2)
A crystal of RNase A protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
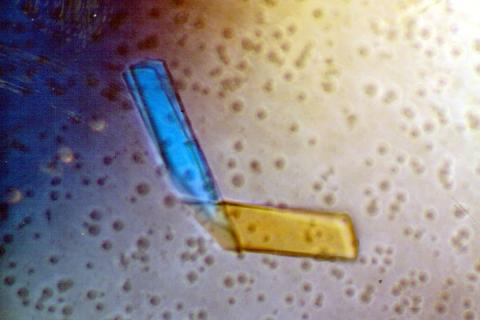
2399: Bence Jones protein MLE
2399: Bence Jones protein MLE
A crystal of Bence Jones protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
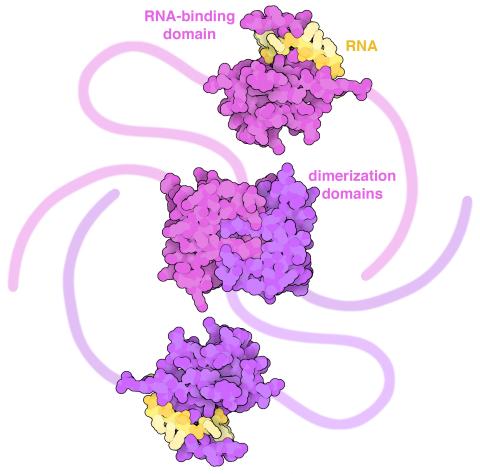
6991: SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
6991: SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid dimer
In SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, nucleocapsid is a complex molecule with many functional parts. One section folds into an RNA-binding domain, with a groove that grips a short segment of the viral genomic RNA. Another section folds into a dimerization domain that brings two nucleocapsid molecules together. The rest of the protein is intrinsically disordered, forming tails at each end of the protein chain and a flexible linker that connects the two structured domains. These disordered regions assist with RNA binding and orchestrate association of nucleocapsid dimers into larger assemblies that package the RNA in the small space inside virions. Nucleocapsid is in magenta and purple, and short RNA strands are in yellow.
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: RNA-binding domain (PDB entry 7ACT) and Dimerization domain (PDB entry 6WJI).
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: RNA-binding domain (PDB entry 7ACT) and Dimerization domain (PDB entry 6WJI).
Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank.
View Media

1336: Life in balance
1336: Life in balance
Mitosis creates cells, and apoptosis kills them. The processes often work together to keep us healthy.
Judith Stoffer
View Media

3266: Biopixels
3266: Biopixels
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. This image shows a small chip with about 500 blinking bacterial colonies or biopixels. Related to images 3265 and 3268. From a UC San Diego news release, "Researchers create living 'neon signs' composed of millions of glowing bacteria."
Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego
View Media
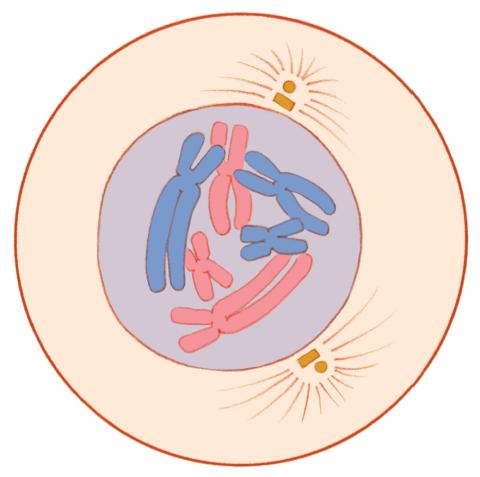
1330: Mitosis - prophase
1330: Mitosis - prophase
A cell in prophase, near the start of mitosis: In the nucleus, chromosomes condense and become visible. In the cytoplasm, the spindle forms. Mitosis is responsible for growth and development, as well as for replacing injured or worn out cells throughout the body. For simplicity, mitosis is illustrated here with only six chromosomes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
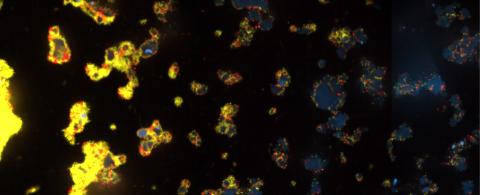
3580: V. Cholerae Biofilm
3580: V. Cholerae Biofilm
Industrious V. cholerae bacteria (yellow) tend to thrive in denser biofilms (left) while moochers (red) thrive in weaker biofilms (right). More information about the research behind this image can be found in a Biomedical Beat Blog posting from February 2014.
View Media
2432: ARTS triggers apoptosis
2432: ARTS triggers apoptosis
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Image is featured in October 2015 Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Images: A Halloween-Inspired Cell Collection.
Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University
View Media
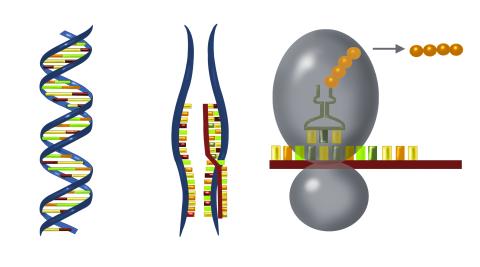
2547: Central dogma, illustrated
2547: Central dogma, illustrated
DNA encodes RNA, which encodes protein. DNA is transcribed to make messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence (dark red strand) is complementary to the DNA sequence (blue strand). On ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA) reads three nucleotides at a time in mRNA to bring together the amino acids that link up to make a protein. See image 2548 for a labeled version of this illustration and 2549 for a labeled and numbered version. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
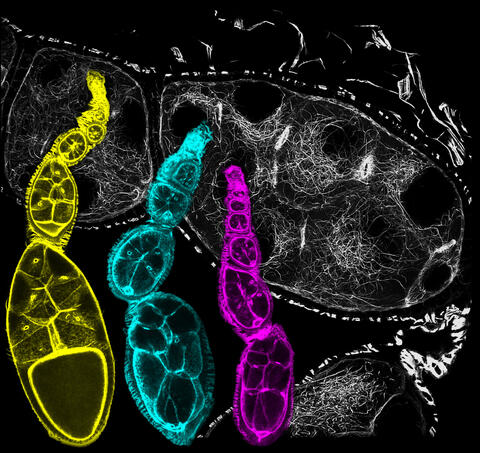
6810: Fruit fly ovarioles
6810: Fruit fly ovarioles
Three fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovarioles (yellow, blue, and magenta) with egg cells visible inside them. Ovarioles are tubes in the reproductive systems of female insects. Egg cells form at one end of an ovariole and complete their development as they reach the other end, as shown in the yellow wild-type ovariole. This process requires an important protein that is missing in the blue and magenta ovarioles. This image was created using confocal microscopy.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Current Biology paper “Gatekeeper function for Short stop at the ring canals of the Drosophila ovary” by Lu et al.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Current Biology paper “Gatekeeper function for Short stop at the ring canals of the Drosophila ovary” by Lu et al.
Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University.
View Media
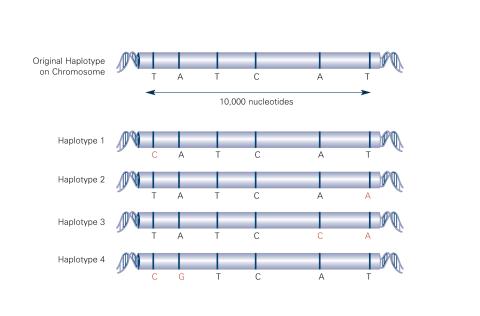
2567: Haplotypes (with labels)
2567: Haplotypes (with labels)
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. In this example, an original haplotype (top) evolved over time to create three newer haplotypes that each differ by a few nucleotides (red). See image 2566 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
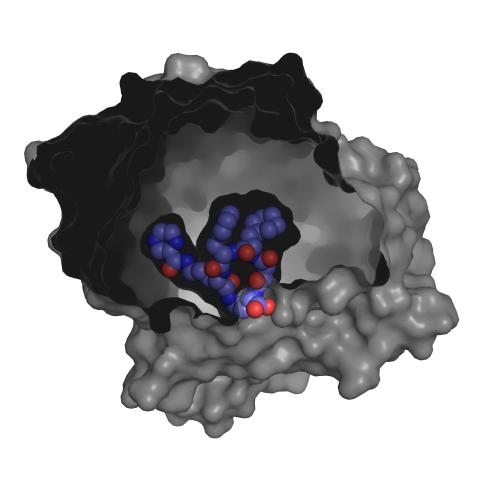
3415: X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 3
3415: X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor 3
X-ray co-crystal structure of Src kinase bound to a DNA-templated macrocycle inhibitor. Related to 3413, 3414, 3416, 3417, 3418, and 3419.
Markus A. Seeliger, Stony Brook University Medical School and David R. Liu, Harvard University
View Media
5752: Genetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
5752: Genetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 2
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Here, scientists set out to find the conditions that help individual bacterial cells survive in the presence of the antibiotic rifampicin. The research team used Mycobacterium smegmatis, a more harmless relative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which infects the lung and other organs to cause serious disease.
In this video, genetically identical mycobacteria are growing in a miniature growth chamber called a microfluidic chamber. Using live imaging, the researchers found that individual mycobacteria will respond differently to the antibiotic, depending on the growth stage and other timing factors. The researchers used genetic tagging with green fluorescent protein to distinguish cells that can resist rifampicin and those that cannot. With this gene tag, cells tolerant of the antibiotic light up in green and those that are susceptible in violet, enabling the team to monitor the cells' responses in real time.
To learn more about how the researchers studied antibiotic resistance in mycobacteria, see this news release from Tufts University. Related to image 5751.
In this video, genetically identical mycobacteria are growing in a miniature growth chamber called a microfluidic chamber. Using live imaging, the researchers found that individual mycobacteria will respond differently to the antibiotic, depending on the growth stage and other timing factors. The researchers used genetic tagging with green fluorescent protein to distinguish cells that can resist rifampicin and those that cannot. With this gene tag, cells tolerant of the antibiotic light up in green and those that are susceptible in violet, enabling the team to monitor the cells' responses in real time.
