Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
2649: Endoplasmic reticulum
2649: Endoplasmic reticulum
Fluorescent markers show the interconnected web of tubes and compartments in the endoplasmic reticulum. The protein atlastin helps build and maintain this critical part of cells. The image is from a July 2009 news release.
Andrea Daga, Eugenio Medea Scientific Institute (Conegliano, Italy)
View Media
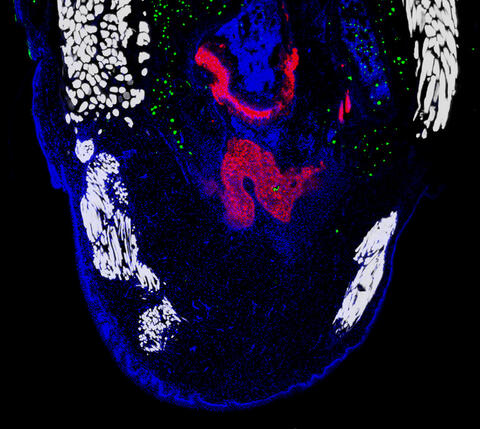
6968: Regenerating lizard tail
6968: Regenerating lizard tail
The interior of a regenerating lizard tail 14 days after the original tail was amputated. Cell nuclei (blue), proliferating cells (green), cartilage (red), and muscle (white) have been visualized with immunofluorescence staining.
Thomas Lozito, University of Southern California.
View Media
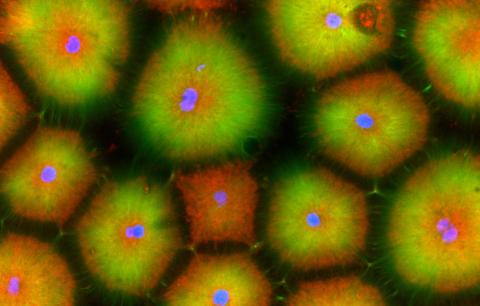
6592: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
6592: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 5
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Image created using confocal microscopy.
For more photos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6584, 6585, 6586, 6591, and 6593.
For videos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6587, 6588, 6589, and 6590.
Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine.
View Media
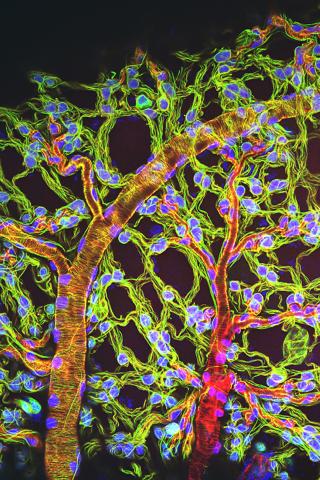
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Unlike mammals, which have red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body, insects have breathing tubes that carry air through their exoskeleton directly to where it's needed. This image shows the breathing tubes embedded in the weblike sheath cells that cover developing egg chambers.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University.
View Media
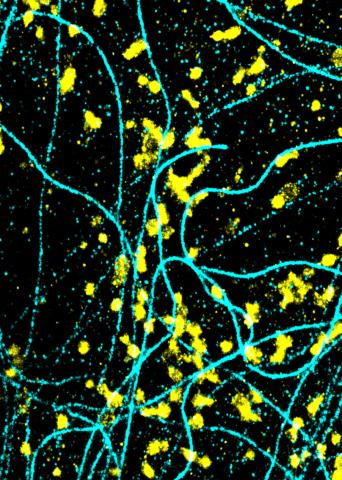
6889: Lysosomes and microtubules
6889: Lysosomes and microtubules
Lysosomes (yellow) and detyrosinated microtubules (light blue). Lysosomes are bubblelike organelles that take in molecules and use enzymes to break them down. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. The researchers who took this image found that in epithelial cells, detyrosinated microtubules are a small subset of fibers, and they concentrate lysosomes around themselves. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6890, 6891, and 6892.
Related to images 6890, 6891, and 6892.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
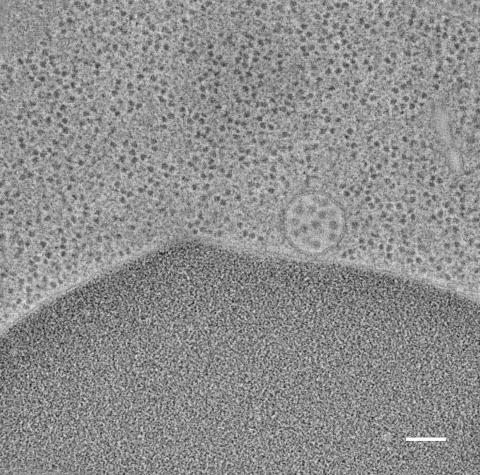
5768: Multivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 2
5768: Multivesicular bodies containing intralumenal vesicles assemble at the vacuole 2
Collecting and transporting cellular waste and sorting it into recylable and nonrecylable pieces is a complex business in the cell. One key player in that process is the endosome, which helps collect, sort and transport worn-out or leftover proteins with the help of a protein assembly called the endosomal sorting complexes for transport (or ESCRT for short). These complexes help package proteins marked for breakdown into intralumenal vesicles, which, in turn, are enclosed in multivesicular bodies for transport to the places where the proteins are recycled or dumped. In this image, a multivesicular body (the round structure slightly to the right of center) contain tiny intralumenal vesicles (with a diameter of only 25 nanometers; the round specks inside the larger round structure) adjacent to the cell's vacuole (below the multivesicular body, shown in darker and more uniform gray).
Scientists working with baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) study the budding inward of the limiting membrane (green lines on top of the yellow lines) into the intralumenal vesicles. This tomogram was shot with a Tecnai F-20 high-energy electron microscope, at 29,000x magnification, with a 0.7-nm pixel, ~4-nm resolution.
To learn more about endosomes, see the Biomedical Beat blog post The Cell’s Mailroom. Related to a color-enhanced version 5767 and image 5769.
