Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
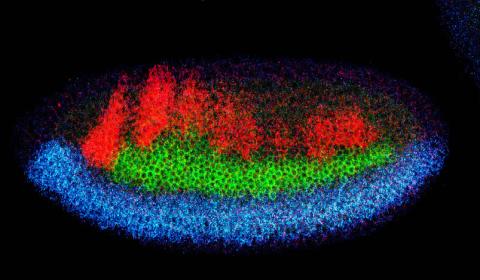
2327: Neural development
2327: Neural development
Using techniques that took 4 years to design, a team of developmental biologists showed that certain proteins can direct the subdivision of fruit fly and chicken nervous system tissue into the regions depicted here in blue, green, and red. Molecules called bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) helped form this fruit fly embryo. While scientists knew that BMPs play a major role earlier in embryonic development, they didn't know how the proteins help organize nervous tissue. The findings suggest that BMPs are part of an evolutionarily conserved mechanism for organizing the nervous system. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke also supported this work.
Mieko Mizutani and Ethan Bier, University of California, San Diego, and Henk Roelink, University of Washington
View Media

5758: Migrating pigment cells
5758: Migrating pigment cells
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. In fishes and amphibians, like frogs and salamanders, pigment cells are responsible for the characteristic skin patterns that help these organisms to blend into their surroundings or attract mates. The pigment cells are derived from neural crest cells, which are cells originating from the neural tube in the early embryo. This image shows neural crest cell-derived, migrating pigment cells in a salamander. Investigating pigment cell formation and migration in animals helps answer important fundamental questions about the factors that control pigmentation in the skin of animals, including humans. Related to images 5754, 5755, 5756 and 5757.
David Parichy, University of Washington
View Media
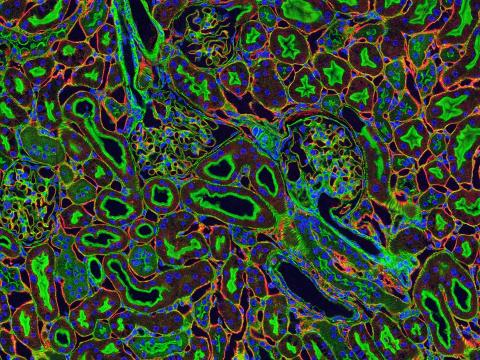
3675: NCMIR kidney-1
3675: NCMIR kidney-1
Stained kidney tissue. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. It also secretes two hormones, erythropoietin (EPO) and calcitriol (a derivative of vitamin D), into the blood. It works like a purifier by pulling break-down products of metabolism, such as urea and ammonium, from the blood stream for excretion in urine. Related to image 3725.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
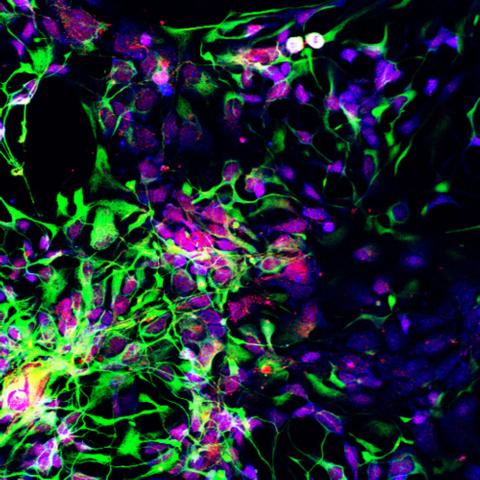
3280: Motor neuron progenitors derived from human ES cells
3280: Motor neuron progenitors derived from human ES cells
Motor neuron progenitors (green) were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Hans Keirstead lab, University of California, Irvine, via CIRM
View Media
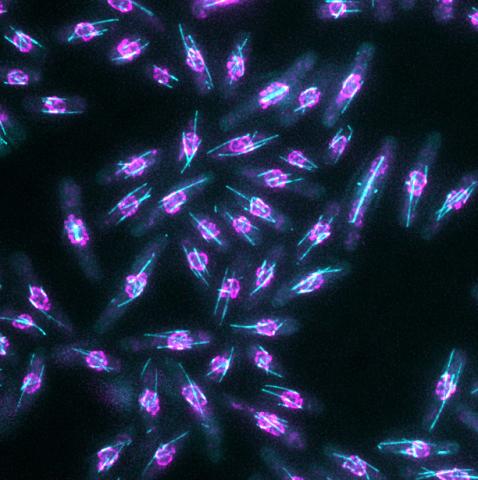
6798: Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
6798: Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes shown in magenta and tubulin shown in light blue. The nuclear envelope defines the borders of the nucleus, which houses DNA. Tubulin is a protein that makes up microtubules—strong, hollow fibers that provide structure to cells and help direct chromosomes during cell division. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University.
View Media
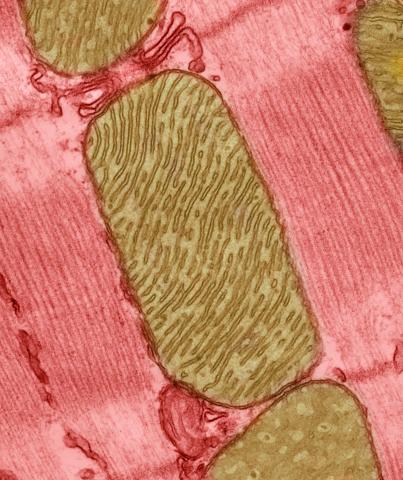
3664: Mitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
3664: Mitochondria from rat heart muscle cell_2
These mitochondria (brown) are from the heart muscle cell of a rat. Mitochondria have an inner membrane that folds in many places (and that appears here as striations). This folding vastly increases the surface area for energy production. Nearly all our cells have mitochondria. Related to image 3661.