To learn more about how the researchers studied antibiotic resistance in mycobacteria, see this news release from Tufts University. Related to image 5751.
Bree Aldridge, Tufts University
View Media
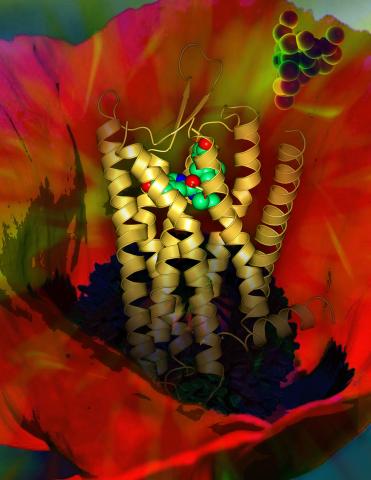
3314: Human opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
3314: Human opioid receptor structure superimposed on poppy
Opioid receptors on the surfaces of brain cells are involved in pleasure, pain, addiction, depression, psychosis, and other conditions. The receptors bind to both innate opioids and drugs ranging from hospital anesthetics to opium. Researchers at The Scripps Research Institute, supported by the NIGMS Protein Structure Initiative, determined the first three-dimensional structure of a human opioid receptor, a kappa-opioid receptor. In this illustration, the submicroscopic receptor structure is shown while bound to an agonist (or activator). The structure is superimposed on a poppy flower, the source of opium.
Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute
View Media
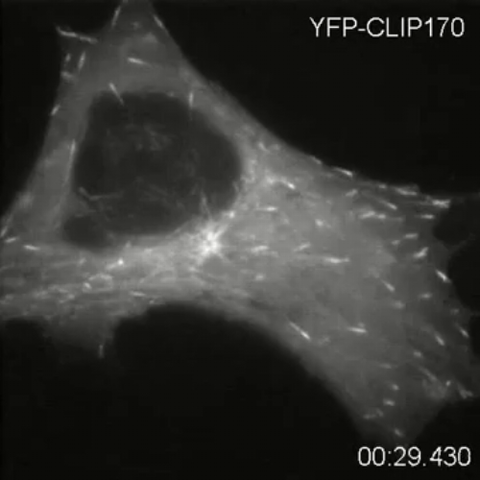
2784: Microtubule dynamics in real time
2784: Microtubule dynamics in real time
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. In this movie, the gene for CLIP-170 has been fused with green fluorescent protein (GFP). When the protein is expressed in cells, the activities can be monitored in real time. Here, you can see CLIP-170 streaming towards the edges of the cell.
Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory
View Media
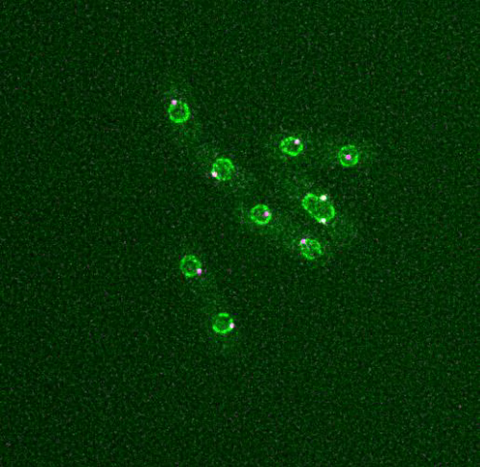
6795: Dividing yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and spindle pole bodies
6795: Dividing yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and spindle pole bodies
Time-lapse video of yeast cells undergoing cell division. Nuclear envelopes are shown in green, and spindle pole bodies, which help pull apart copied genetic information, are shown in magenta. This video was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and video 6796.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and video 6796.
Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University.
View Media

2667: Glowing fish
2667: Glowing fish
Professor Marc Zimmer's family pets, including these fish, glow in the dark in response to blue light. Featured in the September 2009 issue of Findings.
View Media
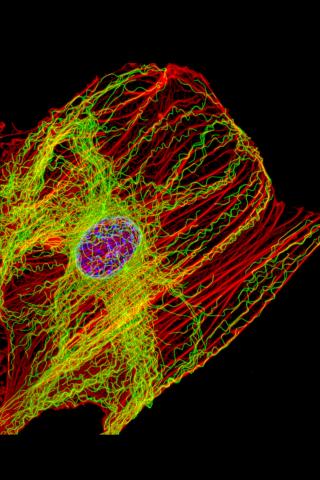
3617: Cells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
3617: Cells keep their shape with actin filaments and microtubules
This image shows a normal fibroblast, a type of cell that is common in connective tissue and frequently studied in research labs. This cell has a healthy skeleton composed of actin (red) and microtubles (green). Actin fibers act like muscles to create tension and microtubules act like bones to withstand compression.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
James J. Faust and David G. Capco, Arizona State University
View Media
