Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
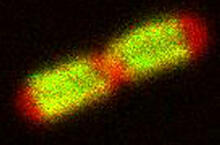
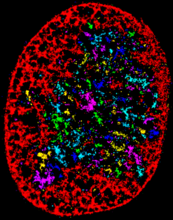
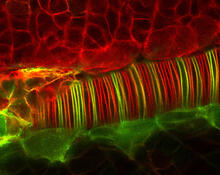
TonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
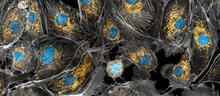
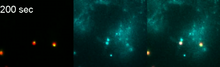
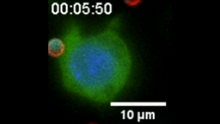
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaHIV-1 virus in the colon
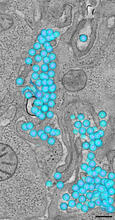
3571
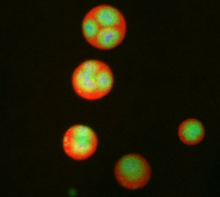
A tomographic reconstruction of the colon shows the location of large pools of HIV-1 virus particles (in blue) located in the spaces between adjacent cells. Mark Ladinsky, California Institute of Technology View MediaImmune cell attacks cell infected with a retrovirus
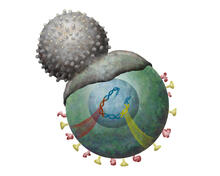
2489
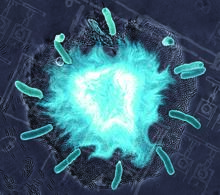
T cells engulf and digest cells displaying markers (or antigens) for retroviruses, such as HIV. Kristy Whitehouse, science illustrator View MediaLily mitosis 12
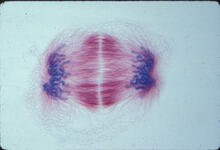
1018
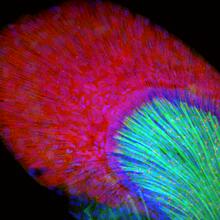
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View MediaPanorama view of golden mitochondria
5762
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cells, generating the energy the cells need to do their tasks and to stay alive. Torsten Wittmann, University of California, San Francisco View MediaHIV Infected Cell
3386
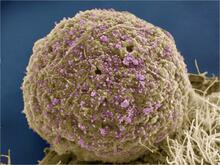
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaEndothelial cell
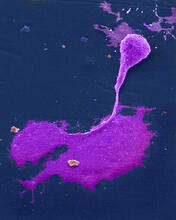
1102
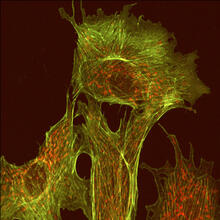
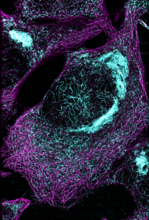
This image shows two components of the cytoskeleton, microtubules (green) and actin filaments (red), in an endothelial cell derived from a cow lung. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMicrotubules in African green monkey cells
6891
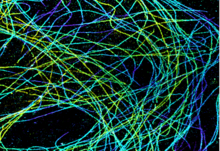
Microtubules in African green monkey cells. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide cells with structural support. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaPhagosome in macrophage cell
6799
A sensor particle being engulfed by a macrophage—an immune cell—and encapsuled in a compartment called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes—another type of compartment. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaMapping brain differences
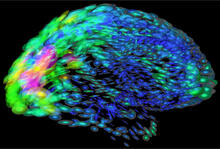
2419
This image of the human brain uses colors and shapes to show neurological differences between two people. Arthur Toga, University of California, Los Angeles View MediaYeast cells with endocytic actin patches
6793
Yeast cells with endocytic actin patches (green). These patches help cells take in outside material. When a cell is in interphase, patches concentrate at its ends. Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University. View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 72 hour
6556
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface from a small i L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaHydra 02
2438
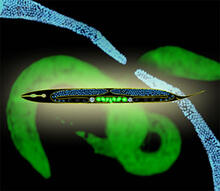
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaWorms and human infertility
2333
This montage of tiny, transparent C. elegans--or roundworms--may offer insight into understanding human infertility. Abby Dernburg, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaPathways: What is It? | Why Scientists Study Cells
6540
Learn how curiosity about the world and our cells is key to scientific discoveries. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaBicycling cell
1337
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell. Judith Stoffer View MediaColor coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
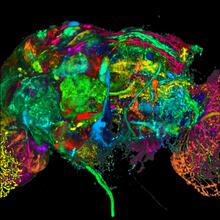
5868
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo. View MediaARTS triggers apoptosis
2432
Cell showing overproduction of the ARTS protein (red). ARTS triggers apoptosis, as shown by the activation of caspase-3 (green) a key tool in the cell's destruction. The nucleus is shown in blue. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