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research
View Media
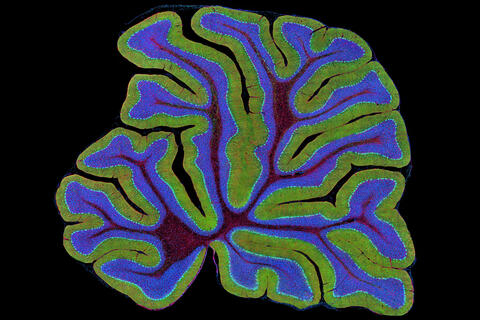
3639: Cerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
3639: Cerebellum: the brain's locomotion control center
The cerebellum of a mouse is shown here in cross-section. The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Every time you shoot a basketball, tie your shoe or chop an onion, your cerebellum fires into action. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. People with damage to this region of the brain often have difficulty with balance, coordination and fine motor skills. For a higher magnification, see image 3371.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Thomas Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego
View Media
6539: Pathways: What is Basic Science?
6539: Pathways: What is Basic Science?
Learn about basic science, sometimes called “pure” or “fundamental” science, and how it contributes to the development of medical treatments. Discover more resources from NIGMS’ Pathways collaboration with Scholastic. View the video on YouTube for closed captioning.
National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
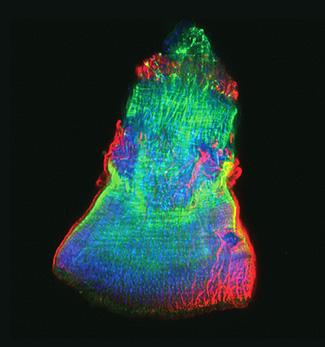
3593: Isolated Planarian Pharynx
3593: Isolated Planarian Pharynx
The feeding tube, or pharynx, of a planarian worm with cilia shown in red and muscle fibers shown in green
View Media
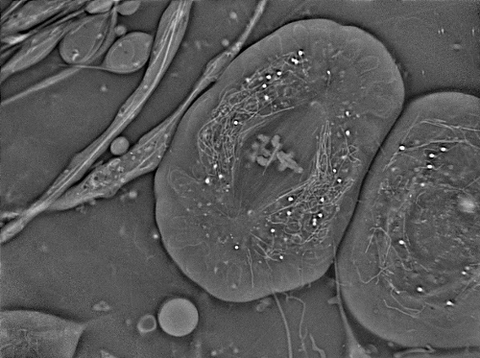
6898: Crane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
6898: Crane fly spermatocyte undergoing meiosis
A crane fly spermatocyte during metaphase of meiosis-I, a step in the production of sperm. A meiotic spindle pulls apart three pairs of autosomal chromosomes, along with a sex chromosome on the right. Tubular mitochondria surround the spindle and chromosomes. This video was captured with quantitative orientation-independent differential interference contrast and is a time lapse showing a 1-second image taken every 30 seconds over the course of 30 minutes.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the J. Biomed Opt. paper “Orientation-Independent Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscopy and Its Combination with Orientation-Independent Polarization System” by Shribak et. al.
More information about the research that produced this video can be found in the J. Biomed Opt. paper “Orientation-Independent Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscopy and Its Combination with Orientation-Independent Polarization System” by Shribak et. al.
Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago.
View Media
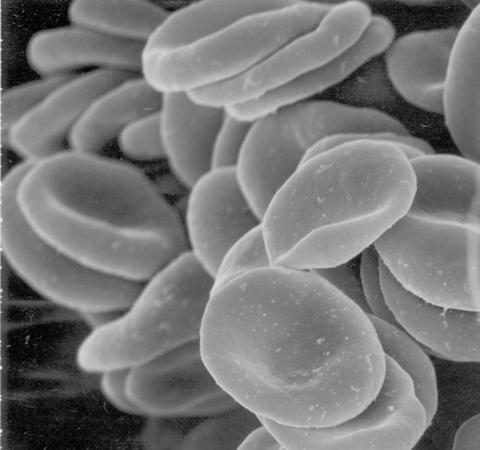
1101: Red blood cells
1101: Red blood cells
This image of human red blood cells was obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope, an instrument that uses a finely focused electron beam to yield detailed images of the surface of a sample.
Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa
View Media
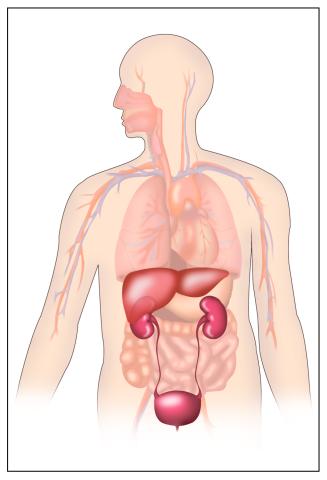
2496: Body toxins
2496: Body toxins
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. See image 2497 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
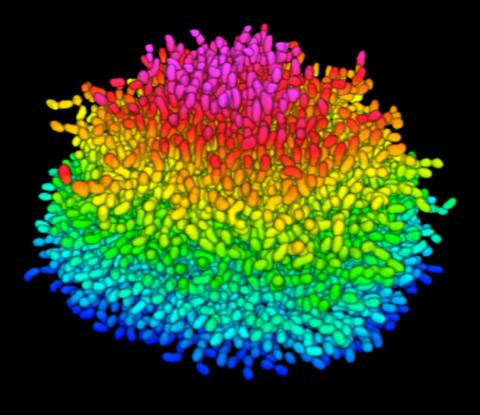
5825: A Growing Bacterial Biofilm
5825: A Growing Bacterial Biofilm
A growing Vibrio cholerae (cholera) biofilm. Cholera bacteria form colonies called biofilms that enable them to resist antibiotic therapy within the body and other challenges to their growth.