Scientists working with baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) study the budding inward of the limiting membrane (green lines on top of the yellow lines) into the intralumenal vesicles. This tomogram was shot with a Tecnai F-20 high-energy electron microscope, at 29,000x magnification, with a 0.7-nm pixel, ~4-nm resolution.
To learn more about endosomes, see the Biomedical Beat blog post The Cell’s Mailroom. Related to a color-enhanced version 5767 and image 5769.
Matthew West and Greg Odorizzi, University of Colorado
View Media
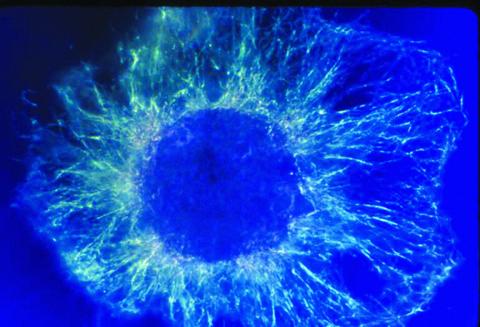
1058: Lily mitosis 01
1058: Lily mitosis 01
A light microscope image shows the chromosomes, stained dark blue, in a dividing cell of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
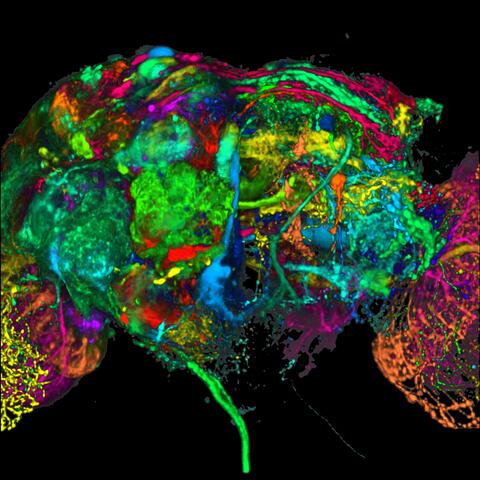
5868: Color coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
5868: Color coding of the Drosophila brain - black background
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. First, researchers collected several thousand fruit fly larvae and fluorescently stained a random stem cell in the brain of each. The idea was to create a population of larvae in which each of the 100 or so neural stem cells was labeled at least once. When the larvae grew to adults, the researchers examined the flies’ brains using confocal microscopy. With this technique, the part of a fly’s brain that derived from a single, labeled stem cell “lights up.” The scientists photographed each brain and digitally colorized its lit-up area. By combining thousands of such photos, they created a three-dimensional, color-coded map that shows which part of the Drosophila brain comes from each of its ~100 neural stem cells. In other words, each colored region shows which neurons are the progeny or “clones” of a single stem cell. This work established a hierarchical structure as well as nomenclature for the neurons in the Drosophila brain. Further research will relate functions to structures of the brain.
Related to image 5838 and video 5843.
Related to image 5838 and video 5843.
Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo.
View Media
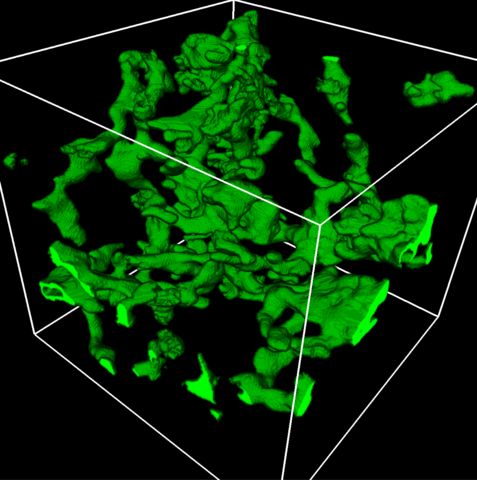
5857: 3D reconstruction of a tubular matrix in peripheral endoplasmic reticulum
5857: 3D reconstruction of a tubular matrix in peripheral endoplasmic reticulum
Detailed three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular matrix in a thin section of the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum between the plasma membranes of the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane that extends like a net from the envelope of the nucleus outward to the cell membrane. The ER plays several roles within the cell, such as in protein and lipid synthesis and transport of materials between organelles. Shown here is a three-dimensional representation of the peripheral ER microtubules. Related to images 5855 and 5856
Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, Virginia
View Media
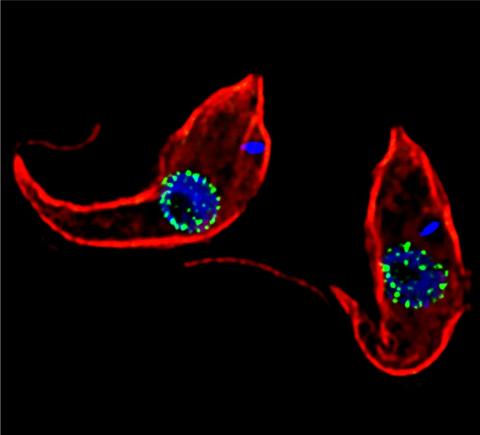
3765: Trypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
3765: Trypanosoma brucei, the cause of sleeping sickness
Trypanosoma brucei is a single-cell parasite that causes sleeping sickness in humans. Scientists have been studying trypanosomes for some time because of their negative effects on human and also animal health, especially in sub-Saharan Africa. Moreover, because these organisms evolved on a separate path from those of animals and plants more than a billion years ago, researchers study trypanosomes to find out what traits they may harbor that are common to or different from those of other eukaryotes (i.e., those organisms having a nucleus and mitochondria). This image shows the T. brucei cell membrane in red, the DNA in the nucleus and kinetoplast (a structure unique to protozoans, including trypanosomes, which contains mitochondrial DNA) in blue and nuclear pore complexes (which allow molecules to pass into or out of the nucleus) in green. Scientists have found that the trypanosome nuclear pore complex has a unique mechanism by which it attaches to the nuclear envelope. In addition, the trypanosome nuclear pore complex differs from those of other eukaryotes because its components have a near-complete symmetry, and it lacks almost all of the proteins that in other eukaryotes studied so far are required to assemble the pore.