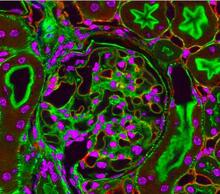
3725
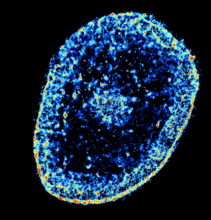
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6887
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 3
3792
What looks a little like distant planets with some mysterious surface features are actually assemblies of proteins normally found in the cell's nucleolus, a small but very important protein complex lo Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaSupernova bacteria
2725
Bacteria engineered to act as genetic clocks flash in synchrony. Here, a "supernova" burst in a colony of coupled genetic clocks just after reaching critical cell density. Jeff Hasty, UCSD View MediaDeveloping zebrafish fin
3598
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. Jessica Plavicki View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa lacking Draper
2759
In the absence of the engulfment receptor Draper, salivary gland cells (light blue) persist in the thorax of a developing Drosophila melanogaster pupa. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View Media“Two-faced” Janus particle activating a macrophage
6801
A macrophage—a type of immune cell that engulfs invaders—“eats” and is activated by a “two-faced” Janus particle. Yan Yu, Indiana University, Bloomington. View MediaMicrotubules and tau aggregates
6892
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaHIV Capsid
3477
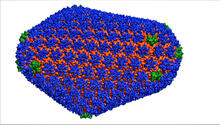
This image is a computer-generated model of the approximately 4.2 million atoms of the HIV capsid, the shell that contains the virus' genetic material. Juan R. Perilla and the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign View MediaChromatin in human tenocyte
6893
The nucleus of a degenerating human tendon cell, also known as a tenocyte. It has been color-coded based on the density of chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaCrab nerve cell
1247
Neuron from a crab showing the cell body (bottom), axon (rope-like extension), and growth cone (top right). Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaBirth of a yeast cell
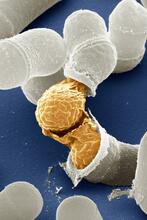
3614
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany View MediaGenetically identical mycobacteria respond differently to antibiotic 1
5751
Antibiotic resistance in microbes is a serious health concern. So researchers have turned their attention to how bacteria undo the action of some antibiotics. Bree Aldridge, Tufts University View MediaTiny strands of tubulin, a protein in a cell's skeleton
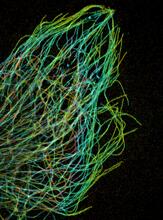
3611
Just as our bodies rely on bones for structural support, our cells rely on a cellular skeleton. Pakorn Kanchanawong, National University of Singapore and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health; and Clare Waterman, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaZebrafish embryo
6897
A zebrafish embryo showing its natural colors. Zebrafish have see-through eggs and embryos, making them ideal research organisms for studying the earliest stages of development. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaSea urchin embryo 02
1048
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaNeural tube development
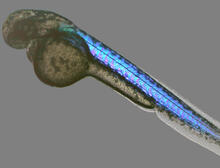
2328
Proteins in the neural tissues of this zebrafish embryo direct cells to line up and form the neural tube, which will become the spinal cord and brain. Alexander Schier, Harvard University View MediaHuman fibroblast undergoing cell division
6519
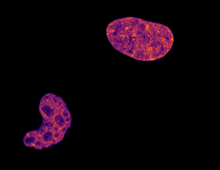
During cell division, cells physically divide after separating their genetic material to create two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nilay Taneja, Vanderbilt University, and Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View MediaCell division and cell death
6790
Two cells over a 2-hour period. The one on the bottom left goes through programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. The one on the top right goes through cell division, also called mitosis. Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. View Media