Switch to List View
Image and Video Gallery
This is a searchable collection of scientific photos, illustrations, and videos. The images and videos in this gallery are licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 3.0. This license lets you remix, tweak, and build upon this work non-commercially, as long as you credit and license your new creations under identical terms.
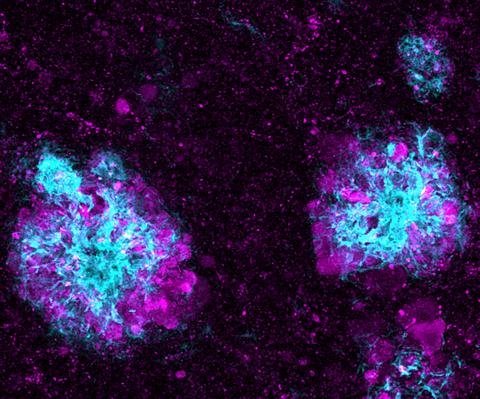
5771: Lysosome clusters around amyloid plaques
5771: Lysosome clusters around amyloid plaques
It's probably most people's least favorite activity, but we still need to do it--take out our trash. Otherwise our homes will get cluttered and smelly, and eventually, we'll get sick. The same is true for our cells: garbage disposal is an ongoing and essential activity, and our cells have a dedicated waste-management system that helps keep them clean and neat. One major waste-removal agent in the cell is the lysosome. Lysosomes are small structures, called organelles, and help the body to dispose of proteins and other molecules that have become damaged or worn out.
This image shows a massive accumulation of lysosomes (visualized with LAMP1 immunofluorescence, in purple) within nerve cells that surround amyloid plaques (visualized with beta-amyloid immunofluorescence, in light blue) in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Scientists have linked accumulation of lysosomes around amyloid plaques to impaired waste disposal in nerve cells, ultimately resulting in cell death.
This image shows a massive accumulation of lysosomes (visualized with LAMP1 immunofluorescence, in purple) within nerve cells that surround amyloid plaques (visualized with beta-amyloid immunofluorescence, in light blue) in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Scientists have linked accumulation of lysosomes around amyloid plaques to impaired waste disposal in nerve cells, ultimately resulting in cell death.
Swetha Gowrishankar and Shawn Ferguson, Yale School of Medicine
View Media

2737: Cytoscape network diagram 1
2737: Cytoscape network diagram 1
Molecular biologists are increasingly relying on bioinformatics software to visualize molecular interaction networks and to integrate these networks with data such as gene expression profiles. Related to 2749.
Keiichiro Ono, Trey Ideker lab, University of California, San Diego
View Media
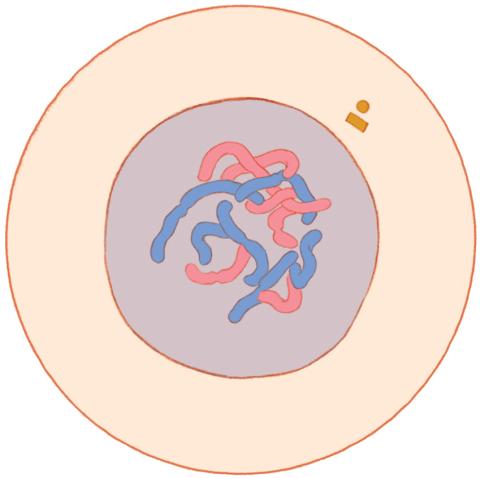
1316: Mitosis - interphase
1316: Mitosis - interphase
A cell in interphase, at the start of mitosis: Chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. Mitosis is responsible for growth and development, as well as for replacing injured or worn out cells throughout the body. For simplicity, mitosis is illustrated here with only six chromosomes.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
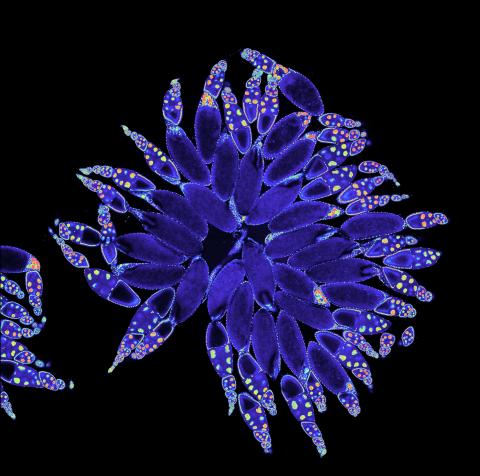
3607: Fruit fly ovary
3607: Fruit fly ovary
A fruit fly ovary, shown here, contains as many as 20 eggs. Fruit flies are not merely tiny insects that buzz around overripe fruit—they are a venerable scientific tool. Research on the flies has shed light on many aspects of human biology, including biological rhythms, learning, memory, and neurodegenerative diseases. Another reason fruit flies are so useful in a lab (and so successful in fruit bowls) is that they reproduce rapidly. About three generations can be studied in a single month.
Related to image 3656. This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Related to image 3656. This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Denise Montell, Johns Hopkins University and University of California, Santa Barbara
View Media
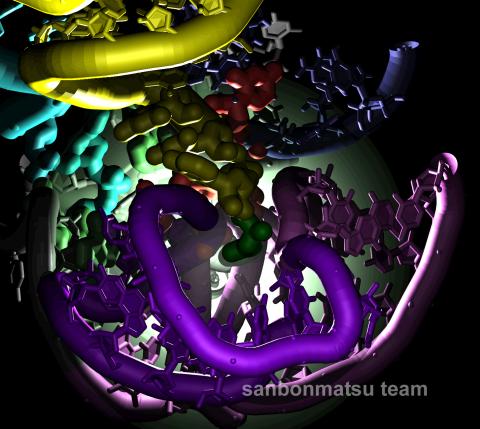
2336: Natural nanomachine in action
2336: Natural nanomachine in action
Using a supercomputer to simulate the movement of atoms in a ribosome, researchers looked into the core of this protein-making nanomachine and took snapshots. The picture shows an amino acid (green) being delivered by transfer RNA (yellow) into a corridor (purple) in the ribosome. In the corridor, a series of chemical reactions will string together amino acids to make a protein. The research project, which tracked the movement of more than 2.6 million atoms, was the largest computer simulation of a biological structure to date. The results shed light on the manufacturing of proteins and could aid the search for new antibiotics, which typically work by disabling the ribosomes of bacteria.
