Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.

6887: Chromatin in human fibroblast
6887: Chromatin in human fibroblast
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Fibroblasts are one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue, and they play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6888 and 6893.
Related to images 6888 and 6893.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
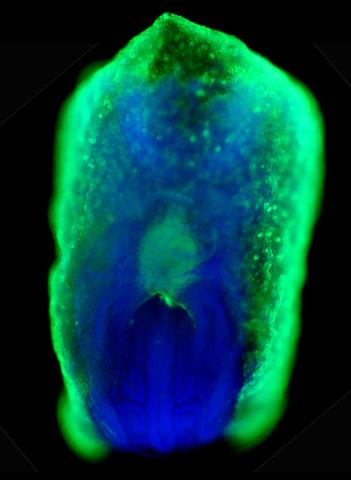
2607: Mouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
2607: Mouse embryo showing Smad4 protein
This eerily glowing blob isn't an alien or a creature from the deep sea--it's a mouse embryo just eight and a half days old. The green shell and core show a protein called Smad4. In the center, Smad4 is telling certain cells to begin forming the mouse's liver and pancreas. Researchers identified a trio of signaling pathways that help switch on Smad4-making genes, starting immature cells on the path to becoming organs. The research could help biologists learn how to grow human liver and pancreas tissue for research, drug testing and regenerative medicine. In addition to NIGMS, NIH's National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases also supported this work.
Kenneth Zaret, Fox Chase Cancer Center
View Media
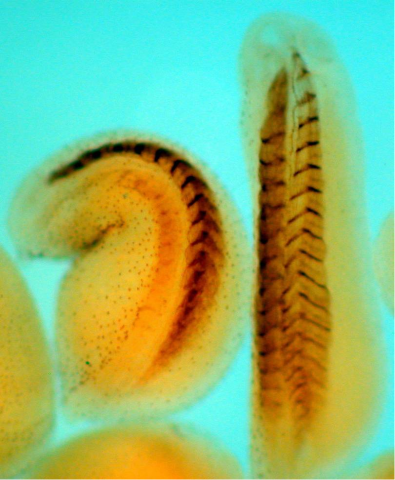
2756: Xenopus laevis embryos
2756: Xenopus laevis embryos
Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, has long been used as a model organism for studying embryonic development. The frog embryo on the left lacks the developmental factor Sizzled. A normal embryo is shown on the right.
Michael Klymkowsky, University of Colorado, Boulder
View Media
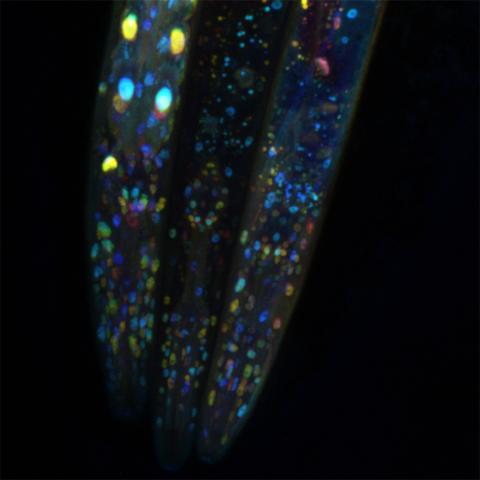
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
6532: Mosaicism in C. elegans (Black Background)
In the worm C. elegans, double-stranded RNA made in neurons can silence matching genes in a variety of cell types through the transport of RNA between cells. The head region of three worms that were genetically modified to express a fluorescent protein were imaged and the images were color-coded based on depth. The worm on the left lacks neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus every cell is fluorescent. In the middle worm, the expression of the fluorescent protein is silenced by neuronal double-stranded RNA and thus most cells are not fluorescent. The worm on the right lacks an enzyme that amplifies RNA for silencing. Surprisingly, the identities of the cells that depend on this enzyme for gene silencing are unpredictable. As a result, worms of identical genotype are nevertheless random mosaics for how the function of gene silencing is carried out. For more, see journal article and press release. Related to image 6534.
Snusha Ravikumar, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park, and Antony M. Jose, Ph.D., University of Maryland, College Park
View Media

6962: Trigonium diatom
6962: Trigonium diatom
A Trigonium diatom imaged by a quantitative orientation-independent differential interference contrast (OI-DIC) microscope. Diatoms are single-celled photosynthetic algae with mineralized cell walls that contain silica and provide protection and support. These organisms form an important part of the plankton at the base of the marine and freshwater food chains. The width of this image is 90 μm.
More information about the microscopy that produced this image can be found in the Journal of Microscopy paper “An Orientation-Independent DIC Microscope Allows High Resolution Imaging of Epithelial Cell Migration and Wound Healing in a Cnidarian Model” by Malamy and Shribak.
More information about the microscopy that produced this image can be found in the Journal of Microscopy paper “An Orientation-Independent DIC Microscope Allows High Resolution Imaging of Epithelial Cell Migration and Wound Healing in a Cnidarian Model” by Malamy and Shribak.
Michael Shribak, Marine Biological Laboratory/University of Chicago.
View Media
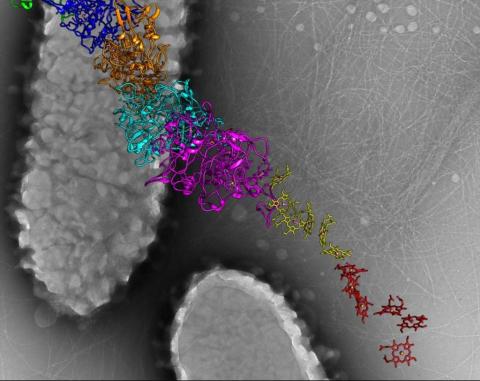
6580: Bacterial nanowire model
6580: Bacterial nanowire model
A model of a Geobacter sulfurreducens nanowire created from cryo-electron microscopy images. The bacterium conducts electricity through these nanowires, which are made up of protein and iron-containing molecules.