Michael Rout, Rockefeller University
View Media
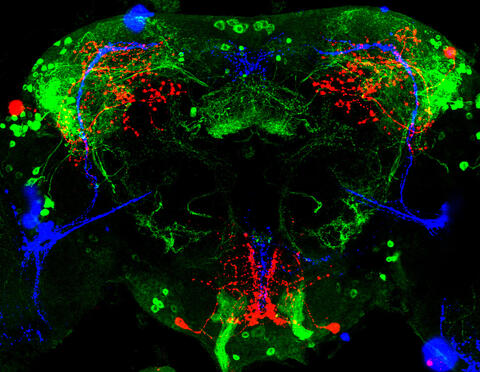
3754: Circadian rhythm neurons in the fruit fly brain
3754: Circadian rhythm neurons in the fruit fly brain
Some nerve cells (neurons) in the brain keep track of the daily cycle. This time-keeping mechanism, called the circadian clock, is found in all animals including us. The circadian clock controls our daily activities such as sleep and wakefulness. Researchers are interested in finding the neuron circuits involved in this time keeping and how the information about daily time in the brain is relayed to the rest of the body. In this image of a brain of the fruit fly Drosophila the time-of-day information flowing through the brain has been visualized by staining the neurons involved: clock neurons (shown in blue) function as "pacemakers" by communicating with neurons that produce a short protein called leucokinin (LK) (red), which, in turn, relays the time signal to other neurons, called LK-R neurons (green). This signaling cascade set in motion by the pacemaker neurons helps synchronize the fly's daily activity with the 24-hour cycle. To learn more about what scientists have found out about circadian pacemaker neurons in the fruit fly see this news release by New York University. This work was featured in the Biomedical Beat blog post Cool Image: A Circadian Circuit.
Justin Blau, New York University
View Media
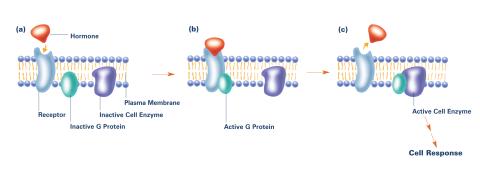
2538: G switch (with labels and stages)
2538: G switch (with labels and stages)
The G switch allows our bodies to respond rapidly to hormones. G proteins act like relay batons to pass messages from circulating hormones into cells. A hormone (red) encounters a receptor (blue) in the membrane of a cell. Next, a G protein (green) becomes activated and makes contact with the receptor to which the hormone is attached. Finally, the G protein passes the hormone's message to the cell by switching on a cell enzyme (purple) that triggers a response. See image 2536 and 2537 for other versions of this image. Featured in Medicines By Design.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
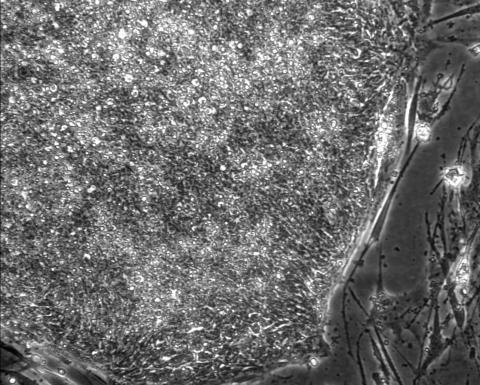
2603: Induced stem cells from adult skin 01
2603: Induced stem cells from adult skin 01
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. The induced stem cells were made potentially safer by removing the introduced genes and the viral vector used to ferry genes into the cells, a loop of DNA called a plasmid. The work was accomplished by geneticist Junying Yu in the laboratory of James Thomson, a University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health professor and the director of regenerative biology for the Morgridge Institute for Research.
James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison
View Media
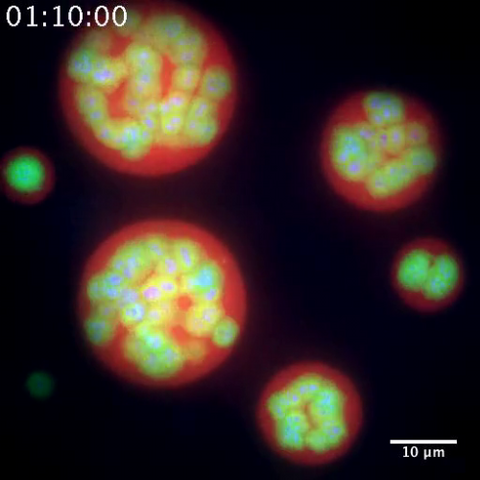
3791: Nucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
3791: Nucleolus subcompartments spontaneously self-assemble 2
The nucleolus is a small but very important protein complex located in the cell's nucleus. It forms on the chromosomes at the location where the genes for the RNAs are that make up the structure of the ribosome, the indispensable cellular machine that makes proteins from messenger RNAs.
However, how the nucleolus grows and maintains its structure has puzzled scientists for some time. It turns out that even though it looks like a simple liquid blob, it's rather well-organized, consisting of three distinct layers: the fibrillar center, where the RNA polymerase is active; the dense fibrillar component, which is enriched in the protein fibrillarin; and the granular component, which contains a protein called nucleophosmin. Researchers have now discovered that this multilayer structure of the nucleolus arises from differences in how the proteins in each compartment mix with water and with each other. These differences let the proteins readily separate from each other into the three nucleolus compartments.
This video of nucleoli in the eggs of a commonly used lab animal, the frog Xenopus laevis, shows how each of the compartments (the granular component is shown in red, the fibrillarin in yellow-green, and the fibrillar center in blue) spontaneously fuse with each other on encounter without mixing with the other compartments.
For more details on this research, see this press release from Princeton. Related to video 3789, image 3792 and image 3793.
However, how the nucleolus grows and maintains its structure has puzzled scientists for some time. It turns out that even though it looks like a simple liquid blob, it's rather well-organized, consisting of three distinct layers: the fibrillar center, where the RNA polymerase is active; the dense fibrillar component, which is enriched in the protein fibrillarin; and the granular component, which contains a protein called nucleophosmin. Researchers have now discovered that this multilayer structure of the nucleolus arises from differences in how the proteins in each compartment mix with water and with each other. These differences let the proteins readily separate from each other into the three nucleolus compartments.