Each slightly curved comma shape represents an individual bacterium from assembled confocal microscopy images. Different colors show each bacterium’s position in the biofilm in relation to the surface on which the film is growing.
Each slightly curved comma shape represents an individual bacterium from assembled confocal microscopy images. Different colors show each bacterium’s position in the biofilm in relation to the surface on which the film is growing.
Jing Yan, Ph.D., and Bonnie Bassler, Ph.D., Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ.
View Media
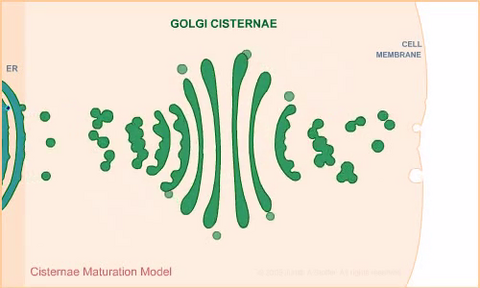
1307: Cisternae maturation model
1307: Cisternae maturation model
Animation for the cisternae maturation model of Golgi transport.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
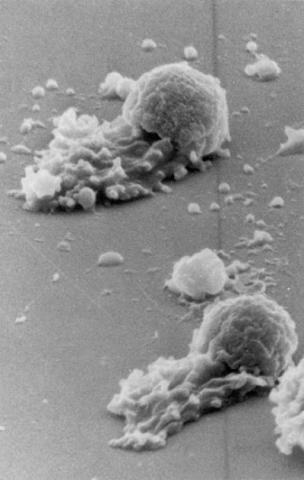
3489: Worm sperm
3489: Worm sperm
To develop a system for studying cell motility in unnatrual conditions -- a microscope slide instead of the body -- Tom Roberts and Katsuya Shimabukuro at Florida State University disassembled and reconstituted the motility parts used by worm sperm cells.
Tom Roberts, Florida State University
View Media
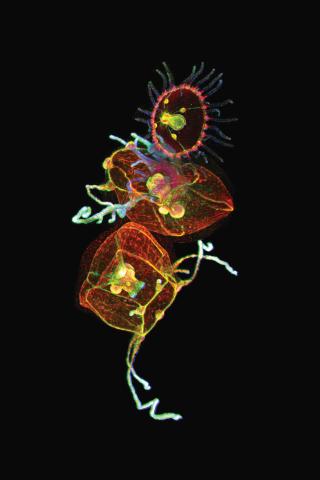
3636: Jellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
3636: Jellyfish, viewed with ZEISS Lightsheet Z.1 microscope
Jellyfish are especially good models for studying the evolution of embryonic tissue layers. Despite being primitive, jellyfish have a nervous system (stained green here) and musculature (red). Cell nuclei are stained blue. By studying how tissues are distributed in this simple organism, scientists can learn about the evolution of the shapes and features of diverse animals.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Helena Parra, Pompeu Fabra University, Spain
View Media

6344: Drosophila
6344: Drosophila
Two adult fruit flies (Drosophila)
Dr. Vicki Losick, MDI Biological Laboratory, www.mdibl.org
View Media
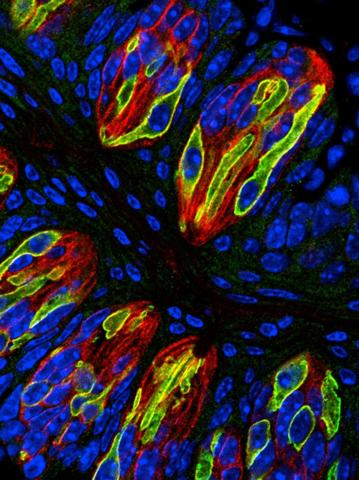
3444: Taste buds signal different tastes through ATP release
3444: Taste buds signal different tastes through ATP release
Taste buds in a mouse tongue epithelium with types I, II, and III taste cells visualized by cell-type-specific fluorescent antibodies. Type II taste bud cells signal sweet, bitter, and umami tastes to the central nervous system by releasing ATP through the voltage-gated ion channel CALHM1. Researchers used a confocal microscope to capture this image, which shows all taste buds in red, type II taste buds in green, and DNA in blue.
More information about this work can be found in the Nature letter "CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes” by Taruno et. al.
More information about this work can be found in the Nature letter "CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes” by Taruno et. al.
Aki Taruno, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania
View Media
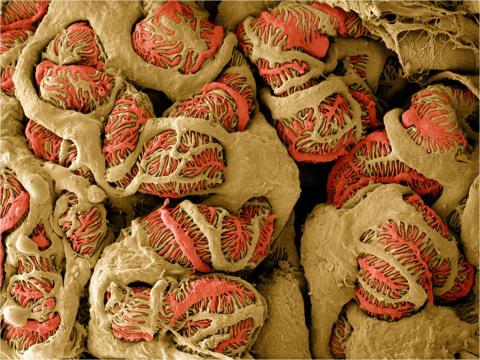
3392: NCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
3392: NCMIR Kidney Glomeruli
Stained glomeruli in the kidney. The kidney is an essential organ responsible for disposing wastes from the body and for maintaining healthy ion levels in the blood. It works like a purifier by pulling break-down products of metabolism, such as urea and ammonium, from the bloodstream for excretion in urine. The glomerulus is a structure that helps filter the waste compounds from the blood. It consists of a network of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman's capsule of a nephron, which is the structure in which ions exit or re-enter the blood in the kidney.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
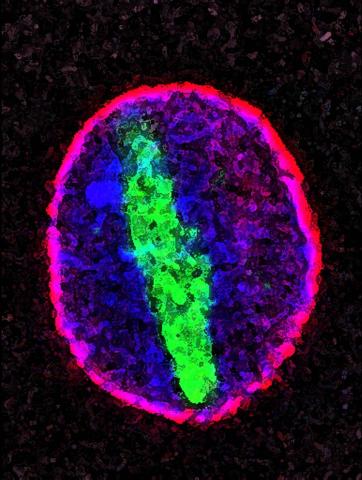
2578: Cellular aging
2578: Cellular aging
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Normally, this protein is kept out of the nucleus with the help of gatekeepers known as nuclear pore complexes. But NIGMS-funded researchers found that wear and tear to long-lived components of the complexes eventually lowers the gatekeepers' guard. As a result, cytoplasmic proteins like tubulin gain entry to the nucleus while proteins normally confined to the nucleus seep out. The work suggests that finding ways to stop the leakage could slow the cellular aging process and possibly lead to new therapies for age-related diseases.
Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute
View Media
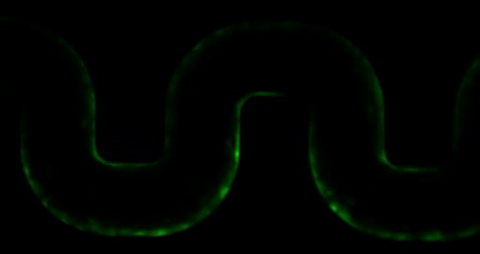
3446: Biofilm blocking fluid flow
3446: Biofilm blocking fluid flow
This time-lapse movie shows that bacterial communities called biofilms can create blockages that prevent fluid flow in devices such as stents and catheters over a period of about 56 hours. This video was featured in a news release from Princeton University.
Bonnie Bassler, Princeton University
View Media
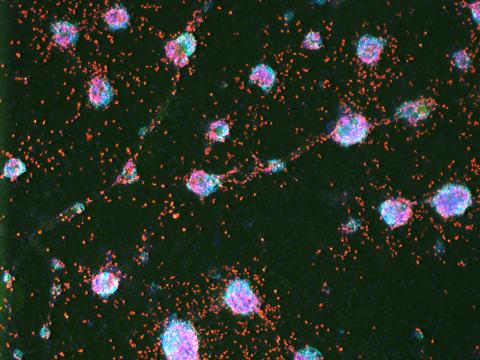
3277: Human ES cells turn into insulin-producing cells
3277: Human ES cells turn into insulin-producing cells
Human embryonic stem cells were differentiated into cells like those found in the pancreas (blue), which give rise to insulin-producing cells (red). When implanted in mice, the stem cell-derived pancreatic cells can replace the insulin that isn't produced in type 1 diabetes. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Eugene Brandon, ViaCyte, via CIRM
View Media
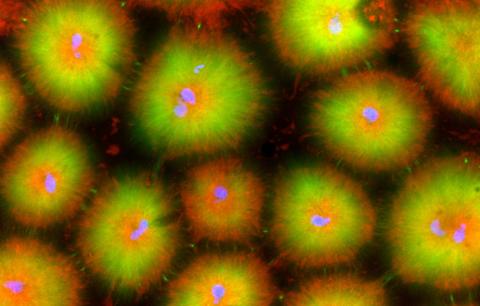
6591: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
6591: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 4
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Image created using confocal microscopy.
For more photos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6584, 6585, 6586, 6592, and 6593.
For videos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6587, 6588, 6589, and 6590.
Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine.
View Media
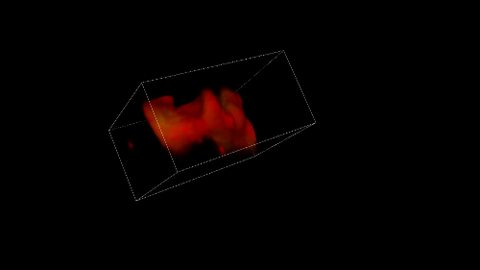
5877: Misfolded proteins in mitochondria, 3-D video
5877: Misfolded proteins in mitochondria, 3-D video
Three-dimensional image of misfolded proteins (green) within mitochondria (red). Related to image 5878. Learn more in this press release by The American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Rong Li, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University
View Media
2763: Fused, dicentric chromosomes
2763: Fused, dicentric chromosomes
This fused chromosome has two functional centromeres, shown as two sets of red and green dots. Centromeres are DNA/protein complexes that are key to splitting the chromosomes evenly during cell division. When dicentric chromosomes like this one are formed in a person, fertility problems or other difficulties may arise. Normal chromosomes carrying a single centromere (one set of red and green dots) are also visible in this image.
Beth A. Sullivan, Duke University
View Media
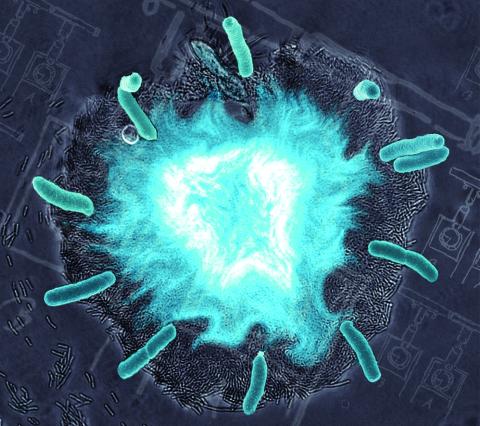
2725: Supernova bacteria
2725: Supernova bacteria
Bacteria engineered to act as genetic clocks flash in synchrony. Here, a "supernova" burst in a colony of coupled genetic clocks just after reaching critical cell density. Superimposed: A diagram from the notebook of Christiaan Huygens, who first characterized synchronized oscillators in the 17th century.