Edward Egelman, University of Virginia.
View Media
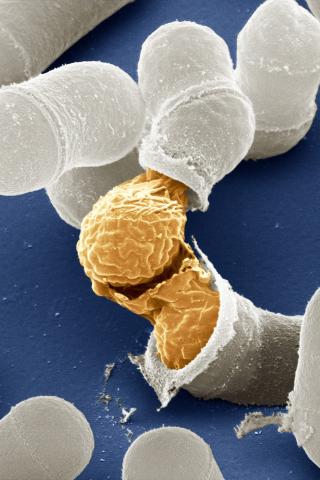
3614: Birth of a yeast cell
3614: Birth of a yeast cell
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. When environmental conditions are favorable, the offspring are released, as shown here. Yeast are also a popular study subject for scientists. Research on yeast has yielded vast knowledge about basic cellular and molecular biology as well as about myriad human diseases, including colon cancer and various metabolic disorders.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany
View Media
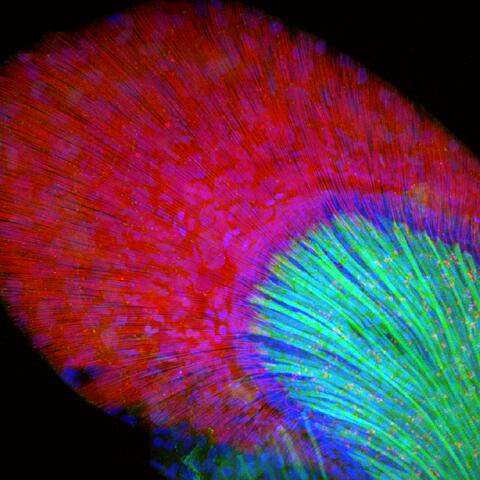
3598: Developing zebrafish fin
3598: Developing zebrafish fin
Originally from the waters of India, Nepal, and neighboring countries, zebrafish can now be found swimming in science labs (and home aquariums) throughout the world. This fish is a favorite study subject for scientists interested in how genes guide the early stages of prenatal development (including the developing fin shown here) and in the effects of environmental contamination on embryos.
In this image, green fluorescent protein (GFP) is expressed where the gene sox9b is expressed. Collagen (red) marks the fin rays, and DNA, stained with a dye called DAPI, is in blue. sox9b plays many important roles during development, including the building of the heart and brain, and is also necessary for skeletal development. At the University of Wisconsin, researchers have found that exposure to contaminants that bind the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor results in the downregulation of sox9b. Loss of sox9b severely disrupts development in zebrafish and causes a life-threatening disorder called campomelic dysplasia (CD) in humans. CD is characterized by cardiovascular, neural, and skeletal defects. By studying the roles of genes such as sox9b in zebrafish, scientists hope to better understand normal development in humans as well as how to treat developmental disorders and diseases.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
In this image, green fluorescent protein (GFP) is expressed where the gene sox9b is expressed. Collagen (red) marks the fin rays, and DNA, stained with a dye called DAPI, is in blue. sox9b plays many important roles during development, including the building of the heart and brain, and is also necessary for skeletal development. At the University of Wisconsin, researchers have found that exposure to contaminants that bind the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor results in the downregulation of sox9b. Loss of sox9b severely disrupts development in zebrafish and causes a life-threatening disorder called campomelic dysplasia (CD) in humans. CD is characterized by cardiovascular, neural, and skeletal defects. By studying the roles of genes such as sox9b in zebrafish, scientists hope to better understand normal development in humans as well as how to treat developmental disorders and diseases.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Jessica Plavicki
View Media
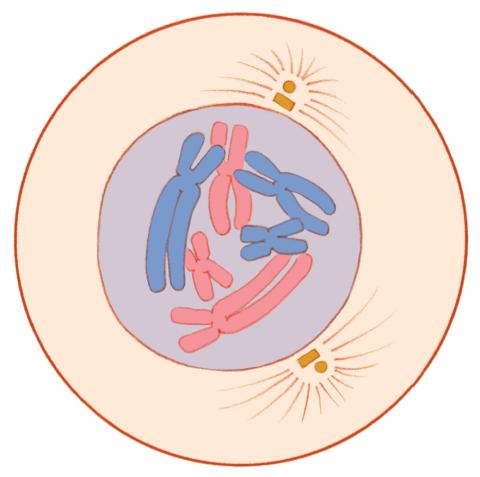
1330: Mitosis - prophase
1330: Mitosis - prophase
A cell in prophase, near the start of mitosis: In the nucleus, chromosomes condense and become visible. In the cytoplasm, the spindle forms. Mitosis is responsible for growth and development, as well as for replacing injured or worn out cells throughout the body. For simplicity, mitosis is illustrated here with only six chromosomes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
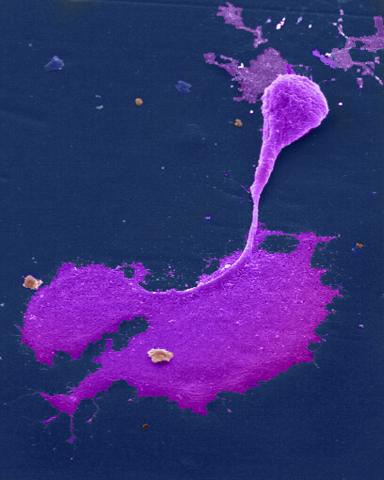
1247: Crab nerve cell
1247: Crab nerve cell
Neuron from a crab showing the cell body (bottom), axon (rope-like extension), and growth cone (top right).