This video of nucleoli in the eggs of a commonly used lab animal, the frog Xenopus laevis, shows how each of the compartments (the granular component is shown in red, the fibrillarin in yellow-green, and the fibrillar center in blue) spontaneously fuse with each other on encounter without mixing with the other compartments.
For more details on this research, see this press release from Princeton. Related to video 3789, image 3792 and image 3793.
Nilesh Vaidya, Princeton University
View Media
2441: Hydra 05
2441: Hydra 05
Hydra magnipapillata is an invertebrate animal used as a model organism to study developmental questions, for example the formation of the body axis.
Hiroshi Shimizu, National Institute of Genetics in Mishima, Japan
View Media
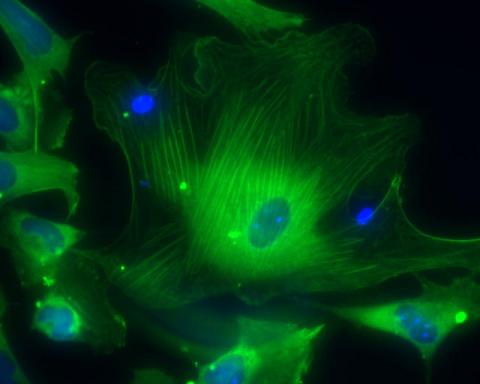
3288: Smooth muscle from human ES cells
3288: Smooth muscle from human ES cells
These smooth muscle cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells. The nuclei are stained blue, and the proteins of the cytoskeleton are stained green. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Alexey Terskikh lab, Burnham Institute for Medical Research, via CIRM
View Media
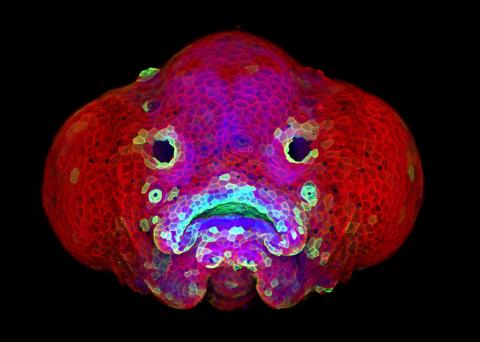
5881: Zebrafish larva
5881: Zebrafish larva
You are face to face with a 6-day-old zebrafish larva. What look like eyes will become nostrils, and the bulges on either side will become eyes. Scientists use fast-growing, transparent zebrafish to see body shapes form and organs develop over the course of just a few days. Images like this one help researchers understand how gene mutations can lead to facial abnormalities such as cleft lip and palate in people.
This image won a 2016 FASEB BioArt award. In addition, NIH Director Francis Collins featured this on his blog on January 26, 2017.
This image won a 2016 FASEB BioArt award. In addition, NIH Director Francis Collins featured this on his blog on January 26, 2017.
Oscar Ruiz and George Eisenhoffer, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston
View Media
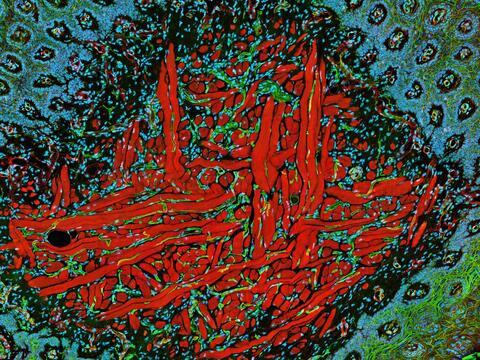
5811: NCMIR Tongue 2
5811: NCMIR Tongue 2
Microscopy image of a tongue. One in a series of two, see image 5810
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
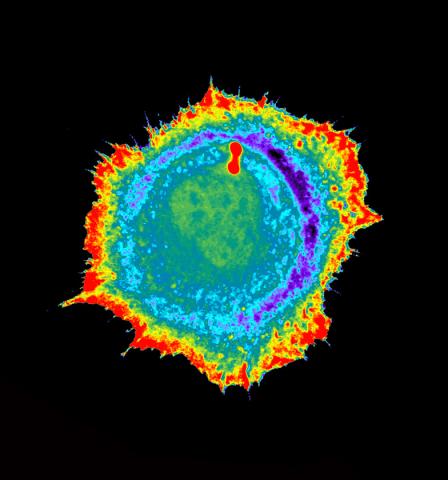
2451: Seeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
2451: Seeing signaling protein activation in cells 01
Cdc42, a member of the Rho family of small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins, regulates multiple cell functions, including motility, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell morphology. In order to fulfill these diverse roles, the timing and location of Cdc42 activation must be tightly controlled. Klaus Hahn and his research group use special dyes designed to report protein conformational changes and interactions, here in living neutrophil cells. Warmer colors in this image indicate higher levels of activation. Cdc42 looks to be activated at cell protrusions.
Related to images 2452, 2453, and 2454.
Related to images 2452, 2453, and 2454.
Klaus Hahn, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Medical School
View Media

2702: Thermotoga maritima and its metabolic network
2702: Thermotoga maritima and its metabolic network
A combination of protein structures determined experimentally and computationally shows us the complete metabolic network of a heat-loving bacterium.
View Media
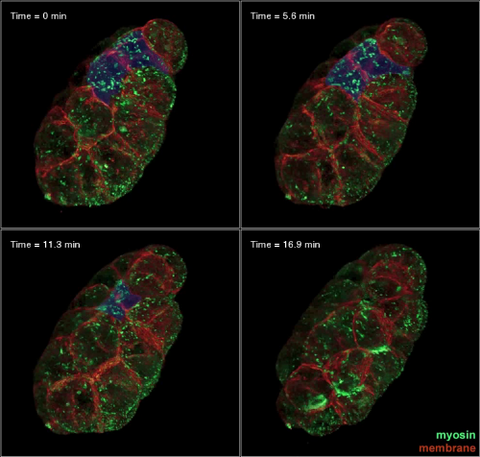
3334: Four timepoints in gastrulation
3334: Four timepoints in gastrulation
It has been said that gastrulation is the most important event in a person's life. This part of early embryonic development transforms a simple ball of cells and begins to define cell fate and the body axis. In a study published in Science magazine, NIGMS grantee Bob Goldstein and his research group studied how contractions of actomyosin filaments in C. elegans and Drosophila embryos lead to dramatic rearrangements of cell and embryonic structure. In these images, myosin (green) and plasma membrane (red) are highlighted at four timepoints in gastrulation in the roundworm C. elegans. The blue highlights in the top three frames show how cells are internalized, and the site of closure around the involuting cells is marked with an arrow in the last frame. See related image 3297.
