Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
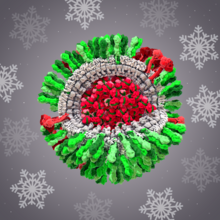
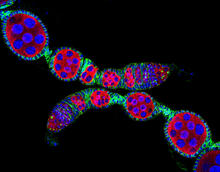
H1N1 Influenza Virus
6355
CellPack image of the H1N1 influenza virus, with hemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins in green and red, respectively, on the outer envelope (white); matrix protein in gray, and ribonucleoprot Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaDolly the sheep
2690
Scientists in Scotland were the first to clone an animal, this sheep named Dolly. She later gave birth to Bonnie, the lamb next to her. View MediaA Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
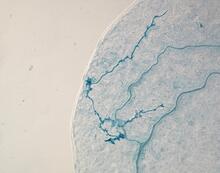
3718
Bacterial biofilms are tightly knit communities of bacterial cells growing on, for example, solid surfaces, such as in water pipes or on teeth. Gürol Süel, UCSD View MediaSuicidal Stem Cells
3341
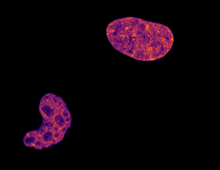
Embryonic stem cells store pre-activated Bax (red) in the Golgi, near the nucleus (blue). Featured in the June 21, 2012, issue of Biomedical Beat. Mohanish Deshmukh View MediaCell division and cell death
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaGenetic imprinting in Arabidopsis
2418
This delicate, birdlike projection is an immature seed of the Arabidopsis plant. The part in blue shows the cell that gives rise to the endosperm, the tissue that nourishes the embryo. Robert Fischer, University of California, Berkeley View MediaThree neurons and human ES cells
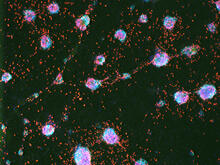
3290
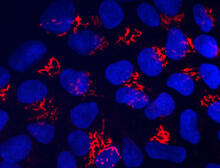
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6887
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaBacterial spore
2752
A spore from the bacterium Bacillus subtilis shows four outer layers that protect the cell from harsh environmental conditions. Patrick Eichenberger, New York University View MediaHuman ES cells turn into insulin-producing cells
3277
Human embryonic stem cells were differentiated into cells like those found in the pancreas (blue), which give rise to insulin-producing cells (red). Eugene Brandon, ViaCyte, via CIRM View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
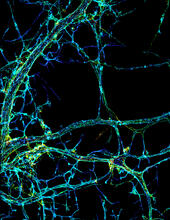
3678
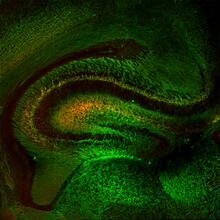
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaMouse Brain Cross Section
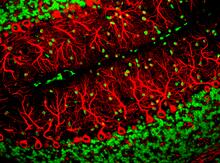
5886
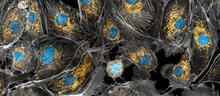
The brain sections are treated with fluorescent antibodies specific to a particular protein and visualized using serial electron microscopy (SEM). Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
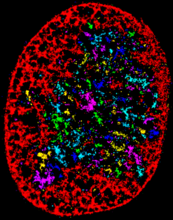
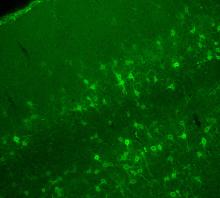
3742
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaFruit fly ovary
3607
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaThe Proteasome: The Cell's Trash Processor in Action
3772
Our cells are constantly removing and recycling molecular waste. This video shows one way cells process their trash. View MediaVibrio bacteria
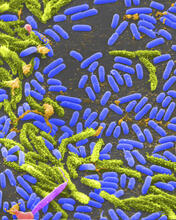
1160
Vibrio, a type (genus) of rod-shaped bacteria. Some Vibrio species cause cholera in humans. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaFlower-forming cells in a small plant related to cabbage (Arabidopsis)
3606
In plants, as in animals, stem cells can transform into a variety of different cell types. The stem cells at the growing tip of this Arabidopsis plant will soon become flowers. Arun Sampathkumar and Elliot Meyerowitz, California Institute of Technology View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaSkin cross-section
1056
Cross-section of skin anatomy shows layers and different tissue types. National Institutes of Health Medical Arts View MediaMouse cerebellum close-up
3371
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaConfocal microscopy image of two Drosophila ovarioles
5772
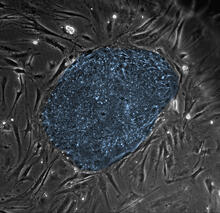
Ovarioles in female insects are tubes in which egg cells (called oocytes) form at one end and complete their development as they reach the other end of the tube. 2004 Olympus BioScapes Competition View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells
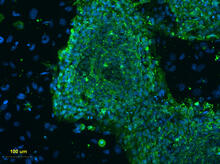
2608
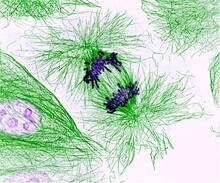
The center cluster of cells, colored blue, shows a colony of human embryonic stem cells. James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison View MediaDividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
3631
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaAldolase
6350
2.5Å resolution reconstruction of rabbit muscle aldolase collected on a FEI/Thermo Fisher Titan Krios with energy filter and image corrector. National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher View MediaDraper, shown in the fatbody of a Drosophila melanogaster larva
2757