Tina Weatherby Carvalho, University of Hawaii at Manoa
View Media
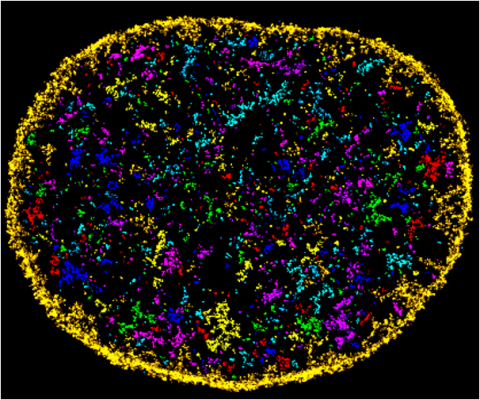
6888: Chromatin in human fibroblast
6888: Chromatin in human fibroblast
The nucleus of a human fibroblast cell with chromatin—a substance made up of DNA and proteins—shown in various colors. Fibroblasts are one of the most common types of cells in mammalian connective tissue, and they play a key role in wound healing and tissue repair. This image was captured using Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM).
Related to images 6887 and 6893.
Related to images 6887 and 6893.
Melike Lakadamyali, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
View Media
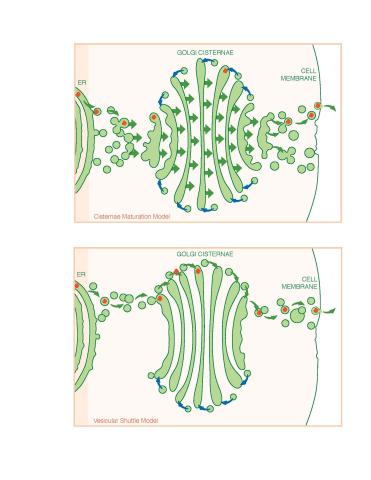
1278: Golgi theories
1278: Golgi theories
Two models for how material passes through the Golgi apparatus: the vesicular shuttle model and the cisternae maturation model.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
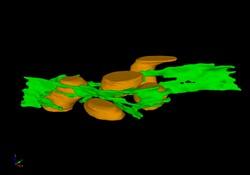
2635: Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
2635: Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
A computer model shows how the endoplasmic reticulum is close to and almost wraps around mitochondria in the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is lime green and the mitochondria are yellow. This image relates to a July 27, 2009 article in Computing Life.
Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico
View Media

3718: A Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
3718: A Bacillus subtilis biofilm grown in a Petri dish
Bacterial biofilms are tightly knit communities of bacterial cells growing on, for example, solid surfaces, such as in water pipes or on teeth. Here, cells of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis have formed a biofilm in a laboratory culture. Researchers have discovered that the bacterial cells in a biofilm communicate with each other through electrical signals via specialized potassium ion channels to share resources, such as nutrients, with each other. This insight may help scientists to improve sanitation systems to prevent biofilms, which often resist common treatments, from forming and to develop better medicines to combat bacterial infections. See the Biomedical Beat blog post Bacterial Biofilms: A Charged Environment for more information.
Gürol Süel, UCSD
View Media

3526: 800 MHz NMR magnet
3526: 800 MHz NMR magnet
Scientists use nuclear magnetic spectroscopy (NMR) to determine the detailed, 3D structures of molecules.
Asokan Anbanandam, University of Kansas
View Media
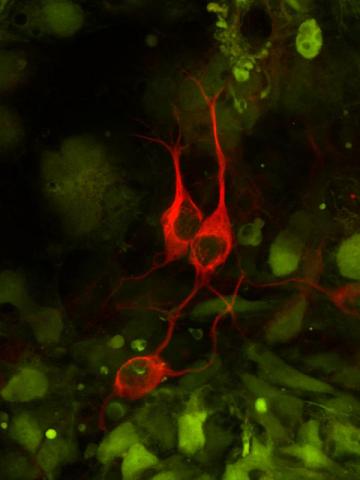
3290: Three neurons and human ES cells
3290: Three neurons and human ES cells
The three neurons (red) visible in this image were derived from human embryonic stem cells. Undifferentiated stem cells are green here. Image and caption information courtesy of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
Anirvan Ghosh lab, University of California, San Diego, via CIRM
View Media

3730: A molecular interaction network in yeast 1
3730: A molecular interaction network in yeast 1
The image visualizes a part of the yeast molecular interaction network. The lines in the network represent connections among genes (shown as little dots) and different-colored networks indicate subnetworks, for instance, those in specific locations or pathways in the cell. Researchers use gene or protein expression data to build these networks; the network shown here was visualized with a program called Cytoscape. By following changes in the architectures of these networks in response to altered environmental conditions, scientists can home in on those genes that become central "hubs" (highly connected genes), for example, when a cell encounters stress. They can then further investigate the precise role of these genes to uncover how a cell's molecular machinery deals with stress or other factors. Related to images 3732 and 3733.