Bob Goldstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
View Media
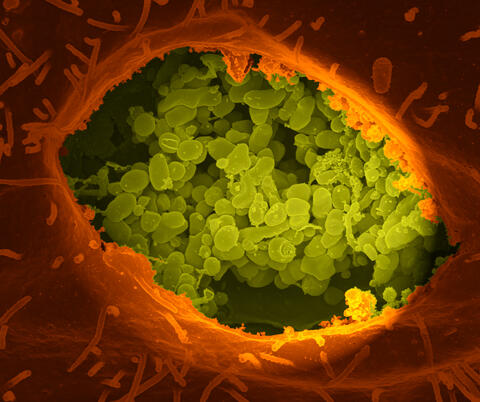
3621: Q fever bacteria in an infected cell
3621: Q fever bacteria in an infected cell
This image shows Q fever bacteria (yellow), which infect cows, sheep, and goats around the world and can infect humans, as well. When caught early, Q fever can be cured with antibiotics. A small fraction of people can develop a more serious, chronic form of the disease.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Robert Heinzen, Elizabeth Fischer, and Anita Mora, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health
View Media
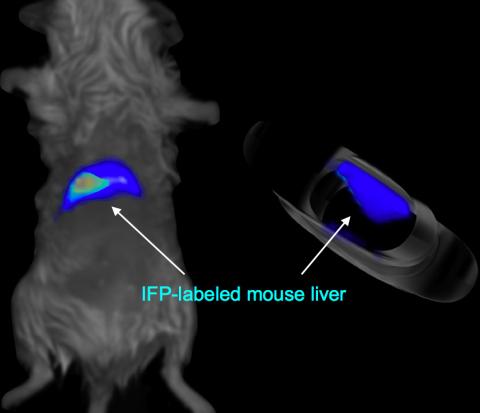
2601: Mouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
2601: Mouse liver labeled with fluorescent probe
A mouse liver glows after being tagged with specially designed infrared-fluorescent protein (IFP). Since its discovery in 1962, green fluorescent protein (GFP) has become an invaluable resource in biomedical imaging. But because of its short wavelength, the light that makes GFP glow doesn't penetrate far in whole animals. So University of California, San Diego cell biologist Roger Tsien--who shared the 2008 Nobel Prize in chemistry for groundbreaking work with GFP--made infrared-fluorescent proteins (IFPs) that shine under longer-wavelength light, allowing whole-body imaging in small animals.
Xiaokun Shu, University of California, San Diego
View Media
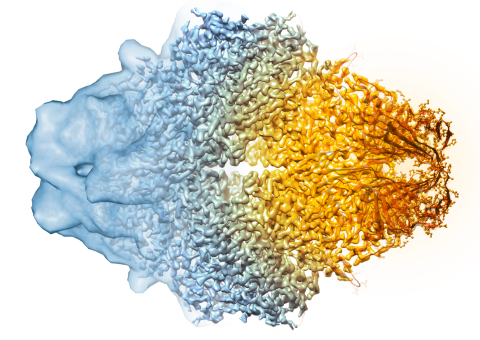
5882: Beta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
5882: Beta-galactosidase montage showing cryo-EM improvement--transparent background
Composite image of beta-galactosidase showing how cryo-EM’s resolution has improved dramatically in recent years. Older images to the left, more recent to the right. Related to image 5883. NIH Director Francis Collins featured this on his blog on January 14, 2016.
Veronica Falconieri, Sriram Subramaniam Lab, National Cancer Institute
View Media
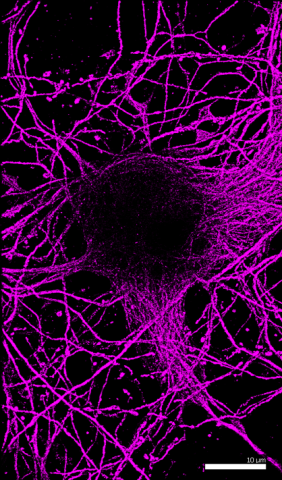
6890: Microtubules in hippocampal neurons
6890: Microtubules in hippocampal neurons
Microtubules (magenta) in neurons of the hippocampus, a part of the brain involved in learning and memory. Microtubules are strong, hollow fibers that provide structural support to cells. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6889, 6891, and 6892.
Related to images 6889, 6891, and 6892.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
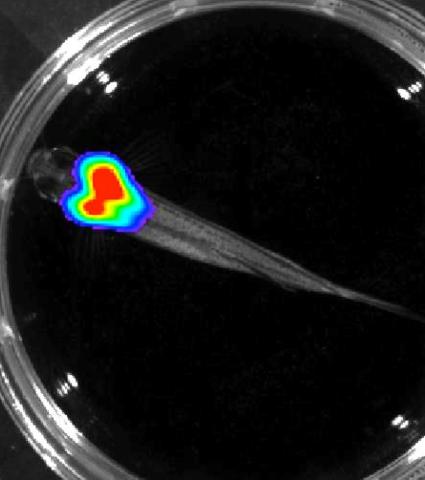
3557: Bioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
3557: Bioluminescent imaging in adult zebrafish - overhead view
Luciferase-based imaging enables visualization and quantification of internal organs and transplanted cells in live adult zebrafish. In this image, a cardiac muscle-restricted promoter drives firefly luciferase expression.
For imagery of both the lateral and overhead view go to 3556.
