Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
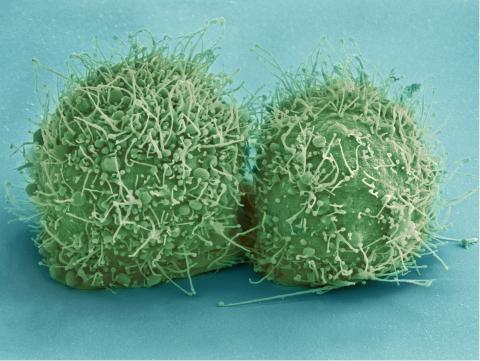
3518: HeLa cells
3518: HeLa cells
Scanning electron micrograph of just-divided HeLa cells. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM. See related images 3519, 3520, 3521, 3522.
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research
View Media
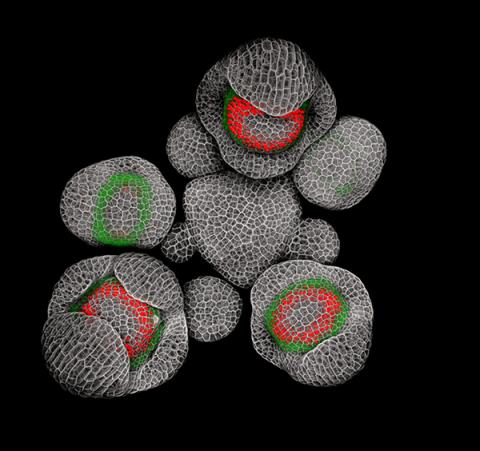
3743: Developing Arabidopsis flower buds
3743: Developing Arabidopsis flower buds
Flower development is a carefully orchestrated, genetically programmed process that ensures that the male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs form in the right place and at the right time in the flower. In this image of young Arabidopsis flower buds, the gene SUPERMAN (red) is activated at the boundary between the cells destined to form the male and female parts. SUPERMAN activity prevents the central cells, which will ultimately become the female pistil, from activating the gene APETALA3 (green), which induces formation of male flower organs. The goal of this research is to find out how plants maintain cells (called stem cells) that have the potential to develop into any type of cell and how genetic and environmental factors cause stem cells to develop and specialize into different cell types. This work informs future studies in agriculture, medicine and other fields.
Nathanaël Prunet, Caltech
View Media
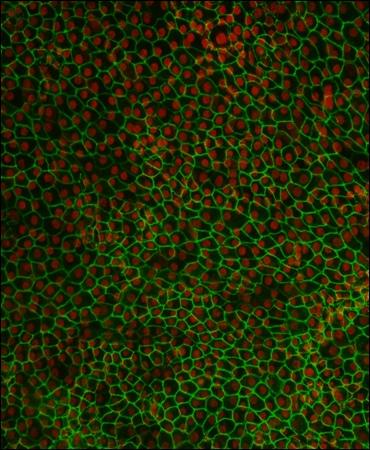
3287: Retinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells 02
3287: Retinal pigment epithelium derived from human ES cells 02
This image shows a layer of retinal pigment epithelium cells derived from human embryonic stem cells, highlighting the nuclei (red) and cell surfaces (green). This kind of retinal cell is responsible for macular degeneration, the most common cause of blindness. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Related to image 3286
David Buckholz and Sherry Hikita, University of California, Santa Barbara, via CIRM
View Media

1311: Housekeeping cell illustration
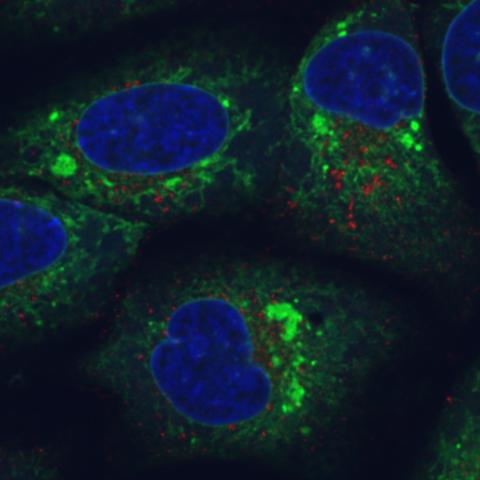
6773: Endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
6773: Endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. Green indicates an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein. The lack of FIT2 affected the structure of the ER and caused the resident protein to cluster in ER membrane aggregates, seen as large, bright-green spots. Red shows where the degradation of cell parts—called autophagy—is taking place, and the nucleus is visible in blue. This image was captured using a confocal microscope.
Michel Becuwe, Harvard University.
View Media
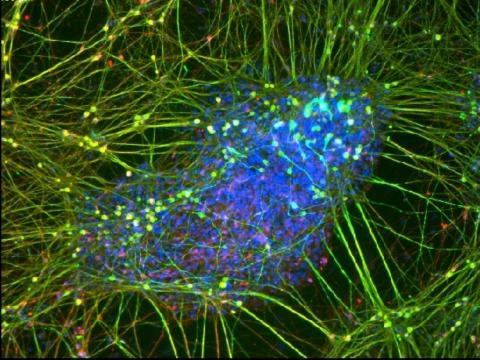
3264: Peripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
3264: Peripheral nerve cell derived from ES cells
A peripheral nerve cell made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. The nucleus is shown in blue, and nerve cell proteins peripherin and beta-tubulin (Tuj1) are shown in green and red, respectively. Related to image 3263.
Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia
View Media

2708: Leading cells with light
2708: Leading cells with light
A blue laser beam turns on a protein that helps this human cancer cell move. Responding to the stimulus, the protein, called Rac1, first creates ruffles at the edge of the cell. Then it stretches the cell forward, following the light like a horse trotting after a carrot on a stick. This new light-based approach can turn Rac1 (and potentially many other proteins) on and off at exact times and places in living cells. By manipulating a protein that controls movement, the technique also offers a new tool to study embryonic development, nerve regeneration and cancer.
Yi Wu, University of North Carolina
View Media
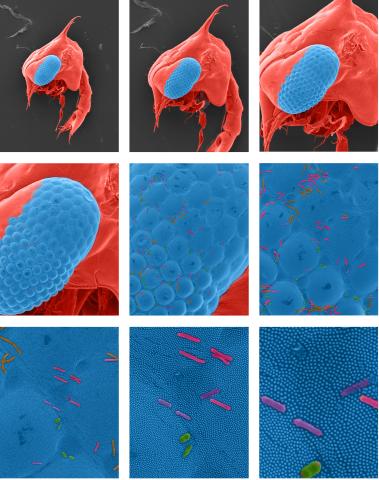
1251: Crab larva eye
1251: Crab larva eye
Colorized scanning electron micrographs progressively zoom in on the eye of a crab larva. In the higher-resolution frames, bacteria are visible on the eye.
Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa
View Media
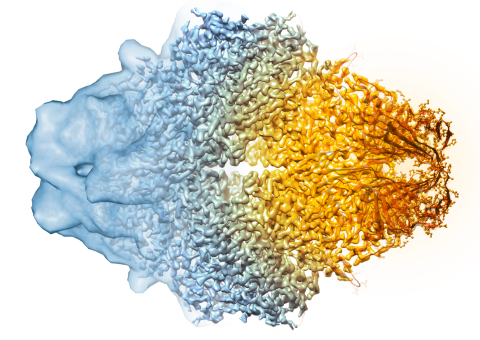
5882: Beta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882: Beta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Related to image 5883. NIH Director Francis Collins featured this on his blog on January 14, 2016.
Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute
View Media

6804: Staphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804: Staphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. The relatively rough surface of an implant is a favorable environment for bacteria to attach and grow. This can lead to the development of biofilms, which can cause infections. The researchers who took this image are working to understand where biofilms are likely to develop. This knowledge could support the prevention and treatment of infections. A scanning electron microscope was used to capture this image.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Antibiotics paper "Free-floating aggregate and single-cell-initiated biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus" by Gupta et al.
Related to image 6803 and video 6805.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Antibiotics paper "Free-floating aggregate and single-cell-initiated biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus" by Gupta et al.
Related to image 6803 and video 6805.
Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University.
View Media
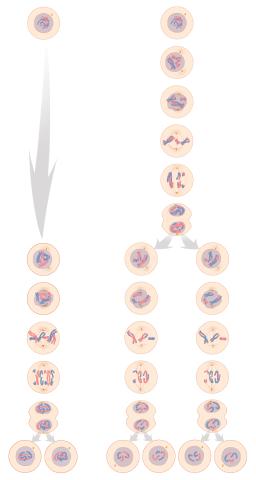
1333: Mitosis and meiosis compared
1333: Mitosis and meiosis compared
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. During mitosis, the chromosomes are copied once, and the cell divides once. For simplicity, cells are illustrated with only three pairs of chromosomes. See image 6788 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
2438: Hydra 02
2438: Hydra 02
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis.
Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan
View Media
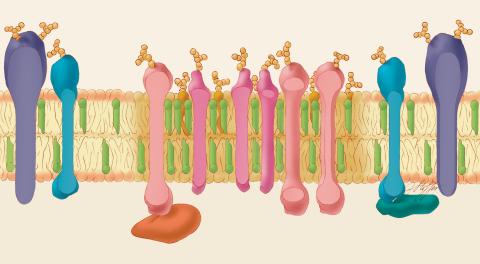
1285: Lipid raft
1285: Lipid raft
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. In artificial membranes, different lipids separate from each other based on their physical properties, forming small islands called lipid rafts.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
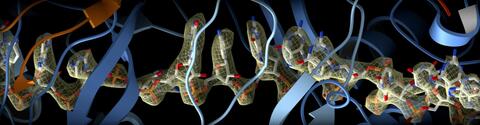
6351: CRISPR
6351: CRISPR
RNA incorporated into the CRISPR surveillance complex is positioned to scan across foreign DNA. Cryo-EM density from a 3Å reconstruction is shown as a yellow mesh.
NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher
View Media
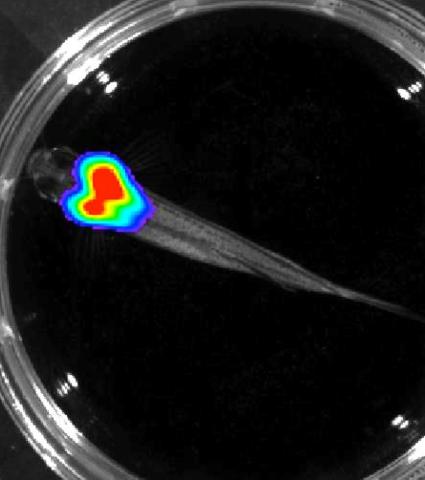
3557: Bioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
3557: Bioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. In this image, a cardiac muscle-restricted promoter drives firefly luciferase expression.