Keiichiro Ono, UCSD
View Media
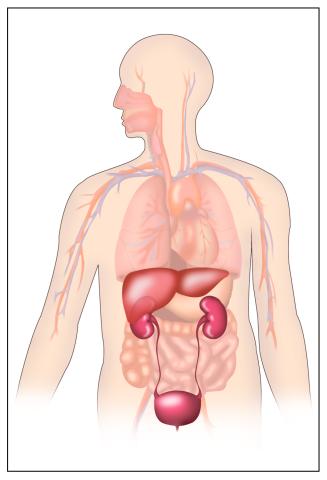
2496: Body toxins
2496: Body toxins
Body organs such as the liver and kidneys process chemicals and toxins. These "target" organs are susceptible to damage caused by these substances. See image 2497 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
2604: Induced stem cells from adult skin 02
2604: Induced stem cells from adult skin 02
These cells are induced stem cells made from human adult skin cells that were genetically reprogrammed to mimic embryonic stem cells. The induced stem cells were made potentially safer by removing the introduced genes and the viral vector used to ferry genes into the cells, a loop of DNA called a plasmid. The work was accomplished by geneticist Junying Yu in the laboratory of James Thomson, a University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health professor and the director of regenerative biology for the Morgridge Institute for Research.
James Thomson, University of Wisconsin-Madison
View Media
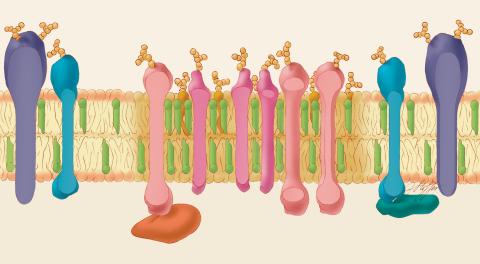
1285: Lipid raft
1285: Lipid raft
Researchers have learned much of what they know about membranes by constructing artificial membranes in the laboratory. In artificial membranes, different lipids separate from each other based on their physical properties, forming small islands called lipid rafts.
Judith Stoffer
View Media

3779: Precisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
3779: Precisely Delivering Chemical Cargo to Cells
Moving protein or other molecules to specific cells to treat or examine them has been a major biological challenge. Scientists have now developed a technique for delivering chemicals to individual cells. The approach involves gold nanowires that, for example, can carry tumor-killing proteins. The advance was possible after researchers developed electric tweezers that could manipulate gold nanowires to help deliver drugs to single cells.
This movie shows the manipulation of the nanowires for drug delivery to a single cell. To learn more about this technique, see this post in the Computing Life series.
This movie shows the manipulation of the nanowires for drug delivery to a single cell. To learn more about this technique, see this post in the Computing Life series.
Nature Nanotechnology
View Media
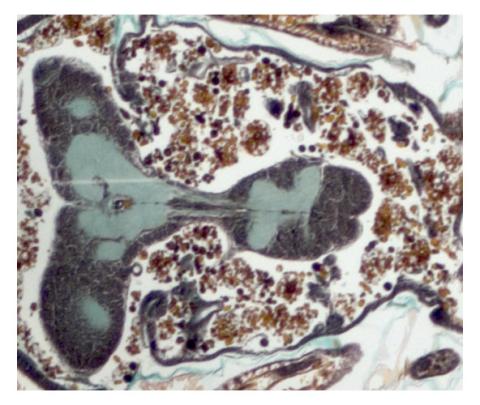
2758: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
2758: Cross section of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa
This photograph shows a magnified view of a Drosophila melanogaster pupa in cross section. Compare this normal pupa to one that lacks an important receptor, shown in image 2759.
Christina McPhee and Eric Baehrecke, University of Massachusetts Medical School
View Media
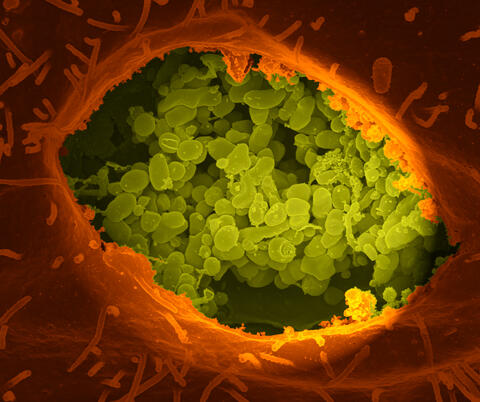
3621: Q fever bacteria in an infected cell
3621: Q fever bacteria in an infected cell
This image shows Q fever bacteria (yellow), which infect cows, sheep, and goats around the world and can infect humans, as well. When caught early, Q fever can be cured with antibiotics. A small fraction of people can develop a more serious, chronic form of the disease.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Robert Heinzen, Elizabeth Fischer, and Anita Mora, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health
View Media
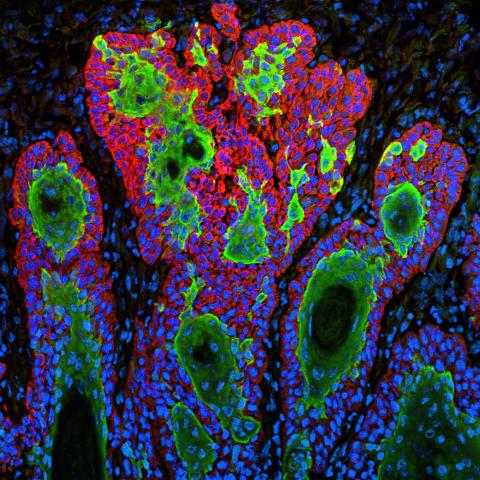
3628: Skin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
3628: Skin cancer cells (squamous cell carcinoma)
This image shows the uncontrolled growth of cells in squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is usually not life-threatening.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Markus Schober and Elaine Fuchs, The Rockefeller University
View Media
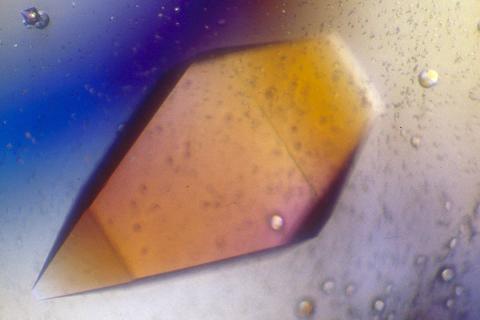
2400: Pig trypsin (1)
2400: Pig trypsin (1)
A crystal of porcine trypsin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
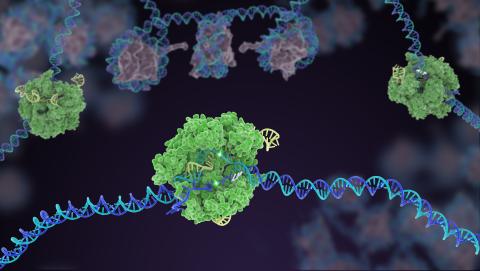
5816: Cas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
5816: Cas9 protein involved in the CRISPR gene-editing technology
In the gene-editing tool CRISPR, a small strand of RNA identifies a specific chunk of DNA. Then the enzyme Cas9 (green) swoops in and cuts the double-stranded DNA (blue/purple) in two places, removing the specific chunk.