Jeff Hasty, UCSD
View Media
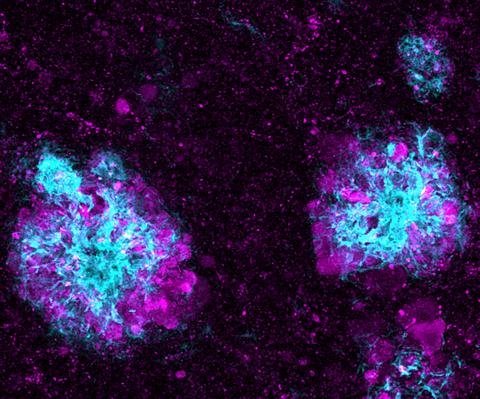
5771: Lysosome clusters around amyloid plaques
5771: Lysosome clusters around amyloid plaques
It's probably most people's least favorite activity, but we still need to do it--take out our trash. Otherwise our homes will get cluttered and smelly, and eventually, we'll get sick. The same is true for our cells: garbage disposal is an ongoing and essential activity, and our cells have a dedicated waste-management system that helps keep them clean and neat. One major waste-removal agent in the cell is the lysosome. Lysosomes are small structures, called organelles, and help the body to dispose of proteins and other molecules that have become damaged or worn out.
This image shows a massive accumulation of lysosomes (visualized with LAMP1 immunofluorescence, in purple) within nerve cells that surround amyloid plaques (visualized with beta-amyloid immunofluorescence, in light blue) in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Scientists have linked accumulation of lysosomes around amyloid plaques to impaired waste disposal in nerve cells, ultimately resulting in cell death.
This image shows a massive accumulation of lysosomes (visualized with LAMP1 immunofluorescence, in purple) within nerve cells that surround amyloid plaques (visualized with beta-amyloid immunofluorescence, in light blue) in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Scientists have linked accumulation of lysosomes around amyloid plaques to impaired waste disposal in nerve cells, ultimately resulting in cell death.
Swetha Gowrishankar and Shawn Ferguson, Yale School of Medicine
View Media

1313: Cell eyes clock
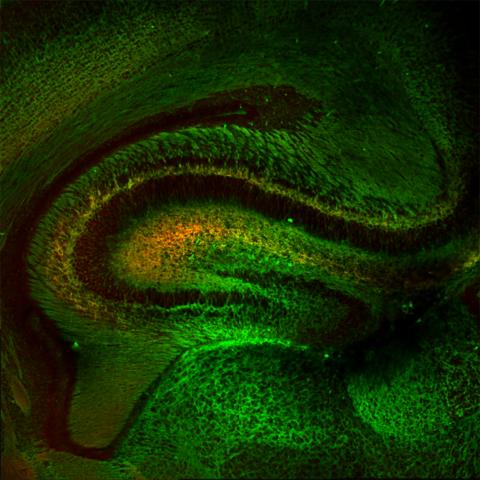
5886: Mouse Brain Cross Section
5886: Mouse Brain Cross Section
The brain sections are treated with fluorescent antibodies specific to a particular protein and visualized using serial electron microscopy (SEM).
Anton Maximov, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA
View Media
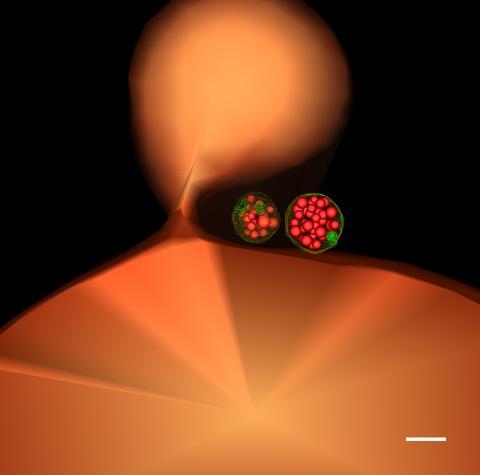
5769: Multivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 1
5769: Multivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 1
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. One key player in that process is the endosome, which helps collect, sort and transport worn-out or leftover proteins with the help of a protein assembly called the endosomal sorting complexes for transport (or ESCRT for short). These complexes help package proteins marked for breakdown into intralumenal vesicles, which, in turn, are enclosed in multivesicular bodies for transport to the places where the proteins are recycled or dumped. In this image, two multivesicular bodies (with yellow membranes) contain tiny intralumenal vesicles (with a diameter of only 25 nanometers; shown in red) adjacent to the cell's vacuole (in orange).
Scientists working with baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) study the budding inward of the limiting membrane (green lines on top of the yellow lines) into the intralumenal vesicles. This tomogram was shot with a Tecnai F-20 high-energy electron microscope, at 29,000x magnification, with a 0.7-nm pixel, ~4-nm resolution.
To learn more about endosomes, see the Biomedical Beat blog post The Cell’s Mailroom. Related to a microscopy photograph 5768 that was used to generate this illustration and a zoomed-in version 5767 of this illustration.
Scientists working with baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) study the budding inward of the limiting membrane (green lines on top of the yellow lines) into the intralumenal vesicles. This tomogram was shot with a Tecnai F-20 high-energy electron microscope, at 29,000x magnification, with a 0.7-nm pixel, ~4-nm resolution.
To learn more about endosomes, see the Biomedical Beat blog post The Cell’s Mailroom. Related to a microscopy photograph 5768 that was used to generate this illustration and a zoomed-in version 5767 of this illustration.
Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado
View Media
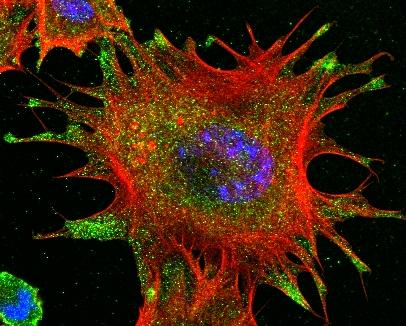
3331: mDia1 antibody staining- 02
3331: mDia1 antibody staining- 02
Cells move forward with lamellipodia and filopodia supported by networks and bundles of actin filaments. Proper, controlled cell movement is a complex process. Recent research has shown that an actin-polymerizing factor called the Arp2/3 complex is the key component of the actin polymerization engine that drives amoeboid cell motility. ARPC3, a component of the Arp2/3 complex, plays a critical role in actin nucleation. In this photo, the ARPC3-/- fibroblast cells were fixed and stained with Alexa 546 phalloidin for F-actin (red), mDia1 (green), and DAPI to visualize the nucleus (blue). In ARPC3-/- fibroblast cells, mDia1 is localized at the tips of the filopodia-like structures. Related to images 3328, 3329, 3330, 3332, and 3333.
Rong Li and Praveen Suraneni, Stowers Institute for Medical Research
View Media
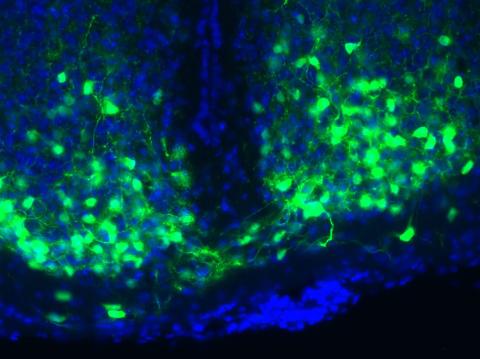
3547: Master clock of the mouse brain
3547: Master clock of the mouse brain
An image of the area of the mouse brain that serves as the 'master clock,' which houses the brain's time-keeping neurons. The nuclei of the clock cells are shown in blue. A small molecule called VIP, shown in green, enables neurons in the central clock in the mammalian brain to synchronize.
Erik Herzog, Washington University in St. Louis
View Media
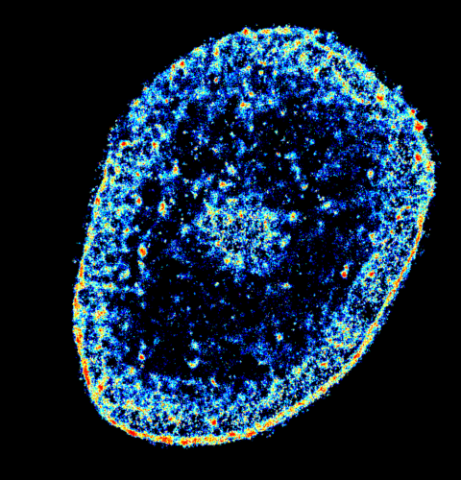
6893: Chromatin in human tenocyte
6893: Chromatin in human tenocyte
The nucleus of a degenerating human tendon cell, also known as a tenocyte. It has been color-coded based on the density of chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins. Areas of low chromatin density are shown in blue, and areas of high chromatin density are shown in red. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6887 and 6888.
Related to images 6887 and 6888.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
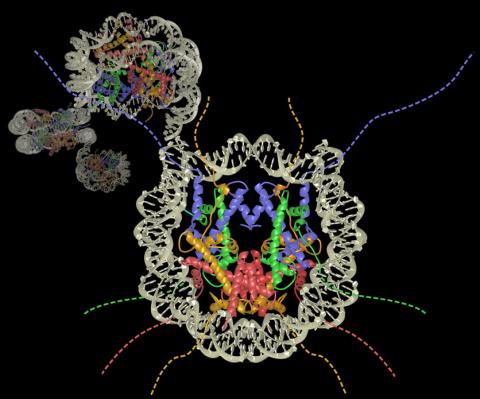
2741: Nucleosome
2741: Nucleosome
Like a strand of white pearls, DNA wraps around an assembly of special proteins called histones (colored) to form the nucleosome, a structure responsible for regulating genes and condensing DNA strands to fit into the cell's nucleus. Researchers once thought that nucleosomes regulated gene activity through their histone tails (dotted lines), but a 2010 study revealed that the structures' core also plays a role. The finding sheds light on how gene expression is regulated and how abnormal gene regulation can lead to cancer.
Karolin Luger, Colorado State University
View Media
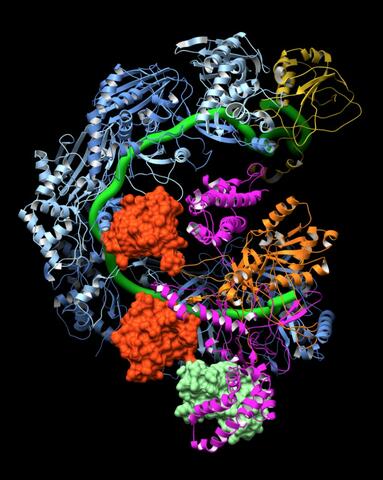
6352: CRISPR surveillance complex
6352: CRISPR surveillance complex
This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). These anti-CRISPRs block access to the CRISPR RNA (green tube) preventing the surveillance complex from scanning and targeting invading viral DNA for destruction.