Kevin Sanbonmatsu, Los Alamos National Laboratory
View Media
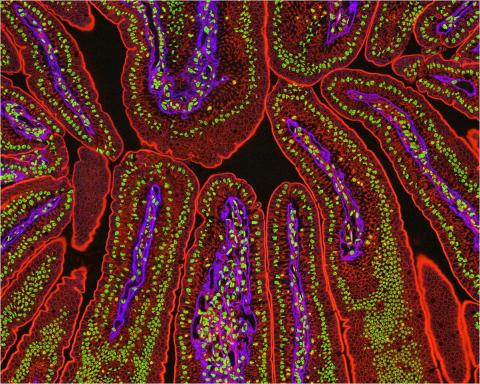
3390: NCMIR Intestine-2
3390: NCMIR Intestine-2
The small intestine is where most of our nutrients from the food we eat are absorbed into the bloodstream. The walls of the intestine contain small finger-like projections called villi which increase the organ's surface area, enhancing nutrient absorption. It consists of the duodenum, which connects to the stomach, the jejenum and the ileum, which connects with the large intestine. Related to image 3389.
Tom Deerinck, National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
1087: Natcher Building 07
1087: Natcher Building 07
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus.
Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
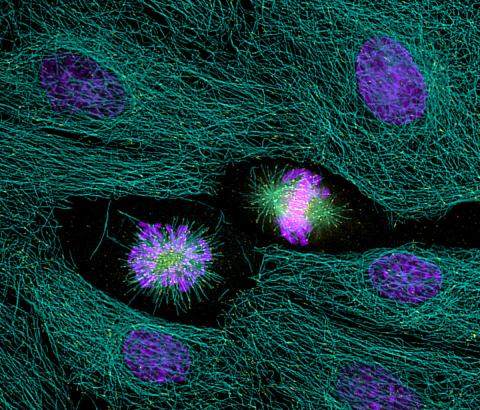
2429: Highlighted cells
2429: Highlighted cells
The cytoskeleton (green) and DNA (purple) are highlighed in these cells by immunofluorescence.
Torsten Wittmann, Scripps Research Institute
View Media
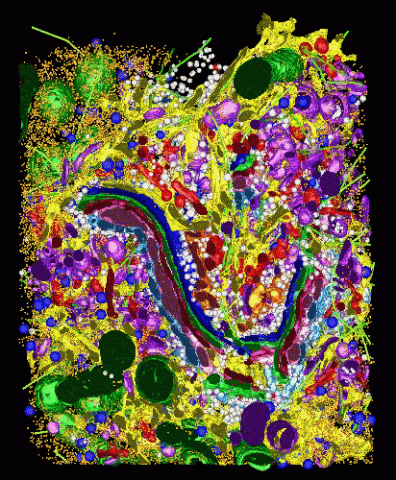
2308: Cellular metropolis
2308: Cellular metropolis
Like a major city, a cell teems with specialized workers that carry out its daily operations--making energy, moving proteins, or helping with other tasks. Researchers took microscopic pictures of thin layers of a cell and then combined them to make this 3-D image featuring color-coded organelles--the cell's "workers." Using this image, scientists can understand how these specialized components fit together in the cell's packed inner world.
Kathryn Howell, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
View Media
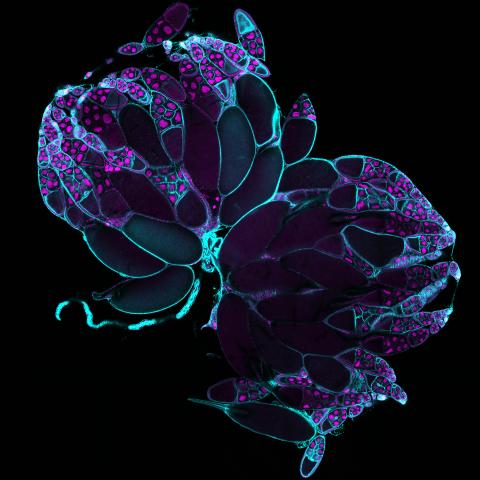
6807: Fruit fly ovaries
6807: Fruit fly ovaries
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ovaries with DNA shown in magenta and actin filaments shown in light blue. This image was captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope.
Related to image 6806.
Related to image 6806.
Vladimir I. Gelfand, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University.
View Media
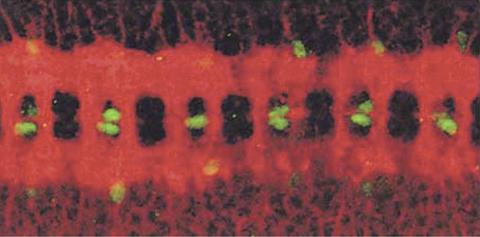
1091: Nerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
1091: Nerve and glial cells in fruit fly embryo
Glial cells (stained green) in a fruit fly developing embryo have survived thanks to a signaling pathway initiated by neighboring nerve cells (stained red).
Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University
View Media
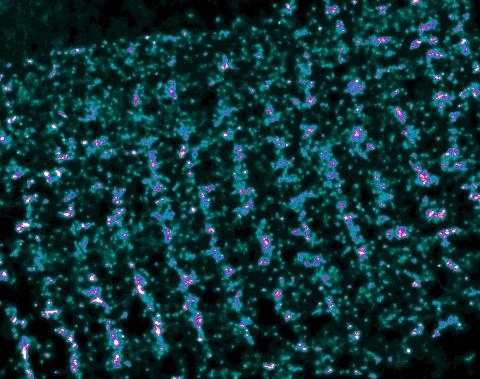
3339: Single-Molecule Imaging
3339: Single-Molecule Imaging
This is a super-resolution light microscope image taken by Hiro Hakozaki and Masa Hoshijima of NCMIR. The image contains highlighted calcium channels in cardiac muscle using a technique called dSTORM. The microscope used in the NCMIR lab was built by Hiro Hakozaki.
Tom Deerinck, NCMIR
View Media
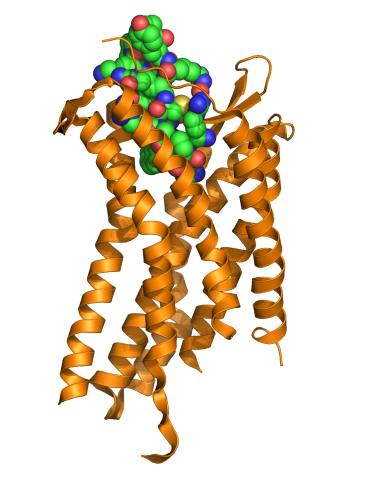
3365: Chemokine CXCR4 receptor
3365: Chemokine CXCR4 receptor
The receptor is shown bound to a small molecule peptide called CVX15.
Raymond Stevens, The Scripps Research Institute
View Media
3391: Protein folding video
3391: Protein folding video
Proteins are long chains of amino acids. Each protein has a unique amino acid sequence. It is still a mystery how a protein folds into the proper shape based on its sequence. Scientists hope that one day they can "watch" this folding process for any given protein. The dream has been realized, at least partially, through the use of computer simulation.
Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group
View Media
2431: Fruit fly embryo
2431: Fruit fly embryo
Cells in an early-stage fruit fly embryo, showing the DIAP1 protein (pink), an inhibitor of apoptosis.
Hermann Steller, Rockefeller University
View Media
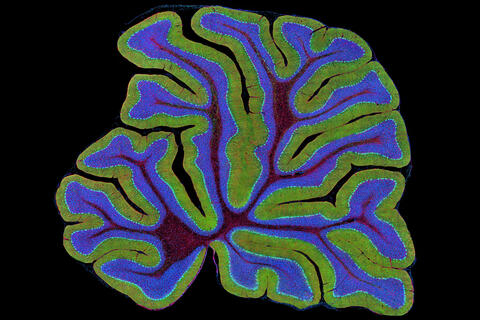
3723: Fluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue
3723: Fluorescent microscopy of kidney tissue
Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of mammals. SA has a characteristic heart-shape structure and is a highly versatile protein. It helps maintain normal water levels in our tissues and carries almost half of all calcium ions in human blood. SA also transports some hormones, nutrients and metals throughout the bloodstream. Despite being very similar to our own SA, those from other animals can cause some mild allergies in people. Therefore, some scientists study SAs from humans and other mammals to learn more about what subtle structural or other differences cause immune responses in the body.
Related to entries 3725 and 3675.
Related to entries 3725 and 3675.
Tom Deerinck , National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research
View Media
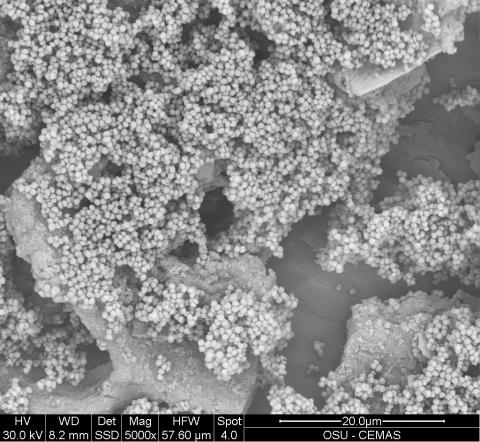

6803: Staphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
6803: Staphylococcus aureus aggregates on microstructured titanium surface
Groups of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (blue) attached to a microstructured titanium surface (green) that mimics an orthopedic implant used in joint replacement. The attachment of pre-formed groups of bacteria may lead to infections because the groups can tolerate antibiotics and evade the immune system. This image was captured using a scanning electron microscope.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Antibiotics paper "Free-floating aggregate and single-cell-initiated biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus" by Gupta et al.
Related to image 6804 and video 6805.
More information on the research that produced this image can be found in the Antibiotics paper "Free-floating aggregate and single-cell-initiated biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus" by Gupta et al.
Related to image 6804 and video 6805.
Paul Stoodley, The Ohio State University.
View Media

5755: Autofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
5755: Autofluorescent xanthophores in zebrafish skin
Pigment cells are cells that give skin its color. In fishes and amphibians, like frogs and salamanders, pigment cells are responsible for the characteristic skin patterns that help these organisms to blend into their surroundings or attract mates. The pigment cells are derived from neural crest cells, which are cells originating from the neural tube in the early embryo. This image shows pigment cells called xanthophores in the skin of zebrafish; the cells glow (autofluoresce) brightly under light giving the fish skin a shiny, lively appearance. Investigating pigment cell formation and migration in animals helps answer important fundamental questions about the factors that control pigmentation in the skin of animals, including humans. Related to images 5754, 5756, 5757 and 5758.
