Switch to Gallery View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
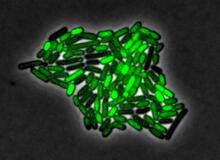
Pulsating response to stress in bacteria
3253
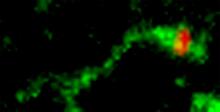
By attaching fluorescent proteins to the genetic circuit responsible for B. subtilis's stress response, researchers can observe the cells' pulses as green flashes. Michael Elowitz, Caltech University View MediaNucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791
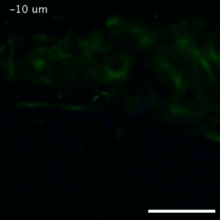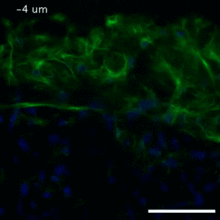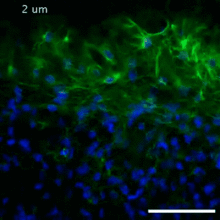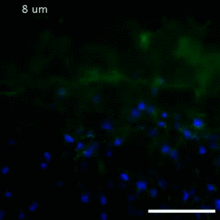
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University View MediaScanning electron microscopy of the ECM on the surface of a calf muscle
3739
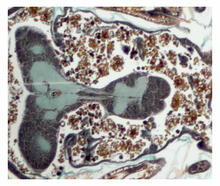
This image shows the extracellular matrix (ECM) on the surface of a soleus (lower calf) muscle in light brown and blood vessels in pink. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759. Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School View MediaInterphase in Xenopus frog cells
3443
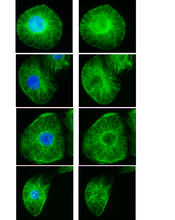
These images show frog cells in interphase. The cells are Xenopus XL177 cells, which are derived from tadpole epithelial cells. The microtubules are green and the chromosomes are blue. Claire Walczak, who took them while working as a postdoc in the laboratory of Timothy Mitchison. View MediaShiga toxin being sorted inside a cell
3488
Shiga toxin (green) is sorted from the endosome into membrane tubules (red), which then pinch off and move to the Golgi apparatus. Somshuvra Mukhopadhyay, The University of Texas at Austin, and Adam D. Linstedt, Carnegie Mellon University View MediaCrab nerve cell
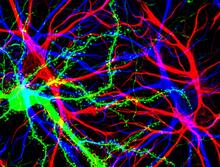
1247
Neuron from a crab showing the cell body (bottom), axon (rope-like extension), and growth cone (top right). Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa View MediaMitosis and meiosis compared
1333
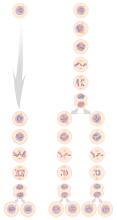
Meiosis is used to make sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a cell's chromosomes are copied once, but the cell divides twice. Judith Stoffer View MediaConfocal microscopy of perineuronal nets in the brain 2
3742
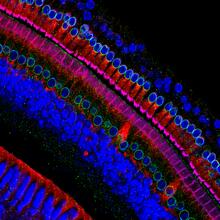
The photo shows a confocal microscopy image of perineuronal nets (PNNs), which are specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) structures in the brain. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaIn vitro assembly of a cell-signaling pathway
3787
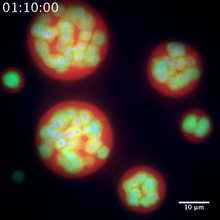
T cells are white blood cells that are important in defending the body against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Xiaolei Su, HHMI Whitman Center of the Marine Biological Laboratory View MediaMultivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 3
5767
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado View MediaMitochondria from rat heart muscle cell
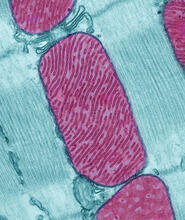
3661
These mitochondria (red) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research View MediaBioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish 04
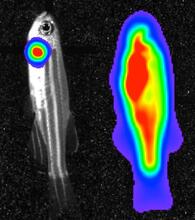
3559
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. View MediaBrain cells in the hippocampus
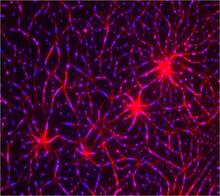
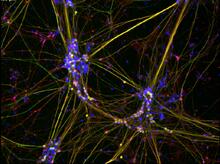
3688
Hippocampal cells in culture with a neuron in green, showing hundreds of the small protrusions known as dendritic spines. Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego View MediaMouse cerebellum in pink and blue
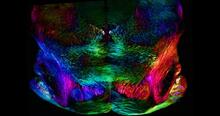
5800
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