For imagery of the lateral view go to 3558.
For more information about the illumated area go to 3559.
For imagery of both the lateral and overhead view go to 3556.
For imagery of the lateral view go to 3558.
For more information about the illumated area go to 3559.
Kenneth Poss, Duke University
View Media

6887: Chromatin in human fibroblast
6887: Chromatin in human fibroblast
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Fibroblasts are one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue, and they play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6888 and 6893.
Related to images 6888 and 6893.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
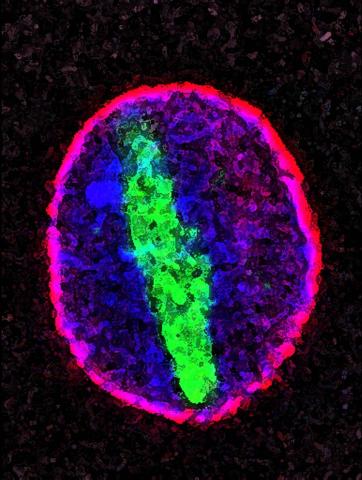
2578: Cellular aging
2578: Cellular aging
A protein called tubulin (green) accumulates in the center of a nucleus (outlined in pink) from an aging cell. Normally, this protein is kept out of the nucleus with the help of gatekeepers known as nuclear pore complexes. But NIGMS-funded researchers found that wear and tear to long-lived components of the complexes eventually lowers the gatekeepers' guard. As a result, cytoplasmic proteins like tubulin gain entry to the nucleus while proteins normally confined to the nucleus seep out. The work suggests that finding ways to stop the leakage could slow the cellular aging process and possibly lead to new therapies for age-related diseases.
Maximiliano D'Angelo and Martin Hetzer, Salk Institute
View Media
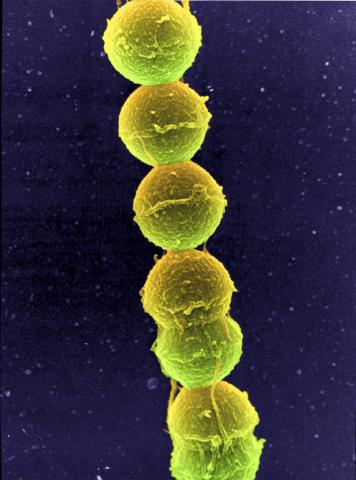
1157: Streptococcus bacteria
1157: Streptococcus bacteria
Image of Streptococcus, a type (genus) of spherical bacteria that can colonize the throat and back of the mouth. Stroptococci often occur in pairs or in chains, as shown here.
Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa
View Media
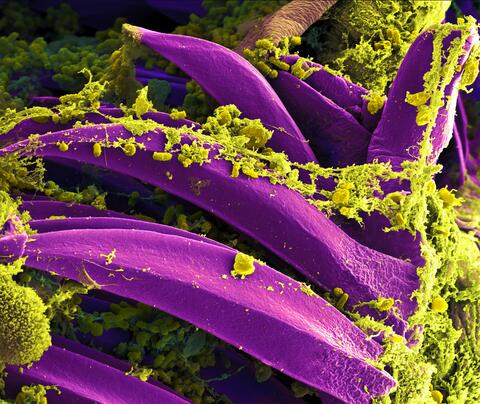
3576: Bubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
3576: Bubonic plague bacteria on part of the digestive system in a rat flea
Here, bubonic plague bacteria (yellow) are shown in the digestive system of a rat flea (purple). The bubonic plague killed a third of Europeans in the mid-14th century. Today, it is still active in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, with as many as 2,000 people infected worldwide each year. If caught early, bubonic plague can be treated with antibiotics.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
NIAID
View Media

1287: Mitochondria
1287: Mitochondria
Bean-shaped mitochondria are cells' power plants. These organelles have their own DNA and replicate independently. The highly folded inner membranes are the site of energy generation.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
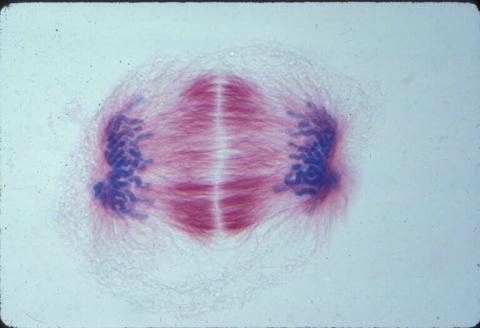
1018: Lily mitosis 12
1018: Lily mitosis 12
A light microscope image of a cell from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue. Here, condensed chromosomes are clearly visible near the end of a round of mitosis.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1019, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1019, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
6555: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 2)
6555: Floral pattern in a mixture of two bacterial species, Acinetobacter baylyi and Escherichia coli, grown on a semi-solid agar for 48 hours (photo 2)
Floral pattern emerging as two bacterial species, motile Acinetobacter baylyi (red) and non-motile Escherichia coli (green), are grown together for 48 hours on 1% agar surface from a small inoculum in the center of a Petri dish.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6553 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
See 6557 for a photo of this process at 24 hours on 0.75% agar surface.
See 6553 for another photo of this process at 48 hours on 1% agar surface.
See 6556 for a photo of this process at 72 hours on 0.5% agar surface.
See 6550 for a video of this process.
L. Xiong et al, eLife 2020;9: e48885
View Media
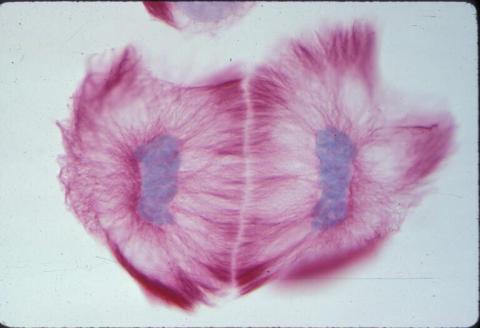
1019: Lily mitosis 13
1019: Lily mitosis 13
A light microscope image of cells from the endosperm of an African globe lily (Scadoxus katherinae). This is one frame of a time-lapse sequence that shows cell division in action. The lily is considered a good organism for studying cell division because its chromosomes are much thicker and easier to see than human ones. Staining shows microtubules in red and chromosomes in blue. Here, two cells have formed after a round of mitosis.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, and 1021.