David Parichy, University of Washington
View Media
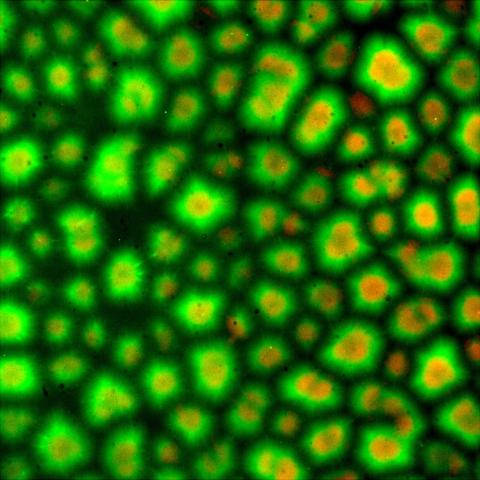
6586: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
6586: Cell-like compartments from frog eggs 3
Cell-like compartments that spontaneously emerged from scrambled frog eggs. Endoplasmic reticulum (red) and microtubules (green) are visible. Image created using epifluorescence microscopy.
For more photos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6584, 6585, 6591, 6592, and 6593.
For videos of cell-like compartments from frog eggs view: 6587, 6588, 6589, and 6590.
Xianrui Cheng, Stanford University School of Medicine.
View Media
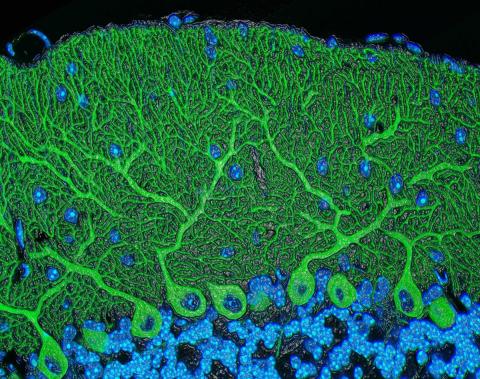
5795: Mouse cerebellum
5795: Mouse cerebellum
The cerebellum is the brain's locomotion control center. Found at the base of your brain, the cerebellum is a single layer of tissue with deep folds like an accordion. People with damage to this region of the brain often have difficulty with balance, coordination and fine motor skills.
This image of a mouse cerebellum is part of a collection of such images in different colors and at different levels of magnification from the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR). Related to image 5800.
This image of a mouse cerebellum is part of a collection of such images in different colors and at different levels of magnification from the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR). Related to image 5800.
National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR)
View Media
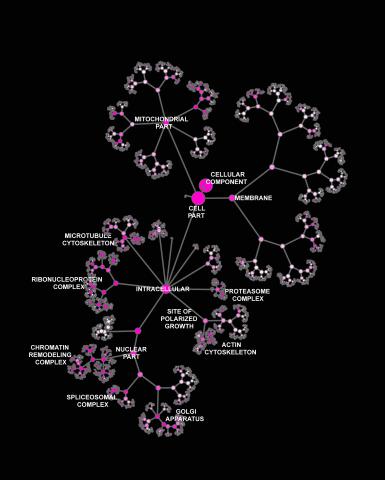
3437: Network diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
3437: Network diagram of genes, cellular components and processes (labeled)
This image shows the hierarchical ontology of genes, cellular components and processes derived from large genomic datasets. From Dutkowski et al. A gene ontology inferred from molecular networks Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;31(1):38-45. Related to 3436.
Janusz Dutkowski and Trey Ideker, University of California, San Diego
View Media
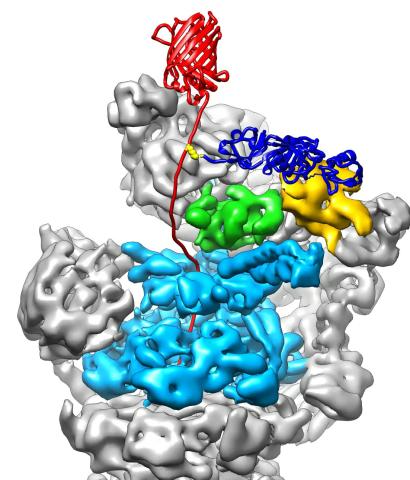
3763: The 26S proteasome engages with a protein substrate
3763: The 26S proteasome engages with a protein substrate
The proteasome is a critical multiprotein complex in the cell that breaks down and recycles proteins that have become damaged or are no longer needed. This illustration shows a protein substrate (red) that is bound through its ubiquitin chain (blue) to one of the ubiquitin receptors of the proteasome (Rpn10, yellow). The substrate's flexible engagement region gets engaged by the AAA+ motor of the proteasome (cyan), which initiates mechanical pulling, unfolding and movement of the protein into the proteasome's interior for cleavage into small shorter protein pieces called peptides. During movement of the substrate, its ubiquitin modification gets cleaved off by the deubiquitinase Rpn11 (green), which sits directly above the entrance to the AAA+ motor pore and acts as a gatekeeper to ensure efficient ubiquitin removal, a prerequisite for fast protein breakdown by the 26S proteasome. Related to video 3764.
Andreas Martin, HHMI
View Media
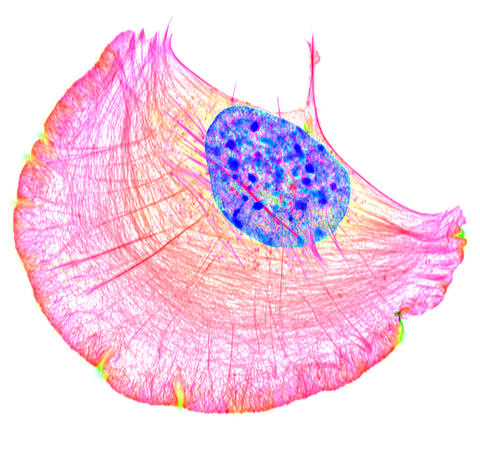
6964: Crawling cell
6964: Crawling cell
A crawling cell with DNA shown in blue and actin filaments, which are a major component of the cytoskeleton, visible in pink. Actin filaments help enable cells to crawl. This image was captured using structured illumination microscopy.
Dylan T. Burnette, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine.