The fly fatbody is a nutrient storage and mobilization organ akin to the mammalian liver. The engulfment receptor Draper (green) is located at the cell surface of fatbody cells. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaCells frozen in time
2307
The fledgling field of X-ray microscopy lets researchers look inside whole cells rapidly frozen to capture their actions at that very moment. Here, a yeast cell buds before dividing into two. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco, and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaTwo mouse fibroblast cells
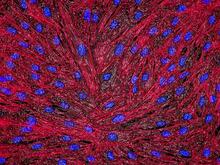
6789
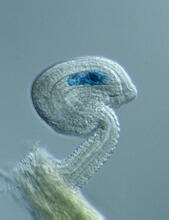
Two mouse fibroblasts, one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue. They play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaHydra 01
2437
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaSea urchin embryo 02
1048
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaFruit fly retina 02
2434
Section of a fruit fly retina showing the light-sensing molecules rhodopsin-5 (blue) and rhodopsin-6 (red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaIndependence Day
5888
This graphic that resembles a firework was created from a picture of a fruit fly spermatid. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaDopaminergic neurons from ES cells
3270
Human embryonic stem cells differentiated into dopaminergic neurons, the type that degenerate in Parkinson's disease. Image courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Jeannie Liu, Lab of Jan Nolta, University of California, Davis, via CIRM View MediaLily mitosis 11
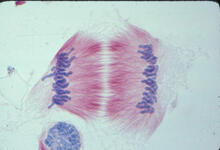
1011
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaArabidopsis leaf injected with a pathogen
2780
This is a magnified view of an Arabidopsis thaliana leaf eight days after being infected with the pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, which is closely related to crop pathogens that Jeff Dangl, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
3664
These mitochondria (brown) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaPurkinje cells are one of the main cell types in the brain
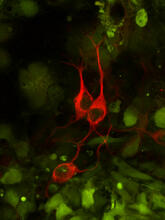
3637
This image captures Purkinje cells (red), one of the main types of nerve cell found in the brain. Yinghua Ma and Timothy Vartanian, Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
3274
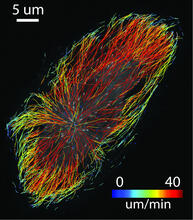
This fluorescent microscope image shows human embryonic stem cells whose nuclei are stained green. Blue staining shows the surrounding supportive feeder cells. Michael Longaker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaMicrotubule growth
2800
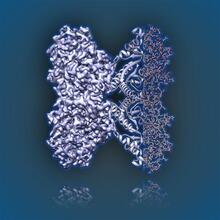
Map of microtubule growth rates. Rates are color coded. This is an example of NIH-supported research on single-cell analysis. Gaudenz Danuser, Harvard Medical School View MediaNucleosome
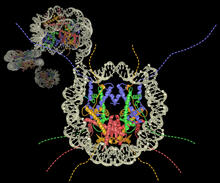
2741
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strand Karolin Luger, Colorado State University View MediaPanorama view of golden mitochondria
5762
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cells, generating the energy the cells need to do their tasks and to stay alive. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaGlowing glycans
2473
Sugars light up the cells in this jaw of a 3-day-old zebrafish embryo and highlight a scientific first: labeling and tracking the movements of sugar chains called glycans in a living organism. Carolyn Bertozzi, University of California, Berkeley View MediaArachnoidiscus diatom
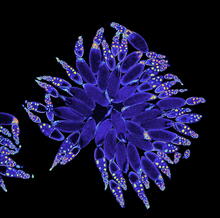
6902
An Arachnoidiscus diatom with a diameter of 190µm. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaMitosis - interphase
1316
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Judith Stoffer View MediaDNA and actin in cultured fibroblast cells
3670
DNA (blue) and actin (red) in cultured fibroblast cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCytonemes in developing fruit fly cells
3574
Scientists have long known that multicellular organisms use biological molecules produced by one cell and sensed by another to transmit messages that, for instance, guide proper development of organs Sougata Roy, University of California, San Francisco View MediaA bundle of myelinated peripheral nerve cells (axons)
3737
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is most prevalent in connective tissues but also is present between the stems (axons) of nerve cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaHow cilia do the wave
3494
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University View MediaNeural circuits in worms similar to those in humans
3252
Green and yellow fluorescence mark the processes and cell bodies of some C. elegans neurons. Shawn Xu, University of Michigan View Media