For imagery of both the lateral and overhead view go to 3556.
For imagery of the lateral view go to 3558.
For more information about the illumated area go to 3559.
For imagery of both the lateral and overhead view go to 3556.
For imagery of the lateral view go to 3558.
For more information about the illumated area go to 3559.
Kenneth Poss, Duke University
View Media
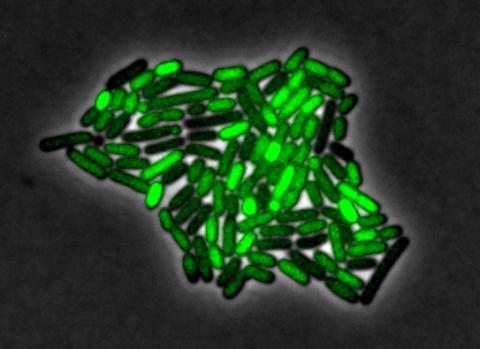
3253: Pulsating response to stress in bacteria
3253: Pulsating response to stress in bacteria
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. In response to a stressful environment like one lacking food, B. subtilis activates a large set of genes that help it respond to the hardship. Instead of leaving those genes on as previously thought, researchers discovered that the bacteria flip the genes on and off, increasing the frequency of these pulses with increasing stress. See entry 3254 for the related video.
Michael Elowitz, Caltech University
View Media

2423: Protein map
2423: Protein map
Network diagram showing a map of protein-protein interactions in a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell. This cluster includes 78 percent of the proteins in the yeast proteome. The color of a node represents the phenotypic effect of removing the corresponding protein (red, lethal; green, nonlethal; orange, slow growth; yellow, unknown).
Hawoong Jeong, KAIST, Korea
View Media
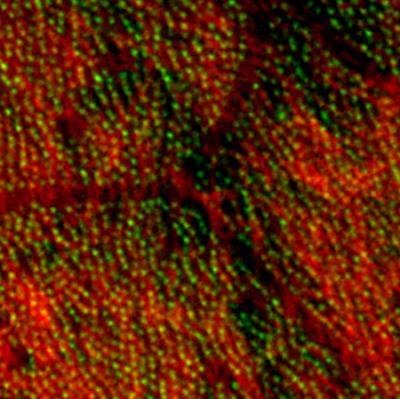
3292: Centrioles anchor cilia in planaria
3292: Centrioles anchor cilia in planaria
Centrioles (green) anchor cilia (red), which project on the surface of pharynx cells of the freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea. Centrioles require cellular structures called centrosomes for assembly in other animal species, but this flatworm known for its regenerative ability was unexpectedly found to lack centrosomes. From a Stowers University news release.
Juliette Azimzadeh, University of California, San Francisco
View Media
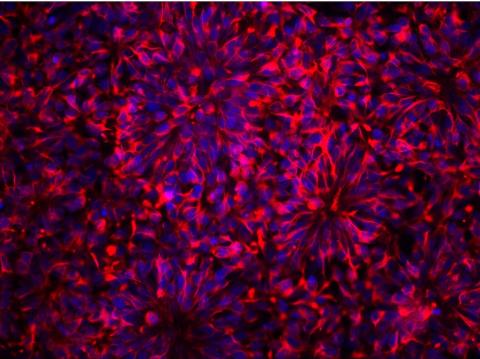
3284: Neurons from human ES cells
3284: Neurons from human ES cells
These neural precursor cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies are stained red, and the nuclei are blue. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM
View Media
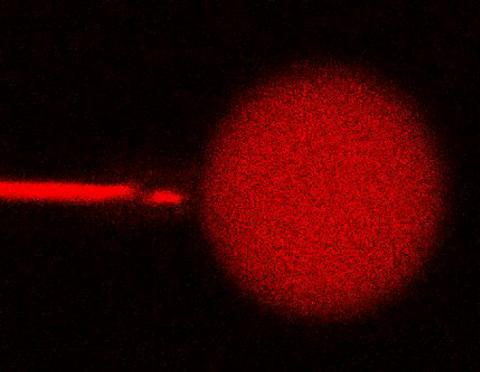
3583: Bee venom toxin destroying a cell
3583: Bee venom toxin destroying a cell
This video condenses 6.5 minutes into less than a minute to show how the toxin in bee venom, called melittin, destroys an animal or bacterial cell. What looks like a red balloon is an artificial cell filled with red dye. Melittin molecules are colored green and float on the cell's surface like twigs on a pond. As melittin accumulates on the cell's membrane, the membrane expands to accommodate it. In the video, the membrane stretches into a column on the left. When melittin levels reach a critical threshold, countless pinhole leaks burst open in the membrane. The cell's vital fluids (red dye in the video) leak out through these pores. Within minutes, the cell collapses.