Janet Iwasa
View Media
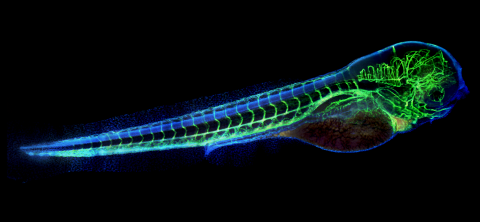
6661: Zebrafish embryo showing vasculature
6661: Zebrafish embryo showing vasculature
A zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies, the green lines are blood vessels, and the red glow is blood. This image was created by stitching together five individual images captured with a hyperspectral multipoint confocal fluorescence microscope that was developed at the Eliceiri Lab.
Kevin Eliceiri, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
View Media
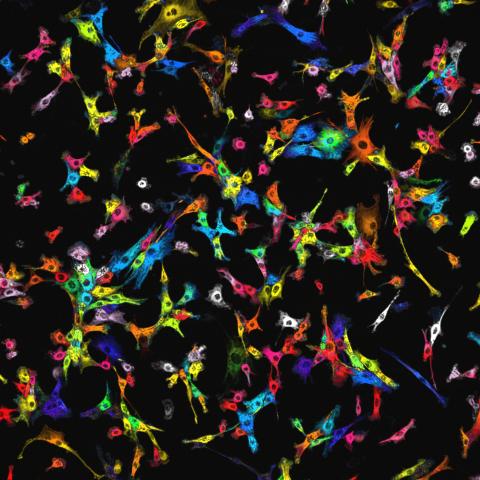
7021: Single-cell “radios” image
7021: Single-cell “radios” image
Individual cells are color-coded based on their identity and signaling activity using a protein circuit technology developed by the Coyle Lab. Just as a radio allows you to listen to an individual frequency, this technology allows researchers to tune into the specific “radio station” of each cell through genetically encoded proteins from a bacterial system called MinDE. The proteins generate an oscillating fluorescent signal that transmits information about cell shape, state, and identity that can be decoded using digital signal processing tools originally designed for telecommunications. The approach allows researchers to look at the dynamics of a single cell in the presence of many other cells.
Related to video 7022.
Related to video 7022.
Scott Coyle, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
View Media
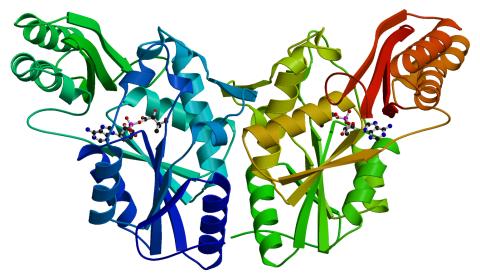
2383: PanC from M. tuberculosis
2383: PanC from M. tuberculosis
Model of an enzyme, PanC, that is involved in the last step of vitamin B5 biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PanC is essential for the growth of M. tuberculosis, which causes most cases of tuberculosis, and is therefore a potential drug target.
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Center, PSI
View Media
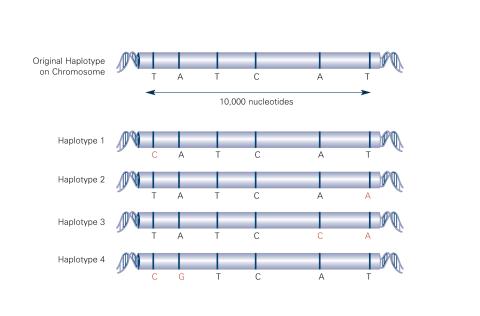
2567: Haplotypes (with labels)
2567: Haplotypes (with labels)
Haplotypes are combinations of gene variants that are likely to be inherited together within the same chromosomal region. In this example, an original haplotype (top) evolved over time to create three newer haplotypes that each differ by a few nucleotides (red). See image 2566 for an unlabeled version of this illustration. Featured in The New Genetics.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
1337: Bicycling cell
1337: Bicycling cell
A humorous treatment of the concept of a cycling cell.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
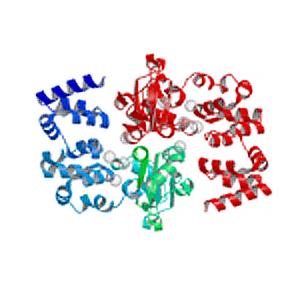
2345: Magnesium transporter protein from E. faecalis
2345: Magnesium transporter protein from E. faecalis
Structure of a magnesium transporter protein from an antibiotic-resistant bacterium (Enterococcus faecalis) found in the human gut. Featured as one of the June 2007 Protein Sructure Initiative Structures of the Month.