Related to images 1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, and 1021.
Andrew S. Bajer, University of Oregon, Eugene
View Media
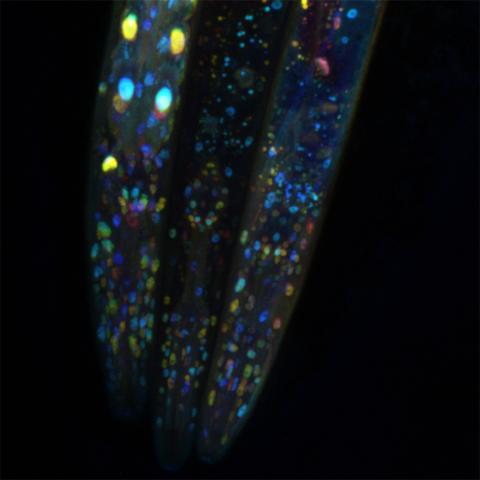
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. The head region of three worms that were genetically modified to express a fluorescent protein were imaged and the images were color-coded based on depth. The worm on the left lacks neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus every cell is fluorescent. In the middle worm, the expression of the fluorescent protein is silenced by neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus most cells are not fluorescent. The worm on the right lacks an enzyme that amplifies RNA for silencing. Surprisingly, the identities of the cells that depend on this enzyme for gene silencing are unpredictable. As a result, worms of identical genotype are nevertheless random mosaics for how the function of gene silencing is carried out. For more, see journal article and press release. Related to image 6534.
Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park
View Media
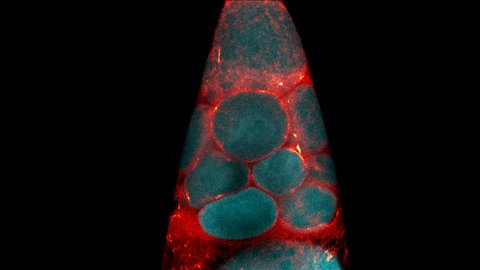
6754: Fruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
6754: Fruit fly nurse cells transporting their contents during egg development
In many animals, the egg cell develops alongside sister cells. These sister cells are called nurse cells in the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), and their job is to “nurse” an immature egg cell, or oocyte. Toward the end of oocyte development, the nurse cells transfer all their contents into the oocyte in a process called nurse cell dumping. This video captures this transfer, showing significant shape changes on the part of the nurse cells (blue), which are powered by wavelike activity of the protein myosin (red). Researchers created the video using a confocal laser scanning microscope. Related to image 6753.
Adam C. Martin, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
View Media
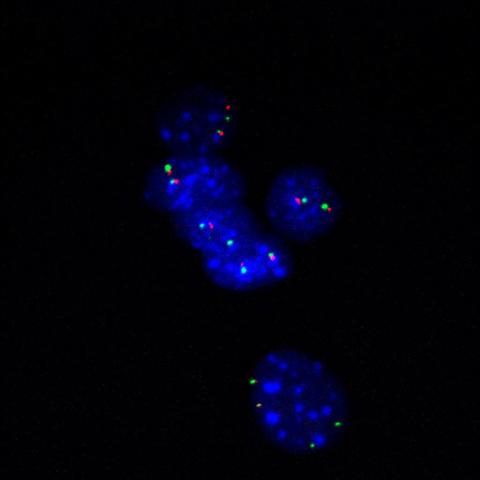
3296: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
3296: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in mouse ES cells shows DNA interactions
Researchers used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to confirm the presence of long range DNA-DNA interactions in mouse embryonic stem cells. Here, two loci labeled in green (Oct4) and red that are 13 Mb apart on linear DNA are frequently found to be in close proximity. DNA-DNA colocalizations like this are thought to both reflect and contribute to cell type specific gene expression programs.
Kathrin Plath, University of California, Los Angeles
View Media
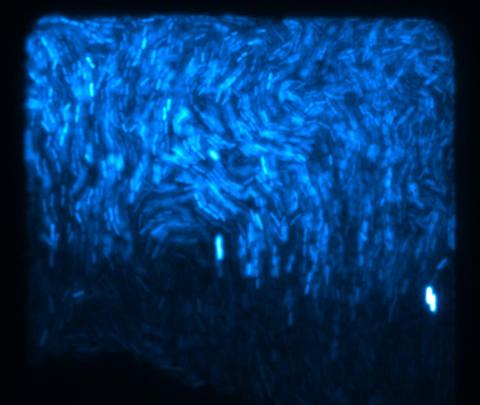
3268: Fluorescent E. coli bacteria
3268: Fluorescent E. coli bacteria
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. They called each blinking bacterial colony a biopixel. Thousands of fluorescent E. coli bacteria, shown here, make up a biopixel. Related to images 3265 and 3266. From a UC San Diego news release, "Researchers create living 'neon signs' composed of millions of glowing bacteria."
Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego
View Media
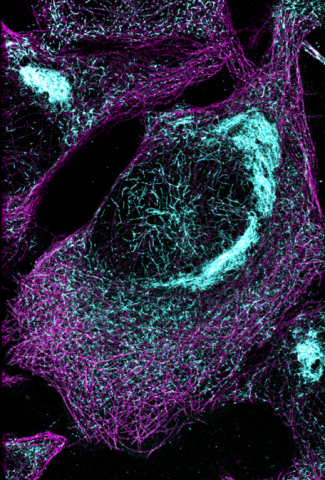
6892: Microtubules and tau aggregates
6892: Microtubules and tau aggregates
Microtubules (magenta) and tau protein (light blue) in a cell model of tauopathy. Researchers believe that tauopathy—the aggregation of tau protein—plays a role in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6889, 6890, and 6891.