Huey Huang, Rice University
View Media
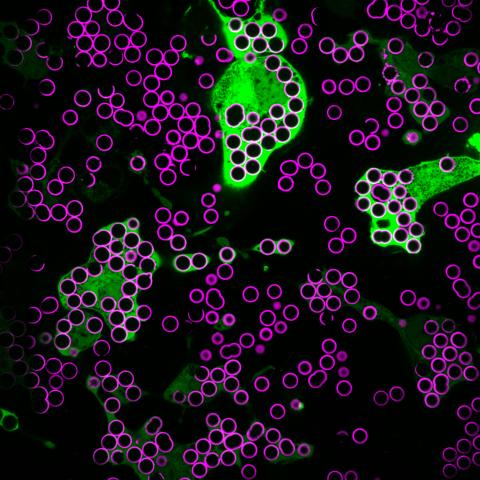
7009: Hungry, hungry macrophages
7009: Hungry, hungry macrophages
Macrophages (green) are the professional eaters of our immune system. They are constantly surveilling our tissues for targets—such as bacteria, dead cells, or even cancer—and clearing them before they can cause harm. In this image, researchers were testing how macrophages responded to different molecules that were attached to silica beads (magenta) coated with a lipid bilayer to mimic a cell membrane.
Find more information on this image in the NIH Director’s Blog post "How to Feed a Macrophage."
Find more information on this image in the NIH Director’s Blog post "How to Feed a Macrophage."
Meghan Morrissey, University of California, Santa Barbara.
View Media
3449: Calcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
3449: Calcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Caption from a November 26, 2012 news release from U Penn (Penn Medicine).
Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania
View Media
6777: Human endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex
6777: Human endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex
A 3D model of the human endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) that identifies its nine essential subunits. The EMC plays an important role in making membrane proteins, which are essential for all cellular processes. This is the first atomic-level depiction of the EMC. Its structure was obtained using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy.
Rebecca Voorhees, California Institute of Technology.
View Media
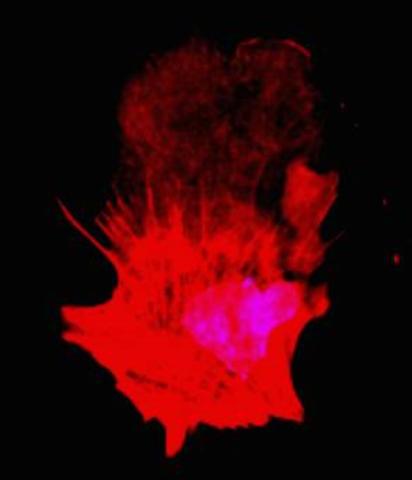
3332: Polarized cells- 01
3332: Polarized cells- 01
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Recent research has shown that an actin-polymerizing factor called the Arp2/3 complex is the key component of the actin polymerization engine that drives amoeboid cell motility. ARPC3, a component of the Arp2/3 complex, plays a critical role in actin nucleation. In this photo, the ARPC3+/+ fibroblast cells were fixed and stained with Alexa 546 phalloidin for F-actin (red) and DAPI to visualize the nucleus (blue). ARPC3+/+ fibroblast cells with lamellipodia leading edge. Related to images 3328, 3329, 3330, 3331, and 3333.
Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
View Media
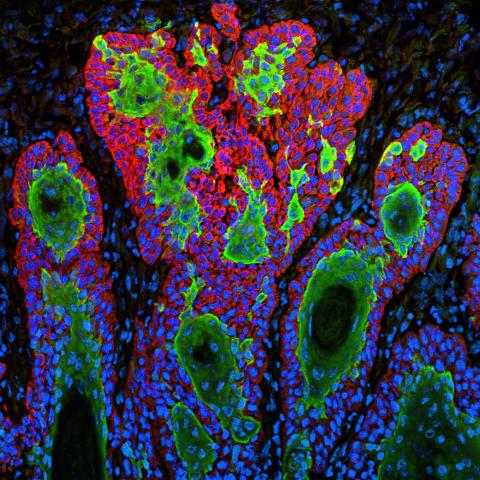
3628: Skin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
3628: Skin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
This image shows the uncontrolled growth of cells in squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is usually not life-threatening.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Markus Schober and Elaine Fuchs, The Rockefeller University
View Media
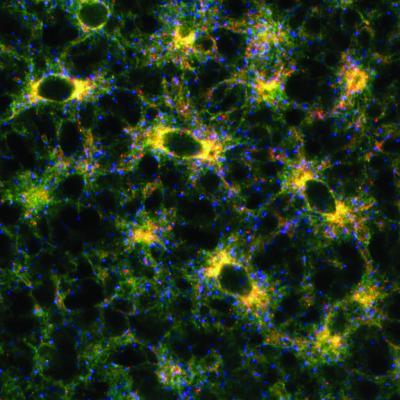
2649: Endoplasmic reticulum
2649: Endoplasmic reticulum
Fluorescent markers show the interconnected web of tubes and compartments in the endoplasmic reticulum. The protein atlastin helps build and maintain this critical part of cells. The image is from a July 2009 news release.