View Media
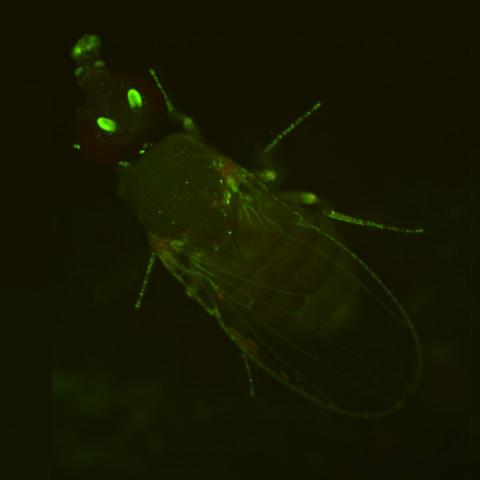

2417: Fly by night
2417: Fly by night
This fruit fly expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the same pattern as the period gene, a gene that regulates circadian rhythm and is expressed in all sensory neurons on the surface of the fly.
Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia
View Media

1271: Cone cell
1271: Cone cell
The cone cell of the eye allows you to see in color. Appears in the NIGMS booklet Inside the Cell.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
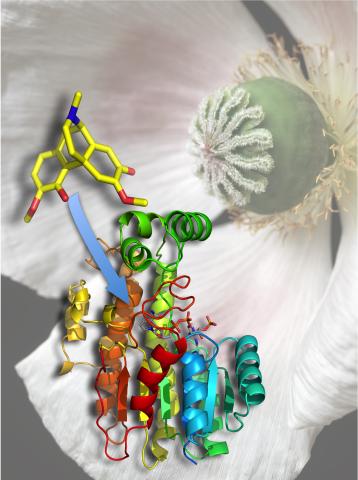
3422: Atomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
3422: Atomic Structure of Poppy Enzyme
The atomic structure of the morphine biosynthetic enzyme salutaridine reductase bound to the cofactor NADPH. The substrate salutaridine is shown entering the active site.
Judy Coyle, Donald Danforth Plant Science Center
View Media
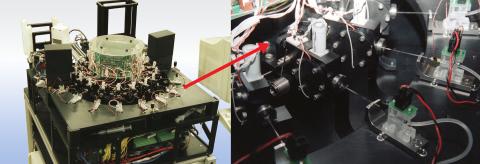
2357: Capillary protein crystallization robot
2357: Capillary protein crystallization robot
This ACAPELLA robot for capillary protein crystallization grows protein crystals, freezes them, and centers them without manual intervention. The close-up is a view of one of the dispensers used for dispensing proteins and reagents.
Structural Genomics of Pathogenic Protozoa Consortium
View Media

1313: Cell eyes clock
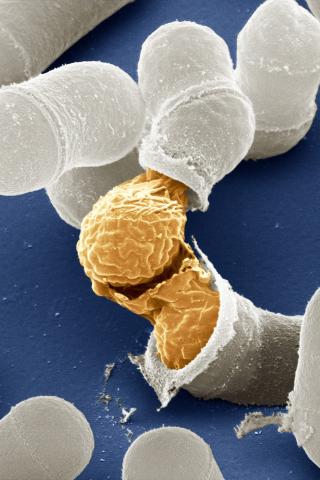
3614: Birth of a yeast cell
3614: Birth of a yeast cell
Yeast make bread, beer, and wine. And like us, yeast can reproduce sexually. A mother and father cell fuse and create one large cell that contains four offspring. When environmental conditions are favorable, the offspring are released, as shown here. Yeast are also a popular study subject for scientists. Research on yeast has yielded vast knowledge about basic cellular and molecular biology as well as about myriad human diseases, including colon cancer and various metabolic disorders.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
This image was part of the Life: Magnified exhibit that ran from June 3, 2014, to January 21, 2015, at Dulles International Airport.
Juergen Berger, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, and Maria Langegger, Friedrich Miescher Laboratory of the Max Planck Society, Germany
View Media
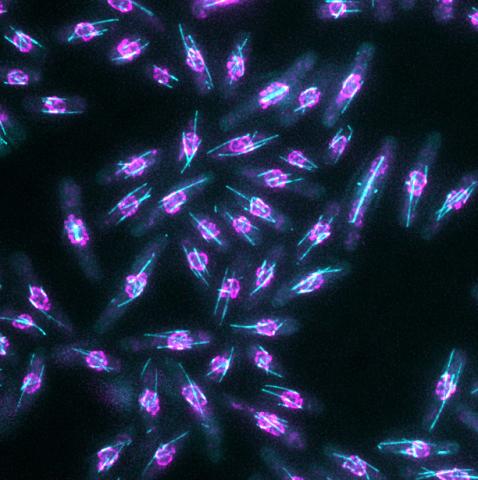
6798: Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
6798: Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes and tubulin
Yeast cells with nuclear envelopes shown in magenta and tubulin shown in light blue. The nuclear envelope defines the borders of the nucleus, which houses DNA. Tubulin is a protein that makes up microtubules—strong, hollow fibers that provide structure to cells and help direct chromosomes during cell division. This image was captured using wide-field microscopy with deconvolution.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Related to images 6791, 6792, 6793, 6794, 6797, and videos 6795 and 6796.
Alaina Willet, Kathy Gould’s lab, Vanderbilt University.
View Media
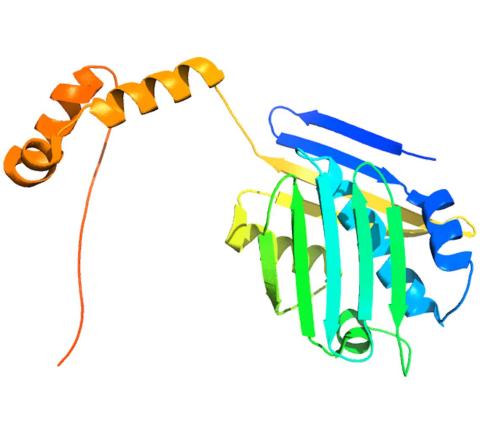
3355: Hsp33 figure 2
3355: Hsp33 figure 2
Featured in the March 15, 2012 issue of Biomedical Beat. Related to Hsp33 Figure 1, image 3354.
