Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
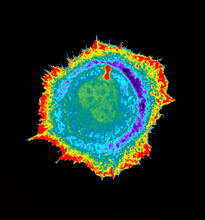
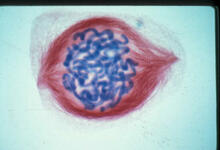
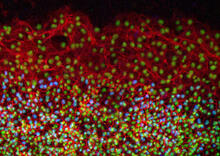
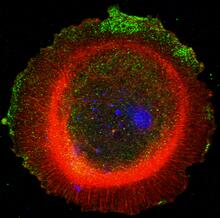
Sea urchin embryo 02
1048
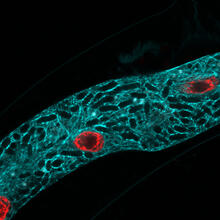
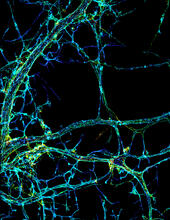
Stereo triplet of a sea urchin embryo stained to reveal actin filaments (orange) and microtubules (blue). George von Dassow, University of Washington View MediaMyelinated axons 1
3396
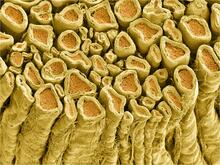
Myelinated axons in a rat spinal root. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaFluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue--close-up
3725
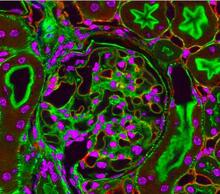
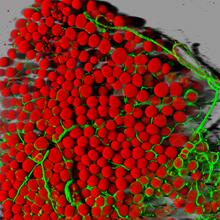
This photograph of kidney tissue, taken using fluorescent light microscopy, shows a close-up view of part of image 3723. Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 2
5778
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View Media3D image of actin in a cell
3749
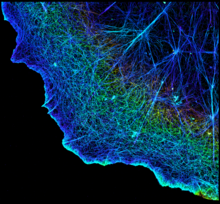
Actin is an essential protein in a cell's skeleton (cytoskeleton). It forms a dense network of thin filaments in the cell. Xiaowei Zhuang, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6887
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View MediaMicrosporidia in roundworm 1
5777
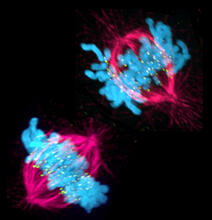
Many disease-causing microbes manipulate their host’s metabolism and cells for their own ends. Keir Balla and Emily Troemel, University of California San Diego View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared
1333
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaSeeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School View MediaPigment cells in fish skin
5756
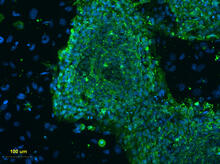
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
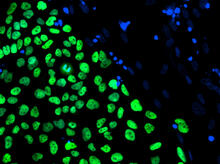
3275
The nuclei stained green highlight human embryonic stem cells grown under controlled conditions in a laboratory. Blue represents the DNA of surrounding, supportive feeder cells. Julie Baker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaHeLa cells
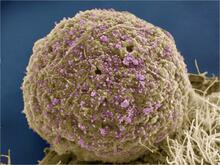
3520
Multiphoton fluorescence image of HeLa cells with cytoskeletal microtubules (magenta) and DNA (cyan). Nikon RTS2000MP custom laser scanning microscope. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaStaphylococcus aureus in the porous coating of a femoral hip stem
6804
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) on the porous coating of a femoral hip stem used in hip replacement surgery. Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University. View MediaSuicidal Stem Cells
3341
Embryonic stem cells store pre-activated Bax (red) in the Golgi, near the nucleus (blue). Featured in the June 21, 2012, issue of Biomedical Beat. Mohanish Deshmukh View MediaSTORM image of axonal cytoskeleton
3678
This image shows the long, branched structures (axons) of nerve cells. Xiaowei Zhuang Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University View MediaFruit fly spermatids
3590
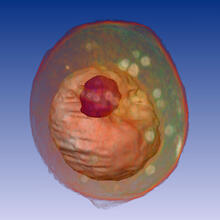
Developing spermatids (precursors of mature sperm cells) begin as small, round cells and mature into long-tailed, tadpole-shaped ones. Lacramioara Fabian, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada View MediaYeast cell
1092
A whole yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell viewed by X-ray microscopy. Inside, the nucleus and a large vacuole (red) are visible. Carolyn Larabell, University of California, San Francisco and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory View MediaHuman embryonic stem cells on feeder cells
3274
This fluorescent microscope image shows human embryonic stem cells whose nuclei are stained green. Blue staining shows the surrounding supportive feeder cells. Michael Longaker lab, Stanford University School of Medicine, via CIRM View MediaLily mitosis 05
1015
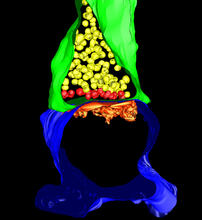
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene View Media3-D Architecture of a Synapse
5885
This image shows the structure of a synapse, or junction between two nerve cells in three dimensions. From the brain of a mouse. Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA View MediaIn vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaEar hair cells derived from embryonic stem cells
3272
Mouse embryonic stem cells matured into this bundle of hair cells similar to the ones that transmit sound in the ear. Stefen Heller, Stanford University, via CIRM View MediaLysosomes and microtubules
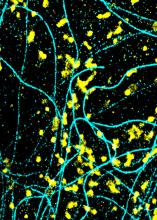
6889
Lysosomes (yellow) and detyrosinated microtubules (light blue). Lysosomes are bubblelike organelles that take in molecules and use enzymes to break them down. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaCell proliferation in a quail embryo