Andrea Daga, Eugenio Medea Scientific Institute (Conegliano, Italy)
View Media
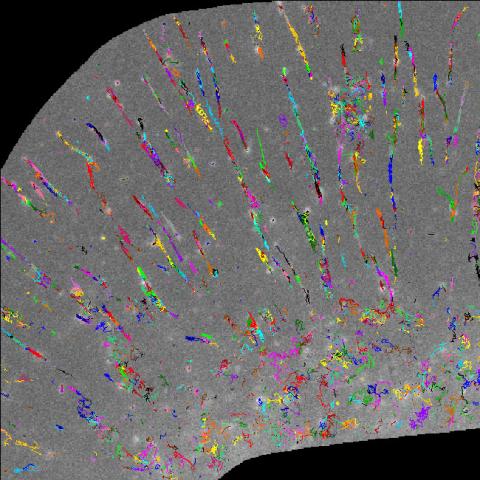
2801: Trajectories of labeled cell receptors
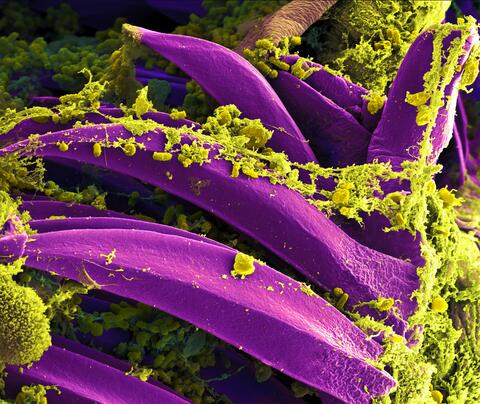
3576: Bubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576: Bubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. Today, it is still active in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, with as many as 2,000 people infected worldwide each year. If caught early, bubonic plague can be treated with antibiotics.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
NIAID
View Media
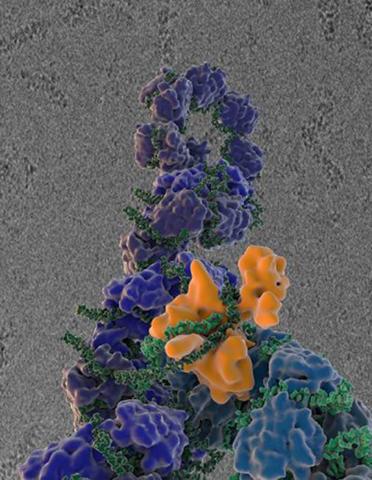
3434: Flu virus proteins during self-replication
3434: Flu virus proteins during self-replication
Influenza (flu) virus proteins in the act of self-replication. Viral nucleoprotein (blue) encapsidates [encapsulates] the RNA genome (green). The influenza virus polymerase (orange) reads and copies the RNA genome. In the background is an image of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes observed using cryo-electron microscopy. This image is from a November 2012 News Release.
Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, CA
View Media
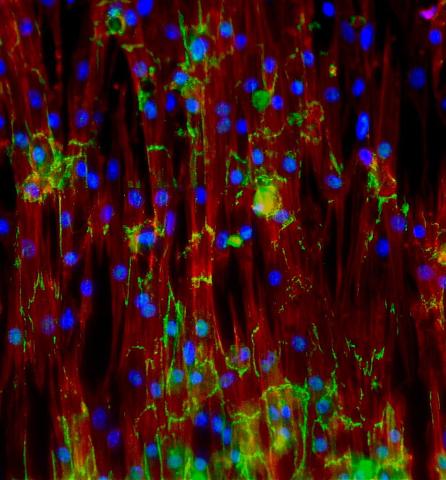
3282: Mouse heart muscle cells
3282: Mouse heart muscle cells
This image shows neonatal mouse heart cells. These cells were grown in the lab on a chip that aligns the cells in a way that mimics what is normally seen in the body. Green shows the protein N-cadherin, which indicates normal connections between cells. Red indicates the muscle protein actin, and blue indicates the cell nuclei. The work shown here was part of a study attempting to grow heart tissue in the lab to repair damage after a heart attack. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Related to images 3281 and 3283.
Kara McCloskey lab, University of California, Merced, via CIRM
View Media
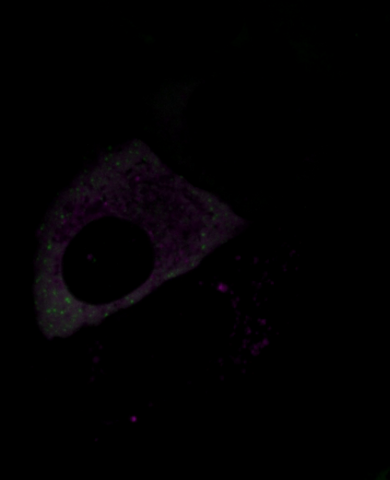
6570: Stress Response in Cells
6570: Stress Response in Cells
Two highly stressed osteosarcoma cells are shown with a set of green droplet-like structures followed by a second set of magenta droplets. These droplets are composed of fluorescently labeled stress-response proteins, either G3BP or UBQLN2 (Ubiquilin-2). Each protein is undergoing a fascinating process, called phase separation, in which a non-membrane bound compartment of the cytoplasm emerges with a distinct environment from the surrounding cytoplasm. Subsequently, the proteins fuse with like proteins to form larger droplets, in much the same way that raindrops merge on a car’s windshield.
Julia F. Riley and Carlos A. Castañeda, Syracuse University
View Media
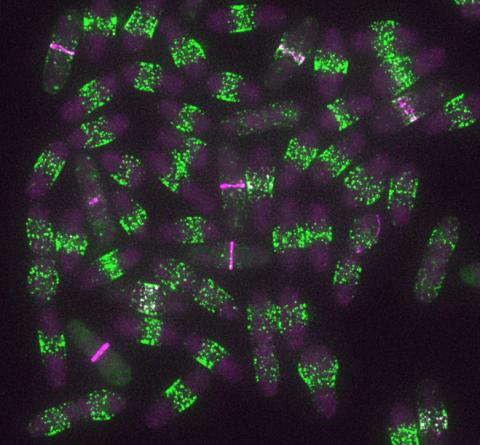
6791: Yeast cells entering mitosis
6791: Yeast cells entering mitosis
Yeast cells entering mitosis, also known as cell division. The green and magenta dots are two proteins that play important roles in mitosis. They show where the cells will split. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.