Ursula Jakob and Dana Reichmann, University of Michigan
View Media
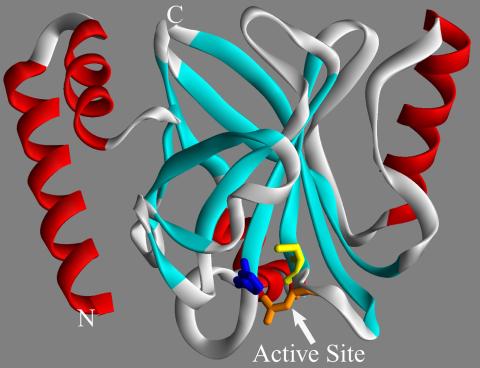
2386: Sortase b from B. anthracis
2386: Sortase b from B. anthracis
Structure of sortase b from the bacterium B. anthracis, which causes anthrax. Sortase b is an enzyme used to rob red blood cells of iron, which the bacteria need to survive.
Midwest Center for Structural Genomics, PSI
View Media
1083: Natcher Building 03
1083: Natcher Building 03
NIGMS staff are located in the Natcher Building on the NIH campus.
Alisa Machalek, National Institute of General Medical Sciences
View Media
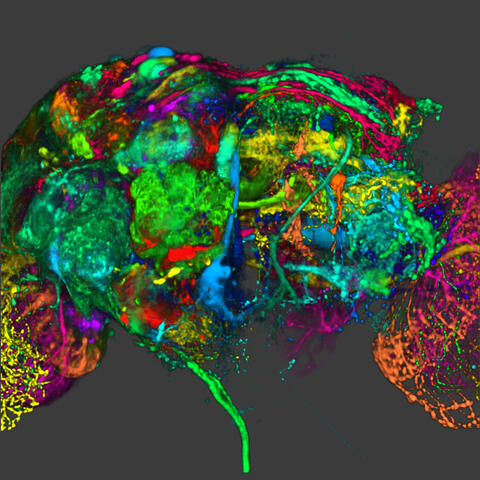
5838: Color coding of the Drosophila brain - image
5838: Color coding of the Drosophila brain - image
This image results from a research project to visualize which regions of the adult fruit fly (Drosophila) brain derive from each neural stem cell. First, researchers collected several thousand fruit fly larvae and fluorescently stained a random stem cell in the brain of each. The idea was to create a population of larvae in which each of the 100 or so neural stem cells was labeled at least once. When the larvae grew to adults, the researchers examined the flies’ brains using confocal microscopy. With this technique, the part of a fly’s brain that derived from a single, labeled stem cell “lights up. The scientists photographed each brain and digitally colorized its lit-up area. By combining thousands of such photos, they created a three-dimensional, color-coded map that shows which part of the Drosophila brain comes from each of its ~100 neural stem cells. In other words, each colored region shows which neurons are the progeny or “clones” of a single stem cell. This work established a hierarchical structure as well as nomenclature for the neurons in the Drosophila brain. Further research will relate functions to structures of the brain.
Related to image 5868 and video 5843
Related to image 5868 and video 5843
Yong Wan from Charles Hansen’s lab, University of Utah. Data preparation and visualization by Masayoshi Ito in the lab of Kei Ito, University of Tokyo.
View Media
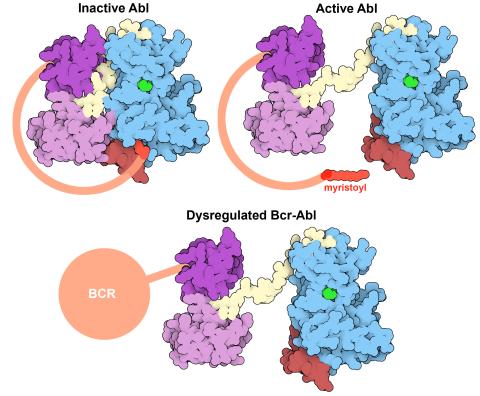
7004: Protein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
7004: Protein kinases as cancer chemotherapy targets
Protein kinases—enzymes that add phosphate groups to molecules—are cancer chemotherapy targets because they play significant roles in almost all aspects of cell function, are tightly regulated, and contribute to the development of cancer and other diseases if any alterations to their regulation occur. Genetic abnormalities affecting the c-Abl tyrosine kinase are linked to chronic myelogenous leukemia, a cancer of immature cells in the bone marrow. In the noncancerous form of the protein, binding of a myristoyl group to the kinase domain inhibits the activity of the protein until it is needed (top left shows the inactive form, top right shows the open and active form). The cancerous variant of the protein, called Bcr-Abl, lacks this autoinhibitory myristoyl group and is continually active (bottom). ATP is shown in green bound in the active site of the kinase.
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: c-Abl tyrosine kinase and regulatory domains (PDB entry 1OPL) and F-actin binding domain (PDB entry 1ZZP).
Find these in the RCSB Protein Data Bank: c-Abl tyrosine kinase and regulatory domains (PDB entry 1OPL) and F-actin binding domain (PDB entry 1ZZP).
Amy Wu and Christine Zardecki, RCSB Protein Data Bank.