6585
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaCalcium uptake during ATP production in mitochondria
3449
Living primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mitochondria (green) stained with the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, rhodamine 123. Nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Lili Guo, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania View MediaGenetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center View MediaBone cancer cell
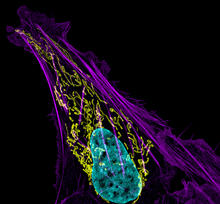
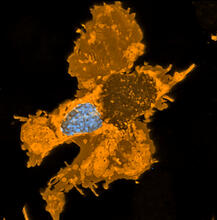
3626
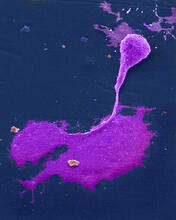
This image shows an osteosarcoma cell with DNA in blue, energy factories (mitochondria) in yellow, and actin filaments—part of the cellular skeleton—in purple. Dylan Burnette and Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, NICHD View MediaG switch
2536
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. See images 2537 and 2538 for labeled versions of this image. Crabtree + Company View MediaTonB protein in gram-negative bacteria
3549
The green in this image highlights a protein called TonB, which is produced by many gram-negative bacteria, including those that cause typhoid fever, meningitis and dysentery. Phillip Klebba, Kansas State University View MediaProteasome
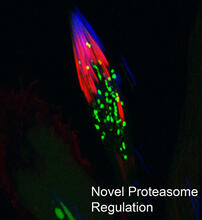
3451
This fruit fly spermatid recycles various molecules, including malformed or damaged proteins. Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Rockefeller University View MediaZ rings in bacterial division
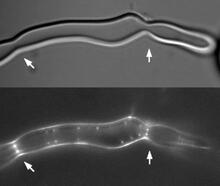
2456
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). Masaki Osawa, Duke University View MediaTransmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
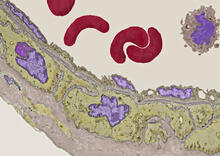
3738
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) View MediaCell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
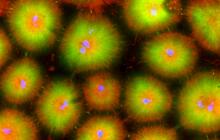
6591
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine. View MediaSkin cross-section
1056
Cross-section of skin anatomy shows layers and different tissue types. National Institutes of Health Medical Arts View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6887
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaWild-type and mutant fruit fly ovaries
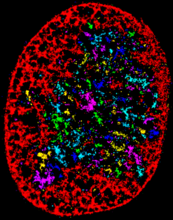
6806
The two large, central, round shapes are ovaries from a typical fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaVideo of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
6781
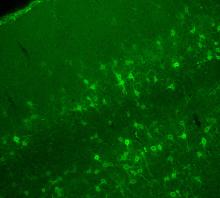
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. NIH Director's Blog View MediaChromatin in human fibroblast
6888
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. View MediaFruit fly retina 02
2434
Section of a fruit fly retina showing the light-sensing molecules rhodopsin-5 (blue) and rhodopsin-6 (red). Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 72 hour
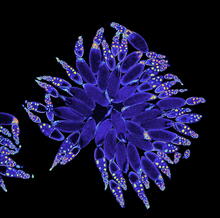
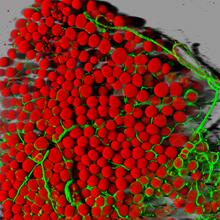
6556
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface from a small i L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaFruit fly ovarioles
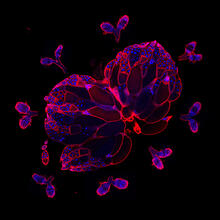
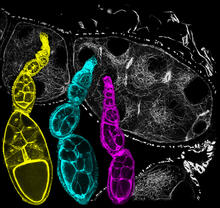
6810
Three fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovarioles (yellow, blue, and magenta) with egg cells visible inside them. Ovarioles are tubes in the reproductive systems of female insects. Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University. View MediaBody toxins (with labels)
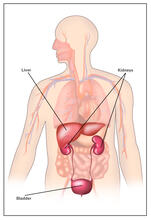
2497
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. Crabtree + Company View MediaMouse retina