New York Structural GenomiX Consortium
View Media
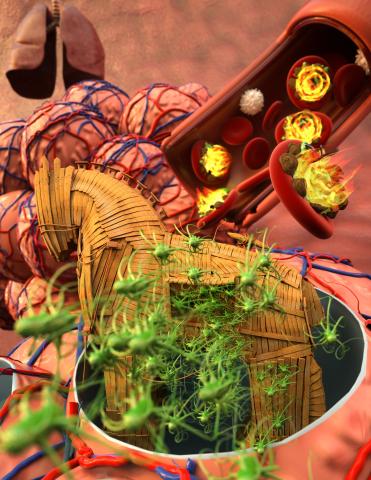
5764: Host infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
5764: Host infection stimulates antibiotic resistance
This illustration shows pathogenic bacteria behave like a Trojan horse: switching from antibiotic susceptibility to resistance during infection. Salmonella are vulnerable to antibiotics while circulating in the blood (depicted by fire on red blood cell) but are highly resistant when residing within host macrophages. This leads to treatment failure with the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
This image was chosen as a winner of the 2016 NIH-funded research image call, and the research was funded in part by NIGMS.
View Media
This image was chosen as a winner of the 2016 NIH-funded research image call, and the research was funded in part by NIGMS.
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
3616: Weblike sheath covering developing egg chambers in a giant grasshopper
The lubber grasshopper, found throughout the southern United States, is frequently used in biology classes to teach students about the respiratory system of insects. Unlike mammals, which have red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body, insects have breathing tubes that carry air through their exoskeleton directly to where it's needed. This image shows the breathing tubes embedded in the weblike sheath cells that cover developing egg chambers.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Kevin Edwards, Johny Shajahan, and Doug Whitman, Illinois State University.
View Media
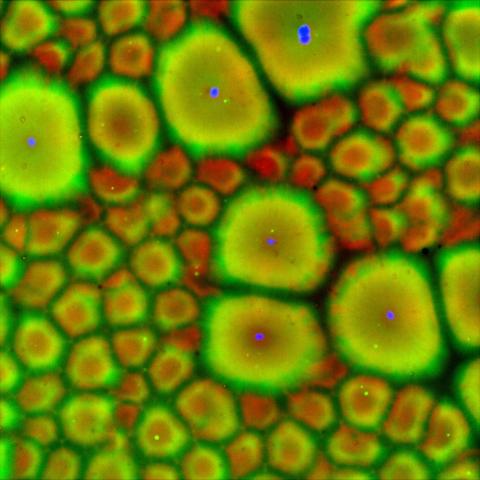
6585: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
6585: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 2
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs, with nuclei (blue) from frog sperm. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are also visible. Regions without nuclei formed smaller compartments. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy.
For more photos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6584, 6586, 6591, 6592, and 6593.
For videos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6587, 6588, 6589, and 6590.
Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine.
View Media
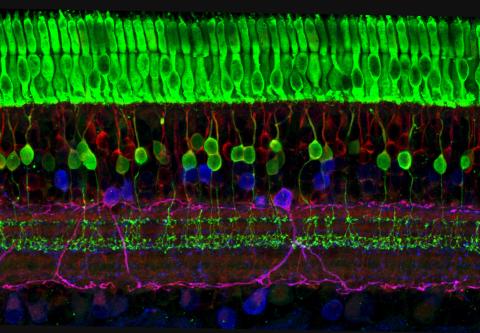
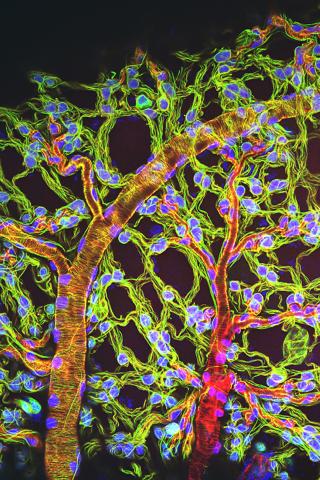
3635: The eye uses many layers of nerve cells to convert light into sight
3635: The eye uses many layers of nerve cells to convert light into sight
This image captures the many layers of nerve cells in the retina. The top layer (green) is made up of cells called photoreceptors that convert light into electrical signals to relay to the brain. The two best-known types of photoreceptor cells are rod- and cone-shaped. Rods help us see under low-light conditions but can't help us distinguish colors. Cones don't function well in the dark but allow us to see vibrant colors in daylight.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Wei Li, National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
View Media
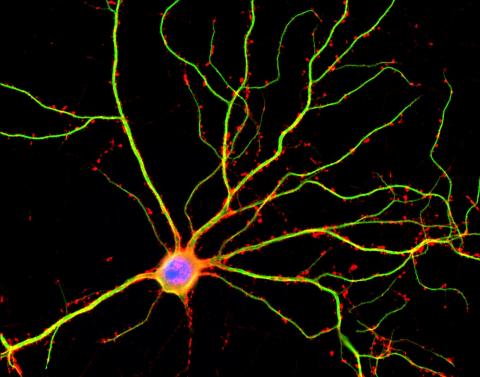
3687: Hippocampal neuron in culture
3687: Hippocampal neuron in culture
Hippocampal neuron in culture. Dendrites are green, dendritic spines are red and DNA in cell's nucleus is blue. Image is featured on Biomedical Beat blog post Anesthesia and Brain Cells: A Temporary Disruption?