NRAMM National Resource for Automated Molecular Microscopy http://nramm.nysbc.org/nramm-images/ Source: Bridget Carragher
View Media
6555: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 2)
6555: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 2)
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a small inoculum in the center of a Petri dish.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6553 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6553 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885
View Media
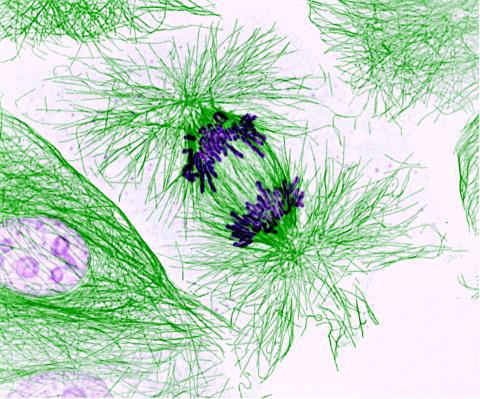
3631: Dividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
3631: Dividing cells showing chromosomes and cell skeleton
This pig cell is in the process of dividing. The chromosomes (purple) have already replicated and the duplicates are being pulled apart by fibers of the cell skeleton known as microtubules (green). Studies of cell division yield knowledge that is critical to advancing understanding of many human diseases, including cancer and birth defects.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Nasser Rusan, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health
View Media
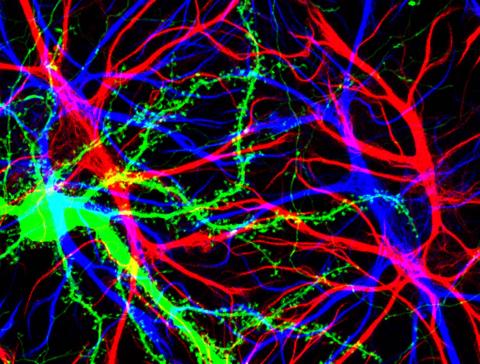
3688: Brain cells in the hippocampus
3688: Brain cells in the hippocampus
Hippocampal cells in culture with a neuron in green, showing hundreds of the small protrusions known as dendritic spines. The dendrites of other neurons are labeled in blue, and adjacent glial cells are shown in red.
Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego
View Media

1283: Vesicle traffic
1283: Vesicle traffic
This illustration shows vesicle traffic inside a cell. The double membrane that bounds the nucleus flows into the ribosome-studded rough endoplasmic reticulum (purple), where membrane-embedded proteins are manufactured. Proteins are processed and lipids are manufactured in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (blue) and Golgi apparatus (green). Vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane release their contents outside the cell. The cell can also take in material from outside by having vesicles pinch off from the cell membrane.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
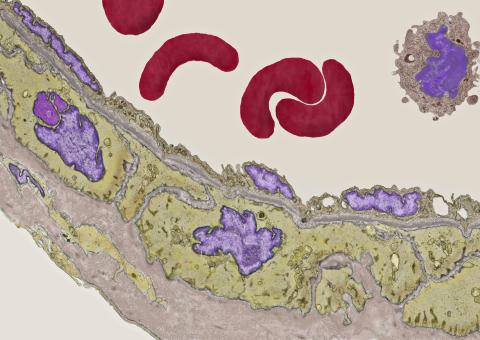
3738: Transmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
3738: Transmission electron microscopy of coronary artery wall with elastin-rich ECM pseudocolored in light brown
Elastin is a fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is abundant in artery walls like the one shown here. As its name indicates, elastin confers elasticity. Elastin fibers are at least five times stretchier than rubber bands of the same size. Tissues that expand, such as blood vessels and lungs, need to be both strong and elastic, so they contain both collagen (another ECM protein) and elastin. In this photo, the elastin-rich ECM is colored grayish brown and is most visible at the bottom of the photo. The curved red structures near the top of the image are red blood cells.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
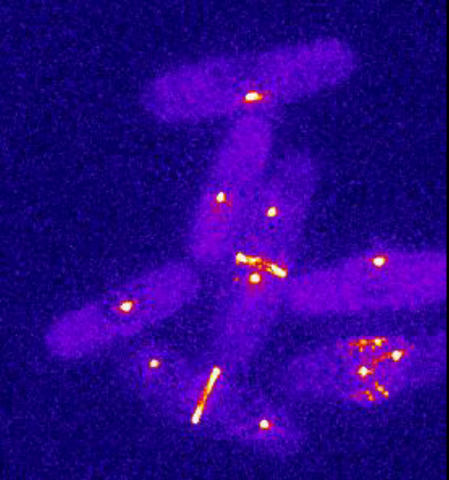

6796: Dividing yeast cells with spindle pole bodies and contractile rings
6796: Dividing yeast cells with spindle pole bodies and contractile rings
During cell division, spindle pole bodies (glowing dots) move toward the ends of yeast cells to separate copied genetic information. Contractile rings (glowing bands) form in cells’ middles and constrict to help them split. This time-lapse video was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and video 6795.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, 6798, and video 6795.
Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University.
View Media
6553: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 1)
6553: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 1)
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a small inoculum in the center of a Petri dish.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6555 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6555 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885
View Media
6520: HeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
6520: HeLa cell undergoing division into two daughter cells
Here, a human HeLa cell (a type of immortal cell line used in laboratory experiments) is undergoing cell division. They come from cervical cancer cells that were obtained in 1951 from Henrietta Lacks, a patient at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. The final stage of division, called cytokinesis, occurs after the genomes—shown in yellow—have split into two new daughter cells. The myosin II is a motor protein shown in blue, and the actin filaments, which are types of protein that support cell structure, are shown in red.
Dylan T. Burnette, Ph.D., Vanderbilt University School of Medicine.