Related to images 6889, 6890, and 6891.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media

2714: Stretch detectors
2714: Stretch detectors
Muscles stretch and contract when we walk, and skin splits open and knits back together when we get a paper cut. To study these contractile forces, researchers built a three-dimensional scaffold that mimics tissue in an organism. Researchers poured a mixture of cells and elastic collagen over microscopic posts in a dish. Then they studied how the cells pulled and released the posts as they formed a web of tissue. To measure forces between posts, the researchers developed a computer model. Their findings--which show that contractile forces vary throughout the tissue--could have a wide range of medical applications.
Christopher Chen, University of Pennsylvania
View Media
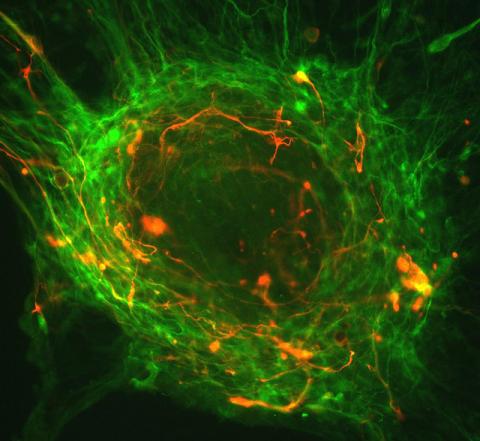
3276: Human ES cells differentiating into neurons
3276: Human ES cells differentiating into neurons
This image shows hundreds of human embryonic stem cells in various stages of differentiating into neurons. Some cells have become neurons (red), while others are still precursors of nerve cells (green). The yellow is an imaging artifact resulting when cells in both stages are on top of each other. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Guoping Fan lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM
View Media
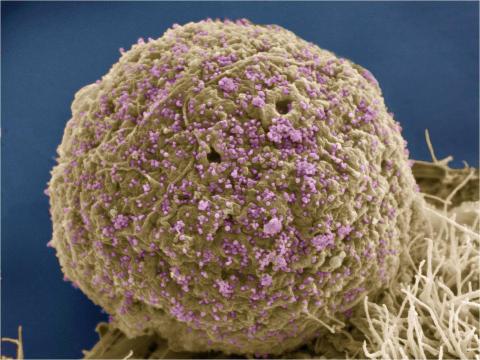
3386: HIV Infected Cell
3386: HIV Infected Cell
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), shown here as tiny purple spheres, causes the disease known as AIDS (for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). HIV can infect multiple cells in your body, including brain cells, but its main target is a cell in the immune system called the CD4 lymphocyte (also called a T-cell or CD4 cell).
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
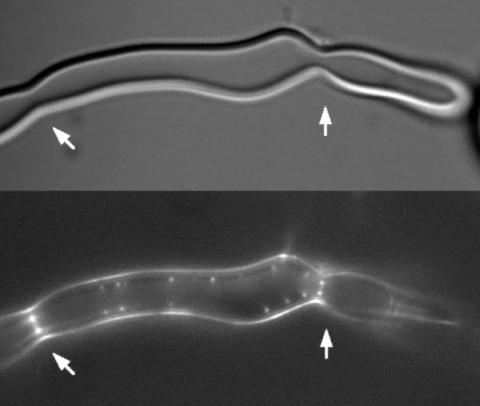
2456: Z rings in bacterial division
2456: Z rings in bacterial division
Lab-made liposomes contract where Z rings have gathered together and the constriction forces are greatest (arrows). The top picture shows a liposome, and the bottom picture shows fluorescence from Z rings (arrows) inside the same liposome simultaneously.
Masaki Osawa, Duke University
View Media
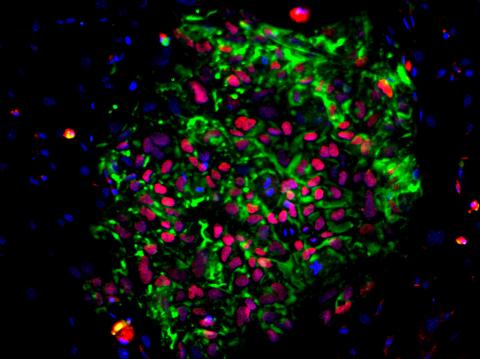
3278: Induced pluripotent stem cells from skin
3278: Induced pluripotent stem cells from skin
These induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) were derived from a woman's skin. Green and red indicate proteins found in reprogrammed cells but not in skin cells (TRA1-62 and NANOG). These cells can then develop into different cell types. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. Related to image 3279.
Kathrin Plath lab, University of California, Los Angeles, via CIRM
View Media
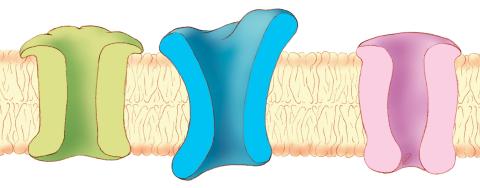
1284: Ion channels
1284: Ion channels
The body uses a variety of ion channels to transport small molecules across cell membranes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
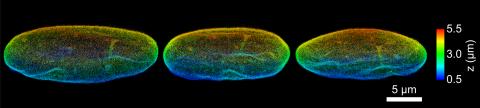
6573: Nuclear Lamina – Three Views
6573: Nuclear Lamina – Three Views
Three views of the entire nuclear lamina of a HeLa cell produced by tilted light sheet 3D single-molecule super-resolution imaging using a platform termed TILT3D.
See 6572 for a 3D view of this structure.
See 6572 for a 3D view of this structure.
Anna-Karin Gustavsson, Ph.D.
View Media
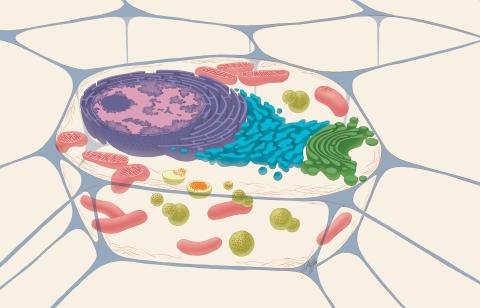
1274: Animal cell
1274: Animal cell
A typical animal cell, sliced open to reveal a cross-section of organelles.
Judith Stoffer
View Media