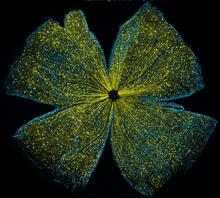
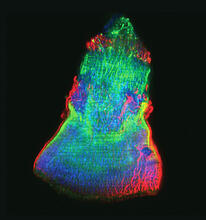
5793
What looks like the gossamer wings of a butterfly is actually the retina of a mouse, delicately snipped to lay flat and sparkling with fluorescent molecules. Tom Deerinck and Keunyoung (“Christine”) Kim, NCMIR View MediaPeripheral nerve cells derived from ES cells
3263
Peripheral nerve cells made from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. Stephen Dalton, University of Georgia View MediaSymmetrically and asymmetrically elongating cells
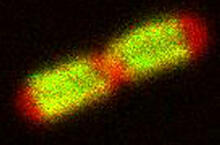
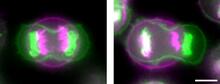
3648
Merged fluorescent images of symmetrically (left) or asymmetrically (right) elongating HeLa cells at the end of early anaphase (magenta) and late anaphase (green). Tomomi Kiyomitsu and Iain M. Cheeseman, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research View MediaFruit fly ovary
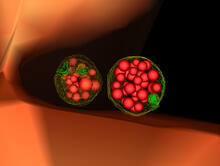
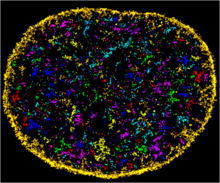
3607
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara View MediaFruit fly embryo
2431
Cells in an early-stage fruit fly embryo, showing the DIAP1 protein (pink), an inhibitor of apoptosis. Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University View MediaVimentin in a quail embryo
2809
Video of high-resolution confocal images depicting vimentin immunofluorescence (green) and nuclei (blue) at the edge of a quail embryo yolk. Andrés Garcia, Georgia Tech View MediaHair cells: the sound-sensing cells in the ear
3618
These cells get their name from the hairlike structures that extend from them into the fluid-filled tube of the inner ear. Henning Horn, Brian Burke, and Colin Stewart, Institute of Medical Biology, Agency for Science, Technology, and Research, Singapore View MediaSingle-cell “radios” video
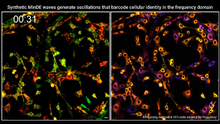
7022
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison. View MediaZebrafish pigment cell
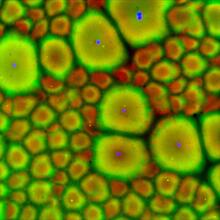
5754
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. David Parichy, University of Washington View MediaMouse brain slice showing nerve cells
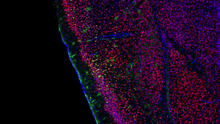
6901
A 20-µm thick section of mouse midbrain. The nerve cells are transparent and weren’t stained. Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago. View MediaFat cells (red) and blood vessels (green)
3600
A mouse's fat cells (red) are shown surrounded by a network of blood vessels (green). Daniela Malide, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health View MediaHeart muscle with reprogrammed skin cells
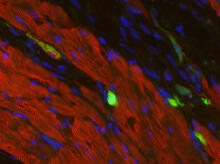
3273
Skins cells were reprogrammed into heart muscle cells. The cells highlighted in green are remaining skin cells. Red indicates a protein that is unique to heart muscle. Deepak Srivastava, Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, via CIRM View MediaHow cilia do the wave
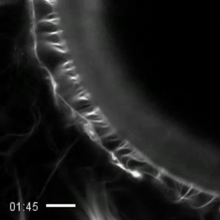
3494
Thin, hair-like biological structures called cilia are tiny but mighty. Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University View MediaActivated mast cell surface
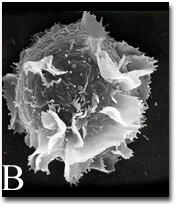
2637
A scanning electron microscope image of an activated mast cell. This image illustrates the interesting topography of the cell membrane, which is populated with receptors. Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico View MediaFloral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 1)
6553
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a sma L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885 View MediaIsolated Planarian Pharynx
3593
The feeding tube, or pharynx, of a planarian worm with cilia shown in red and muscle fibers shown in green View Media