View Media
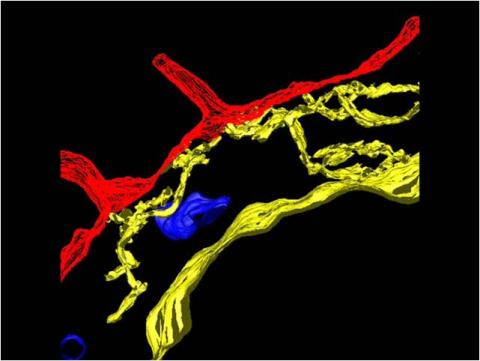
2636: Computer model of cell membrane
2636: Computer model of cell membrane
A computer model of the cell membrane, where the plasma membrane is red, endoplasmic reticulum is yellow, and mitochondria are blue. This image relates to a July 27, 2009 article in Computing Life.
Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico
View Media
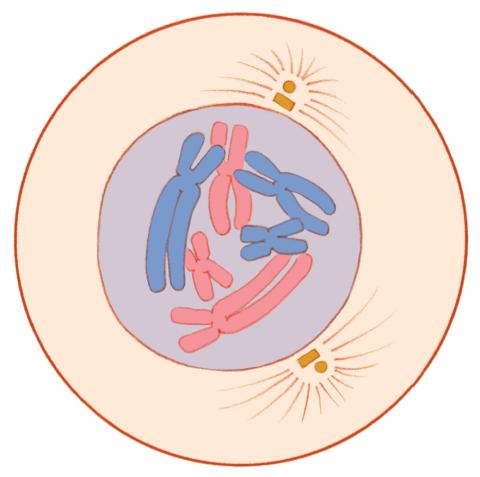
1330: Mitosis - prophase
1330: Mitosis - prophase
A cell in prophase, near the start of mitosis: In the nucleus, chromosomes condense and become visible. In the cytoplasm, the spindle forms. Mitosis is responsible for growth and development, as well as for replacing injured or worn out cells throughout the body. For simplicity, mitosis is illustrated here with only six chromosomes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
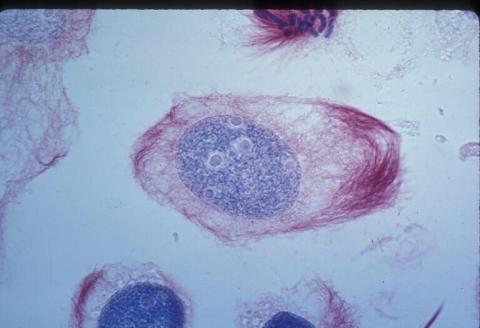
1012: Lily mitosis 02
1012: Lily mitosis 02
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, 1019, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
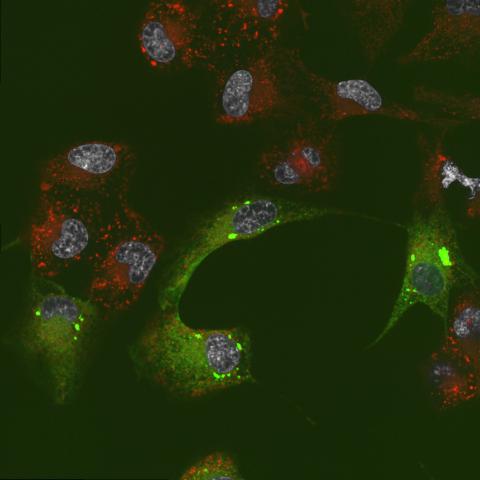
6774: Endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
6774: Endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities 2
Human cells with the gene that codes for the protein FIT2 deleted. After an experimental intervention, they are expressing a nonfunctional version of FIT2, shown in green. The lack of functional FIT2 affected the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and the nonfunctional protein clustered in ER membrane aggregates, seen as large bright-green spots. Lipid droplets are shown in red, and the nucleus is visible in gray. This image was captured using a confocal microscope. Related to image 6773.
Michel Becuwe, Harvard University.
View Media
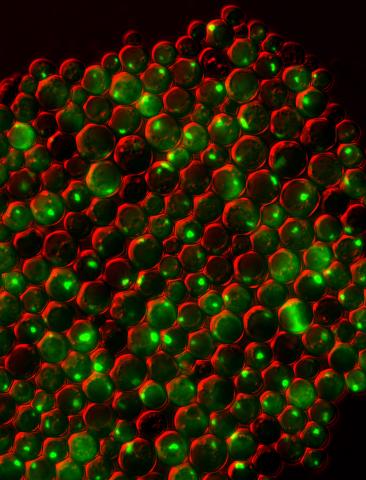
3550: Protein clumping in zinc-deficient yeast cells
3550: Protein clumping in zinc-deficient yeast cells
The green spots in this image are clumps of protein inside yeast cells that are deficient in both zinc and a protein called Tsa1 that prevents clumping. Protein clumping plays a role in many diseases, including Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, where proteins clump together in the brain. Zinc deficiency within a cell can cause proteins to mis-fold and eventually clump together. Normally, in yeast, Tsa1 codes for so-called "chaperone proteins" which help proteins in stressed cells, such as those with a zinc deficiency, fold correctly. The research behind this image was published in 2013 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Colin MacDiarmid and David Eide, University of Wisconsin--Madison
View Media

5810: Tongue 1
5810: Tongue 1
Microscopy image of tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5811
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
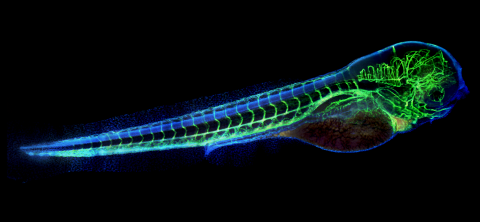
6661: Zebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661: Zebrafish embryo showing vasculature
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. This image was created by stitching together five individual images captured with a hyperspectral multipoint confocal fluorescence microscope that was developed at the Eliceiri Lab.
Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
View Media