View Media
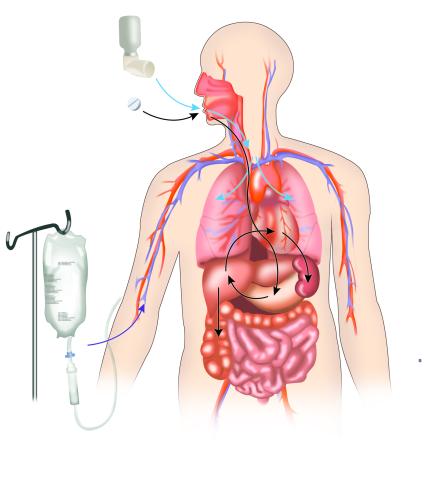
2527: A drug's life in the body
2527: A drug's life in the body
A drug's life in the body. Medicines taken by mouth pass through the liver before they are absorbed into the bloodstream. Other forms of drug administration bypass the liver, entering the blood directly. See 2528 for a labeled version of this illustration. Featured in Medicines By Design.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
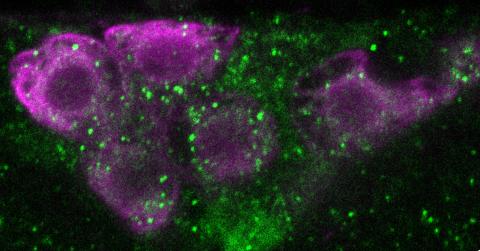
6982: Insulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
6982: Insulin production and fat sensing in fruit flies
Fourteen neurons (magenta) in the adult Drosophila brain produce insulin, and fat tissue sends packets of lipids to the brain via the lipoprotein carriers (green). This image was captured using a confocal microscope and shows a maximum intensity projection of many slices.
Related to images 6983, 6984, and 6985.
Related to images 6983, 6984, and 6985.
Akhila Rajan, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center
View Media
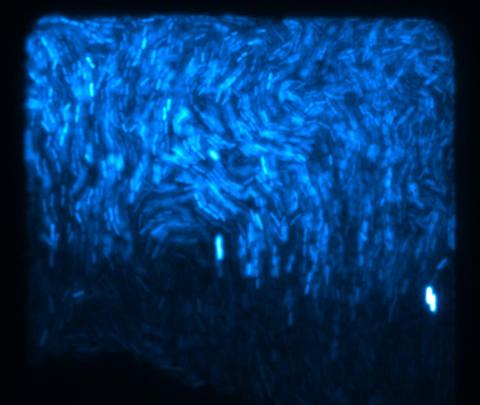
3268: Fluorescent E. coli bacteria
3268: Fluorescent E. coli bacteria
Bioengineers were able to coax bacteria to blink in unison on microfluidic chips. They called each blinking bacterial colony a biopixel. Thousands of fluorescent E. coli bacteria, shown here, make up a biopixel. Related to images 3265 and 3266. From a UC San Diego news release, "Researchers create living 'neon signs' composed of millions of glowing bacteria."
Jeff Hasty Lab, UC San Diego
View Media
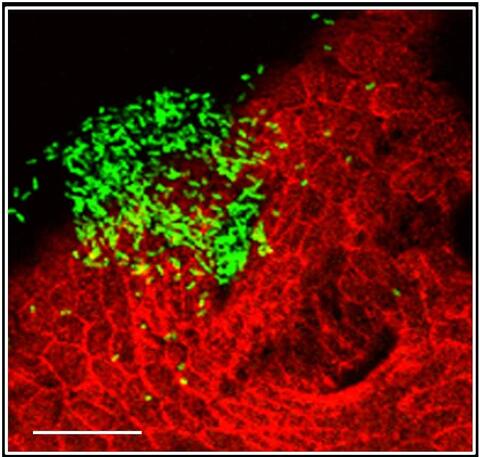
7019: Bacterial cells aggregated above a light-organ pore of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7019: Bacterial cells aggregated above a light-organ pore of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
The beating of cilia on the outside of the Hawaiian bobtail squid’s light organ concentrates Vibrio fischeri cells (green) present in the seawater into aggregates near the pore-containing tissue (red). From there, the bacterial cells (~2 mm) swim to the pores and migrate through a bottleneck into the interior crypts where a population of symbionts grow and remain for the life of the host. This image was taken using confocal fluorescence microscopy.
Related to images 7016, 7017, 7018, and 7020.
Related to images 7016, 7017, 7018, and 7020.
Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology.
View Media
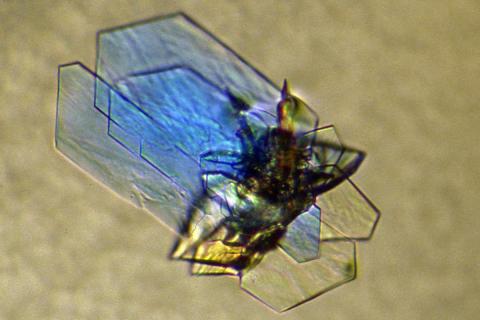
2410: DNase
2410: DNase
Crystals of DNase protein created for X-ray crystallography, which can reveal detailed, three-dimensional protein structures.
Alex McPherson, University of California, Irvine
View Media
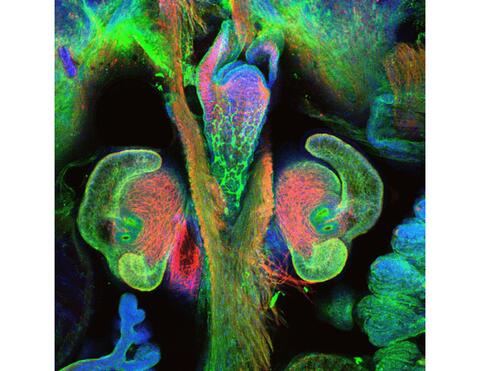
7017: The nascent juvenile light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
7017: The nascent juvenile light organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid
A light organ (~0.5 mm across) of a Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, with different tissues are stained various colors. The two pairs of ciliated appendages, or “arms,” on the sides of the organ move Vibrio fischeri bacterial cells closer to the two sets of three pores (two seen in this image) at the base of the arms that each lead to an interior crypt. This image was taken using a confocal fluorescence microscope.
Related to images 7016, 7018, 7019, and 7020.
Related to images 7016, 7018, 7019, and 7020.
Margaret J. McFall-Ngai, Carnegie Institution for Science/California Institute of Technology, and Edward G. Ruby, California Institute of Technology.