Shelley Halpain, UC San Diego
View Media

2683: GFP sperm
2683: GFP sperm
Fruit fly sperm cells glow bright green when they express the gene for green fluorescent protein (GFP).
View Media
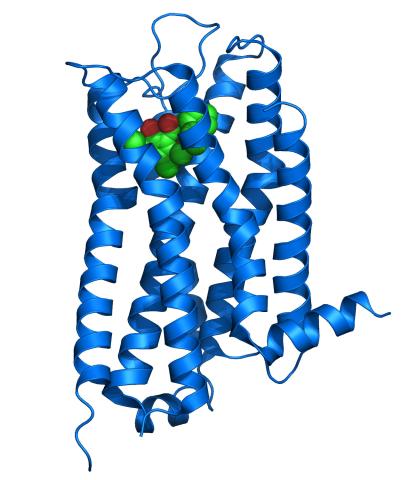
3363: Dopamine D3 receptor
3363: Dopamine D3 receptor
The receptor is shown bound to an antagonist, eticlopride
Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute
View Media
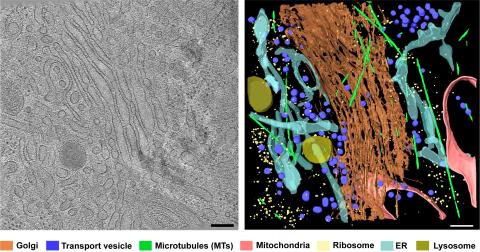
6606: Cryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
6606: Cryo-ET cross-section of the Golgi apparatus
On the left, a cross-section slice of a rat pancreas cell captured using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET). On the right, a 3D, color-coded version of the image highlighting cell structures. Visible features include the folded sacs of the Golgi apparatus (copper), transport vesicles (medium-sized dark-blue circles), microtubules (neon green), ribosomes (small pale-yellow circles), and lysosomes (large yellowish-green circles). Black line (bottom right of the left image) represents 200 nm. This image is a still from video 6609.
Xianjun Zhang, University of Southern California.
View Media
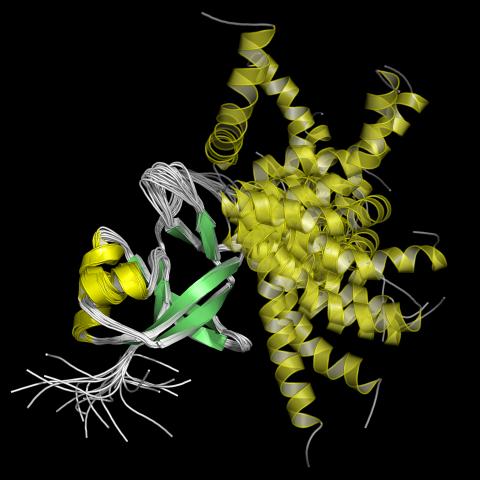
2339: Protein from Arabidopsis thaliana
2339: Protein from Arabidopsis thaliana
NMR solution structure of a plant protein that may function in host defense. This protein was expressed in a convenient and efficient wheat germ cell-free system. Featured as the June 2007 Protein Structure Initiative Structure of the Month.
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics
View Media

2543: DNA replication illustration
2543: DNA replication illustration
During DNA replication, each strand of the original molecule acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary DNA strand. See image 2544 for a labeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
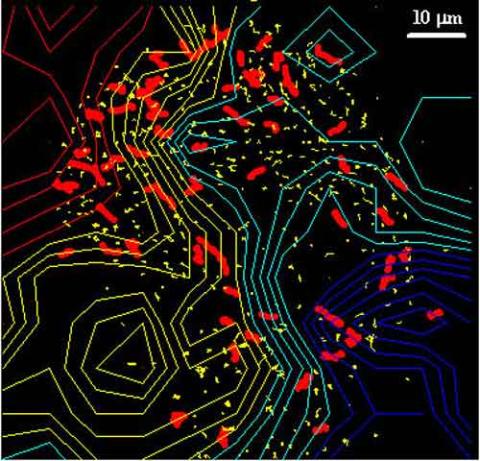
2310: Cellular traffic
2310: Cellular traffic
Like tractor-trailers on a highway, small sacs called vesicles transport substances within cells. This image tracks the motion of vesicles in a living cell. The short red and yellow marks offer information on vesicle movement. The lines spanning the image show overall traffic trends. Typically, the sacs flow from the lower right (blue) to the upper left (red) corner of the picture. Such maps help researchers follow different kinds of cellular processes as they unfold.
Alexey Sharonov and Robin Hochstrasser, University of Pennsylvania
View Media
6983: Genetic mosaicism in fruit flies
6983: Genetic mosaicism in fruit flies
Fat tissue from the abdomen of a genetically mosaic adult fruit fly. Genetic mosaicism means that the fly has cells with different genotypes even though it formed from a single zygote. This specific mosaicism results in accumulation of a critical fly adipokine (blue-green) within the fat tissue cells that have reduced expression a key nutrient sensing gene (in left panel). The dotted line shows the cells lacking the gene that is present and functioning in the rest of the cells. Nuclei are labelled in magenta. This image was captured using a confocal microscope and shows a maximum intensity projection of many slices.
Related to images 6982, 6984, and 6985.