Related to images 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Related to images 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University.
View Media
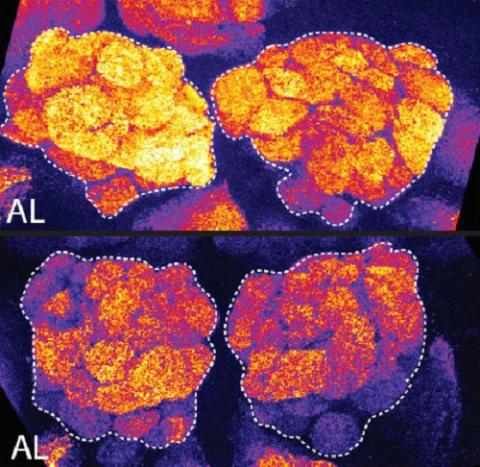
3490: Brains of sleep-deprived and well-rested fruit flies
3490: Brains of sleep-deprived and well-rested fruit flies
On top, the brain of a sleep-deprived fly glows orange because of Bruchpilot, a communication protein between brain cells. These bright orange brain areas are associated with learning. On the bottom, a well-rested fly shows lower levels of Bruchpilot, which might make the fly ready to learn after a good night's rest.
Chiara Cirelli, University of Wisconsin-Madison
View Media
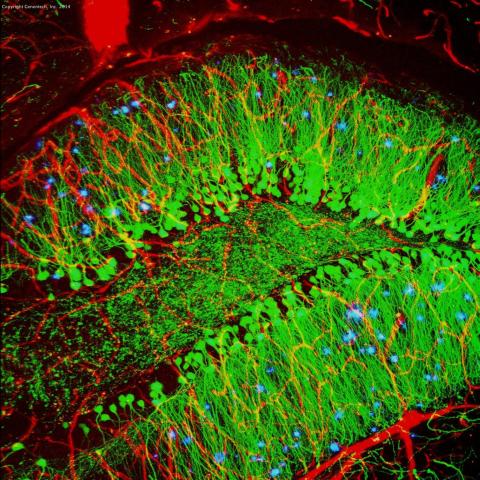
3604: Brain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
3604: Brain showing hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease
Along with blood vessels (red) and nerve cells (green), this mouse brain shows abnormal protein clumps known as plaques (blue). These plaques multiply in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease and are associated with the memory impairment characteristic of the disease. Because mice have genomes nearly identical to our own, they are used to study both the genetic and environmental factors that trigger Alzheimer's disease. Experimental treatments are also tested in mice to identify the best potential therapies for human patients.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Alvin Gogineni, Genentech
View Media
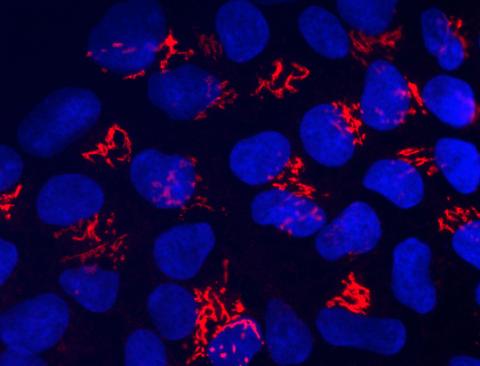
3341: Suicidal Stem Cells
3341: Suicidal Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells store pre-activated Bax (red) in the Golgi, near the nucleus (blue). Featured in the June 21, 2012, issue of Biomedical Beat.
Mohanish Deshmukh
View Media
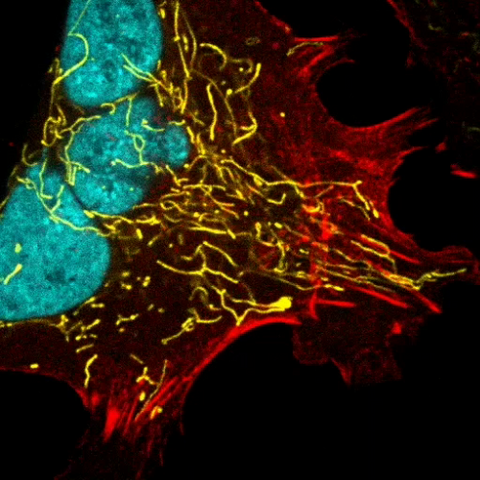
6967: Multinucleated cancer cell
6967: Multinucleated cancer cell
A cancer cell with three nuclei, shown in turquoise. The abnormal number of nuclei indicates that the cell failed to go through cell division, probably more than once. Mitochondria are shown in yellow, and a protein of the cell’s cytoskeleton appears in red. This video was captured using a confocal microscope.
Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine.