2808
Image showing that the edge zone (top of image) of the quail embryo shows no proliferating cells (cyan), unlike the interior zone (bottom of image). Non-proliferating cell nuclei are labeled green. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaHIV Infected Cell
3386
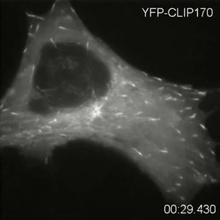
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMicrotubule dynamics in real time
2784
Cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP)-170 is a microtubule plus-end-tracking protein that regulates microtubule dynamics and links microtubule ends to different intracellular structures. Gary Borisy, Marine Biology Laboratory View MediaCell in two stages of division
3541
This image shows a cell in two stages of division: prometaphase (top) and metaphase (bottom). Lilian Kabeche, Dartmouth View MediaH1N1 Influenza Virus
6356
Related to image 6355. Dr. Rommie Amaro, University of California, San Diego View MediaFat cells (red) and blood vessels (green)
3600
A mouse's fat cells (red) are shown surrounded by a network of blood vessels (green). Daniela Malide, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaHuman retinal organoid
6748
A replica of a human retina grown from stem cells. Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 72 hour
6556
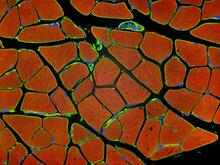
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface from a small i L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaHuman skeletal muscle
3677
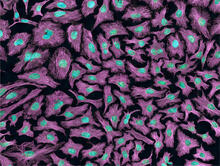
Cross section of human skeletal muscle. Image taken with a confocal fluorescent light microscope. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediamDia1 antibody staining-01
3330
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research View MediaPathways – Bacteria vs. Viruses: What's the Difference?
6597
Learn about how bacteria and viruses differ, how they each can make you sick, and how they can or cannot be treated. National Institute of General Medical Sciences View MediaFruit fly retina 01
2430
Image showing rhabdomeres (red), the light-sensitive structures in the fruit fly retina, and rhodopsin-4 (blue), a light-sensing molecule. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaClathrin-mediated endocytosis
5753
Endocytosis is the process by which cells are able to take up membrane and extracellular materials through the formation of a small intracellular bubble, called a vesicle. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah View MediaHydra 04
2440
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis. Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan View MediaATP Synthase
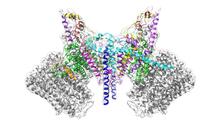
6353
Atomic model of the membrane region of the mitochondrial ATP synthase built into a cryo-EM map at 3.6 Å resolution. ATP synthase is the primary producer of ATP in aerobic cells. Bridget Carragher, <a href="http://nramm.nysbc.org/">NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy</a> View MediaFocal adhesions (with labels)
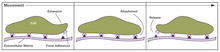
2503
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. Crabtree + Company View MediaDNA and actin in cultured fibroblast cells
3670
DNA (blue) and actin (red) in cultured fibroblast cells. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaMosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park View MediaMitochondria
1287
Bean-shaped mitochondria are cells' power plants. These organelles have their own DNA and replicate independently. The highly folded inner membranes are the site of energy generation. Judith Stoffer View MediaPlasma-Derived Membrane Vesicles
5887
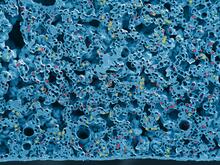
This fiery image doesn’t come from inside a bubbling volcano. Instead, it shows animal cells caught in the act of making bubbles, or blebbing. Jeanne Stachowiak, University of Texas at Austin View MediaDense tubular matrices in the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 1
5855
Superresolution microscopy work on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the peripheral areas of the cell showing details of the structure and arrangement in a complex web of tubes. Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia View MediaBorrelia burgdorferi
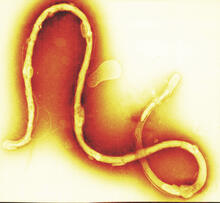
1241
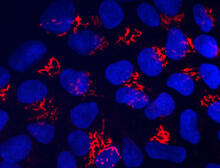
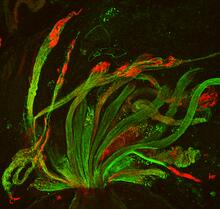
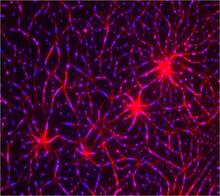
Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete, a class of long, slender bacteria that typically take on a coiled shape. Infection with this bacterium causes Lyme disease. Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaNeurons from human ES cells 02
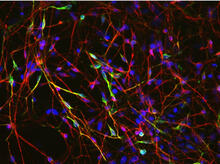
3285
These neurons were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The neural cell bodies with axonal projections are visible in red, and the nuclei in blue. Xianmin Zeng lab, Buck Institute for Age Research, via CIRM View Media