Related to images 6982, 6984, and 6985.
Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center
View Media
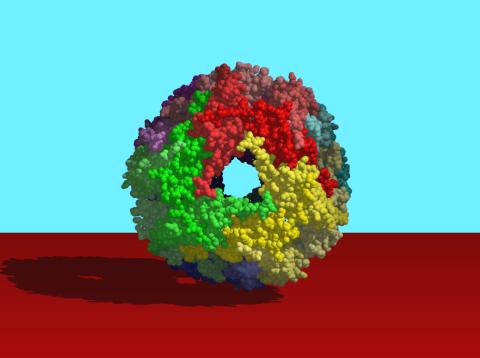
2385: Heat shock protein complex from Methanococcus jannaschii
2385: Heat shock protein complex from Methanococcus jannaschii
Model based on X-ray crystallography of the structure of a small heat shock protein complex from the bacteria, Methanococcus jannaschii. Methanococcus jannaschii is an organism that lives at near boiling temperature, and this protein complex helps it cope with the stress of high temperature. Similar complexes are produced in human cells when they are "stressed" by events such as burns, heart attacks, or strokes. The complexes help cells recover from the stressful event.
Berkeley Structural Genomics Center, PSI-1
View Media
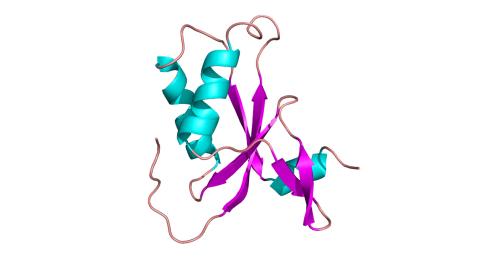
3427: Antitoxin GhoS (Illustration 1)
3427: Antitoxin GhoS (Illustration 1)
Structure of the bacterial antitoxin protein GhoS. GhoS inhibits the production of a bacterial toxin, GhoT, which can contribute to antibiotic resistance. GhoS is the first known bacterial antitoxin that works by cleaving the messenger RNA that carries the instructions for making the toxin. More information can be found in the paper: Wang X, Lord DM, Cheng HY, Osbourne DO, Hong SH, Sanchez-Torres V, Quiroga C, Zheng K, Herrmann T, Peti W, Benedik MJ, Page R, Wood TK. A new type V toxin-antitoxin system where mRNA for toxin GhoT is cleaved by antitoxin GhoS. Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Oct;8(10):855-61. Related to 3428.
Rebecca Page and Wolfgang Peti, Brown University and Thomas K. Wood, Pennsylvania State University
View Media

2392: Sheep hemoglobin crystal
2392: Sheep hemoglobin crystal
A crystal of sheep hemoglobin protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
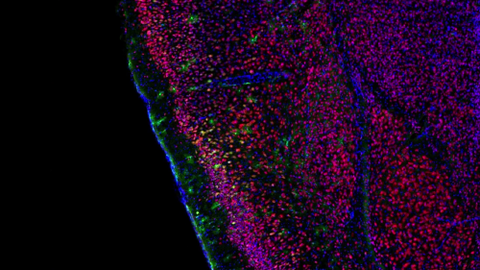
6781: Video of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
6781: Video of Calling Cards in a mouse brain
The green spots in this mouse brain are cells labeled with Calling Cards, a technology that records molecular events in brain cells as they mature. Understanding these processes during healthy development can guide further research into what goes wrong in cases of neuropsychiatric disorders. Also fluorescently labeled in this video are neurons (red) and nuclei (blue). Calling Cards and its application are described in the Cell paper “Self-Reporting Transposons Enable Simultaneous Readout of Gene Expression and Transcription Factor Binding in Single Cells” by Moudgil et al.; and the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences paper “A viral toolkit for recording transcription factor–DNA interactions in live mouse tissues” by Cammack et al. This video was created for the NIH Director’s Blog post The Amazing Brain: Tracking Molecular Events with Calling Cards.
Related to image 6780.
Related to image 6780.
NIH Director's Blog
View Media
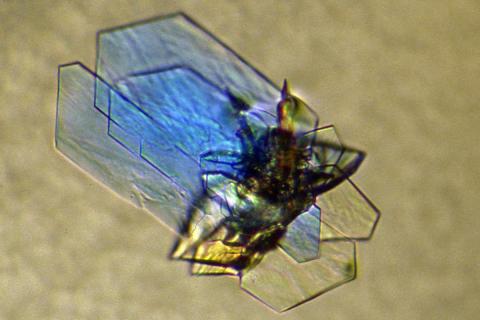
2410: DNase
2410: DNase
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
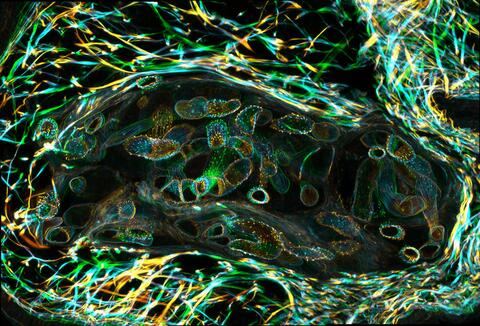
3627: Larvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
3627: Larvae from the parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis
The parasitic worm that causes schistosomiasis hatches in water and grows up in a freshwater snail, as shown here. Once mature, the worm swims back into the water, where it can infect people through skin contact. Initially, an infected person might have a rash, itchy skin, or flu-like symptoms, but the real damage is done over time to internal organs.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Bo Wang and Phillip A. Newmark, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013 FASEB BioArt winner
View Media