View Media
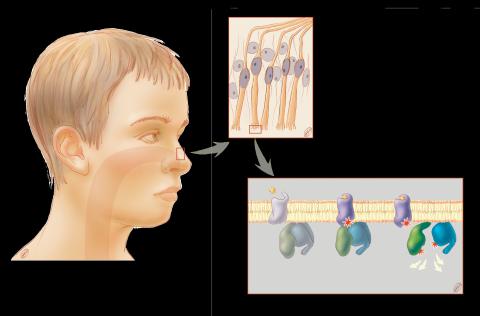
1291: Olfactory system
1291: Olfactory system
Sensory organs have cells equipped for detecting signals from the environment, such as odors. Receptors in the membranes of nerve cells in the nose bind to odor molecules, triggering a cascade of chemical reactions tranferred by G proteins into the cytoplasm.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
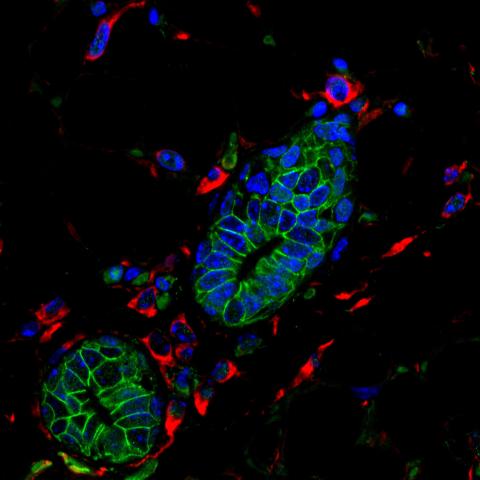
3432: Mouse mammary cells lacking anti-cancer protein
3432: Mouse mammary cells lacking anti-cancer protein
Shortly after a pregnant woman gives birth, her breasts start to secrete milk. This process is triggered by hormonal and genetic cues, including the protein Elf5. Scientists discovered that Elf5 also has another job--it staves off cancer. Early in the development of breast cancer, human breast cells often lose Elf5 proteins. Cells without Elf5 change shape and spread readily--properties associated with metastasis. This image shows cells in the mouse mammary gland that are lacking Elf5, leading to the overproduction of other proteins (red) that increase the likelihood of metastasis.
Nature Cell Biology, November 2012, Volume 14 No 11 pp1113-1231
View Media
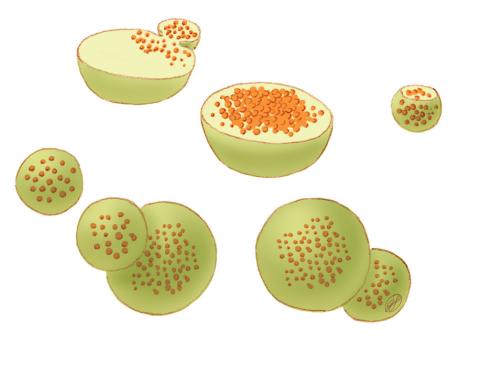
1282: Lysosomes
1282: Lysosomes
Lysosomes have powerful enzymes and acids to digest and recycle cell materials.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
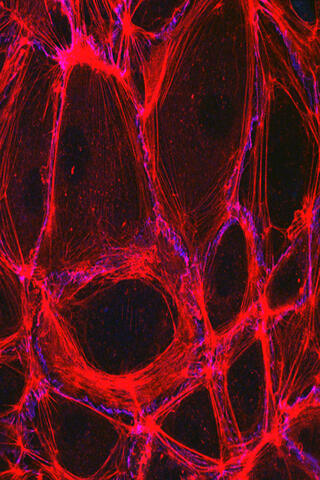
3633: Cells lining the blood vessel walls
3633: Cells lining the blood vessel walls
The structure of the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line our arteries and veins, is visible here. The endothelium is like a gatekeeper, controlling the movement of materials into and out of the bloodstream. Endothelial cells are held tightly together by specialized proteins that function like strong ropes (red) and others that act like cement (blue).
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Christopher V. Carman and Roberta Martinelli, Harvard Medical School.
View Media
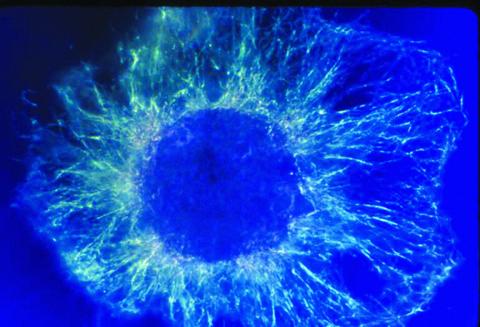
1058: Lily mitosis 01
1058: Lily mitosis 01
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
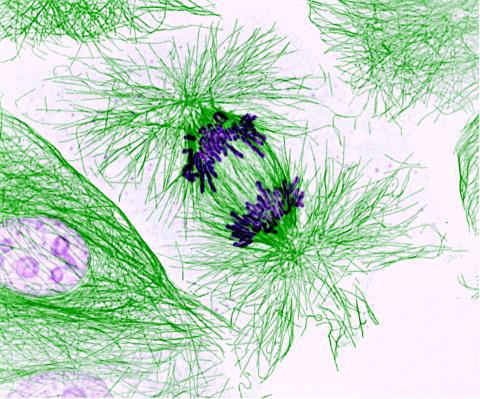
3631: Dividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
3631: Dividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Studies of cell division yield knowledge that is critical to advancing understanding of many human diseases, including cancer and birth defects.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health
View Media
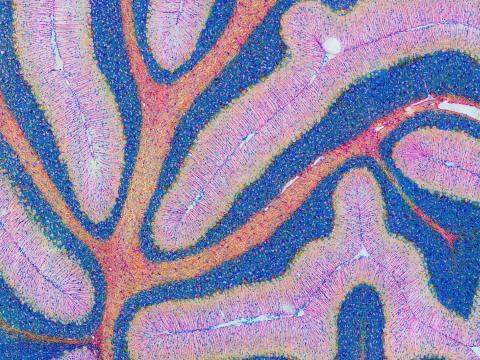
5800: Mouse cerebellum in pink and blue
5800: Mouse cerebellum in pink and blue
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. People with damage to this region of the brain often have difficulty with balance, coordination and fine motor skills.