View Media
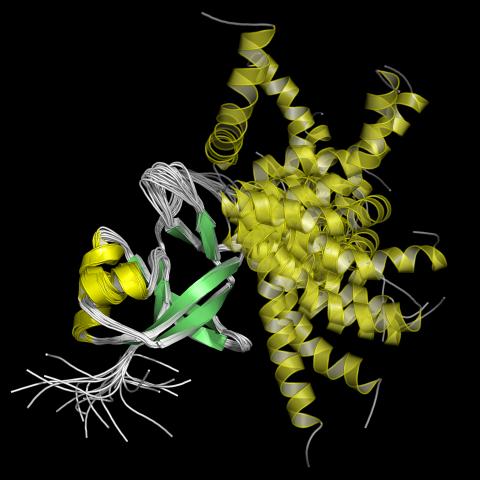
2339: Protein from Arabidopsis thaliana
2339: Protein from Arabidopsis thaliana
NMR solution structure of a plant protein that may function in host defense. This protein was expressed in a convenient and efficient wheat germ cell-free system. Featured as the June 2007 Protein Structure Initiative Structure of the Month.
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics
View Media

1334: Aging book of life
1334: Aging book of life
Damage to each person's genome, often called the "Book of Life," accumulates with time. Such DNA mutations arise from errors in the DNA copying process, as well as from external sources, such as sunlight and cigarette smoke. DNA mutations are known to cause cancer and also may contribute to cellular aging.
Judith Stoffer
View Media
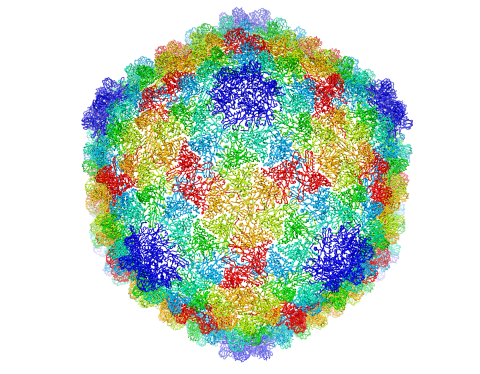
5874: Bacteriophage P22 capsid
5874: Bacteriophage P22 capsid
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has the power to capture details of proteins and other small biological structures at the molecular level. This image shows proteins in the capsid, or outer cover, of bacteriophage P22, a virus that infects the Salmonella bacteria. Each color shows the structure and position of an individual protein in the capsid. Thousands of cryo-EM scans capture the structure and shape of all the individual proteins in the capsid and their position relative to other proteins. A computer model combines these scans into the three-dimension image shown here. Related to image 5875.
Dr. Wah Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine
View Media
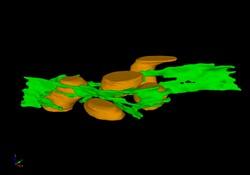
2635: Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
2635: Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
A computer model shows how the endoplasmic reticulum is close to and almost wraps around mitochondria in the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is lime green and the mitochondria are yellow. This image relates to a July 27, 2009 article in Computing Life.
Bridget Wilson, University of New Mexico
View Media
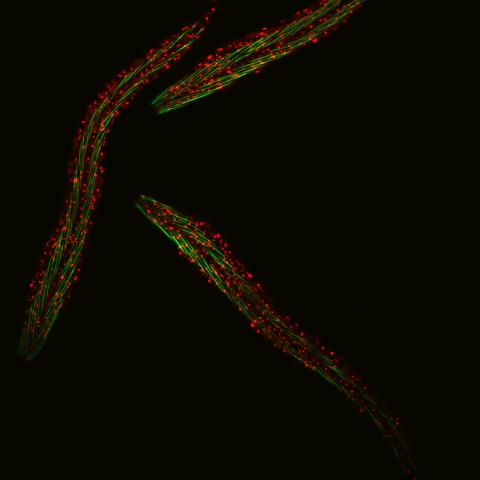
6582: Group of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
6582: Group of fluorescent C. elegans showing muscle and ribosomal protein
Three C. elegans, tiny roundworms, with a ribosomal protein glowing red and muscle fibers glowing green. Researchers used these worms to study a molecular pathway that affects aging. The ribosomal protein is involved in protein translation and may play a role in dietary restriction-induced longevity. Image created using confocal microscopy.
View single roundworm here 6581.
View closeup of roundworms here 6583.
View single roundworm here 6581.
View closeup of roundworms here 6583.
Jarod Rollins, Mount Desert Island Biological Laboratory.
View Media
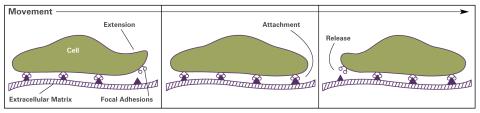
2503: Focal adhesions (with labels)
2503: Focal adhesions (with labels)
Cells walk along body surfaces via tiny "feet," called focal adhesions, that connect with the extracellular matrix. See image 2502 for an unlabeled version of this illustration.
Crabtree + Company
View Media
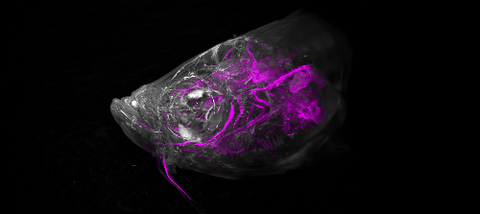
6933: Zebrafish head vasculature video
6933: Zebrafish head vasculature video
Various views of a zebrafish head with blood vessels shown in purple. Researchers often study zebrafish because they share many genes with humans, grow and reproduce quickly, and have see-through eggs and embryos, which make it easy to study early stages of development.
This video was captured using a light sheet microscope.
Related to image 6934.
This video was captured using a light sheet microscope.
Related to image 6934.
Prayag Murawala, MDI Biological Laboratory and Hannover Medical School.
View Media