This image of a mouse cerebellum is part of a collection of such images in different colors and at different levels of magnification from the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR). Related to image 5795.
This image of a mouse cerebellum is part of a collection of such images in different colors and at different levels of magnification from the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR). Related to image 5795.
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
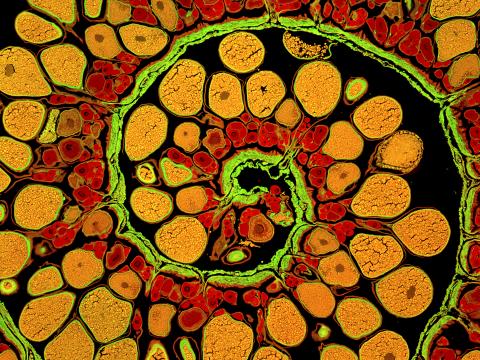
3620: Anglerfish ovary cross-section
3620: Anglerfish ovary cross-section
This image captures the spiral-shaped ovary of an anglerfish in cross-section. Once matured, these eggs will be released in a gelatinous, floating mass. For some species of anglerfish, this egg mass can be up to 3 feet long and include nearly 200,000 eggs.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
James E. Hayden, The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, Pa.
View Media
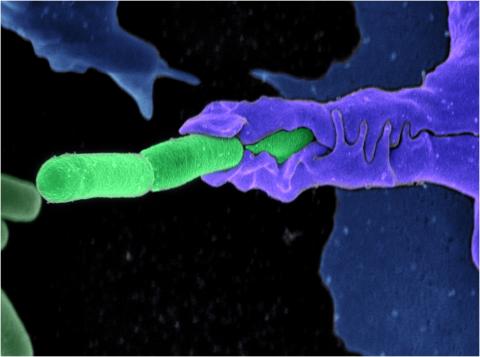
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
3612: Anthrax bacteria (green) being swallowed by an immune system cell
Multiple anthrax bacteria (green) being enveloped by an immune system cell (purple). Anthrax bacteria live in soil and form dormant spores that can survive for decades. When animals eat or inhale these spores, the bacteria activate and rapidly increase in number. Today, a highly effective and widely used vaccine has made the disease uncommon in domesticated animals and rare in humans.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Camenzind G. Robinson, Sarah Guilman, and Arthur Friedlander, United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases
View Media
2763: Fused, dicentric chromosomes
2763: Fused, dicentric chromosomes
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Centromeres are DNA/protein complexes that are key to splitting the chromosomes evenly during cell division. When dicentric chromosomes like this one are formed in a person, fertility problems or other difficulties may arise. Normal chromosomes carrying a single centromere (one set of red and green dots) are also visible in this image.
Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University
View Media
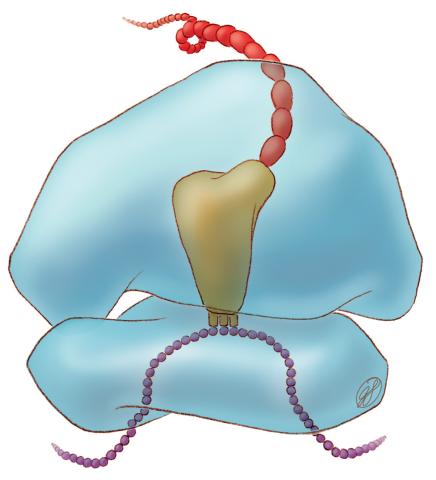
1281: Translation
1281: Translation
Ribosomes manufacture proteins based on mRNA instructions. Each ribosome reads mRNA, recruits tRNA molecules to fetch amino acids, and assembles the amino acids in the proper order.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
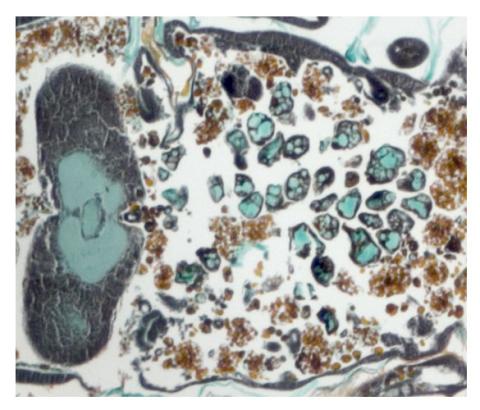
2759: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
2759: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
In the absence of the engulfment receptor Draper, salivary gland cells (light blue) persist in the thorax of a developing Drosophila melanogaster pupa. See image 2758 for a cross section of a normal pupa that does express Draper.
Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School
View Media